Comprehensive Nutritional Strategies to Manage Elevated Cholesterol Levels and Promote Heart Health
This comprehensive guide explores effective dietary strategies for managing high cholesterol levels. It emphasizes the importance of foods like oats, nuts, healthy oils, and soy, along with lifestyle changes, to lower LDL and boost HDL. Regular monitoring and a balanced diet are key to preventing heart disease and promoting overall cardiovascular health. Ideal for those seeking natural ways to control their cholesterol, this article provides practical tips and scientific insights to support heart wellness.
Proven Dietary Approaches for Controlling and Reducing High Cholesterol
High cholesterol remains a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes. Managing cholesterol levels through diet is one of the most effective and non-invasive strategies to improve heart health and reduce associated risks. For individuals facing elevated cholesterol, adopting specific nutritional habits and including heart-friendly foods can make a substantial difference. This comprehensive guide explores proven dietary choices, food options, and lifestyle modifications to help maintain healthy cholesterol levels and support overall cardiovascular wellness.
Understanding the importance of cholesterol management begins with recognizing the different types of cholesterol: low-density lipoprotein (LDL), often termed as 'bad' cholesterol, and high-density lipoprotein (HDL), known as 'good' cholesterol. Elevated LDL levels contribute to plaque buildup in arteries, increasing the risk of atherosclerosis, while higher HDL levels work to clear excess fats from the bloodstream. Therefore, dietary strategies should target both reducing LDL and increasing HDL to optimize heart health.
Here, we delve into detailed dietary modifications, highlighting key foods and nutrients that have been scientifically proven to assist in managing cholesterol effectively. These foods not only help in lowering harmful LDL cholesterol but also promote an increase in beneficial HDL cholesterol levels, creating a balanced approach to cardiovascular health.
Essential Foods for Managing High Cholesterol
Oats and Whole Grains:
One of the most well-known dietary components for lowering LDL cholesterol is oats. Regular consumption of oatmeal, oat bran, or oat-based cereals introduces soluble fiber into your diet, which binds to cholesterol particles in the digestive system and facilitates their removal from the body. Scientific studies indicate that consuming at least 3 grams of soluble fiber daily from oats can significantly reduce LDL levels. The exact amount tailored to individual cholesterol readings can be discussed with healthcare providers or nutritionists based on personal health assessments.
Incorporating a variety of whole grains, such as barley, quinoa, and brown rice, into daily meals can also contribute to heart health. Barley, in particular, contains beta-glucan, a soluble fiber that has been shown to decrease LDL cholesterol effectively. These grains are versatile and can be included in breakfast bowls, salads, or as substitutable ingredients in your favorite recipes.
Nuts and Seeds:
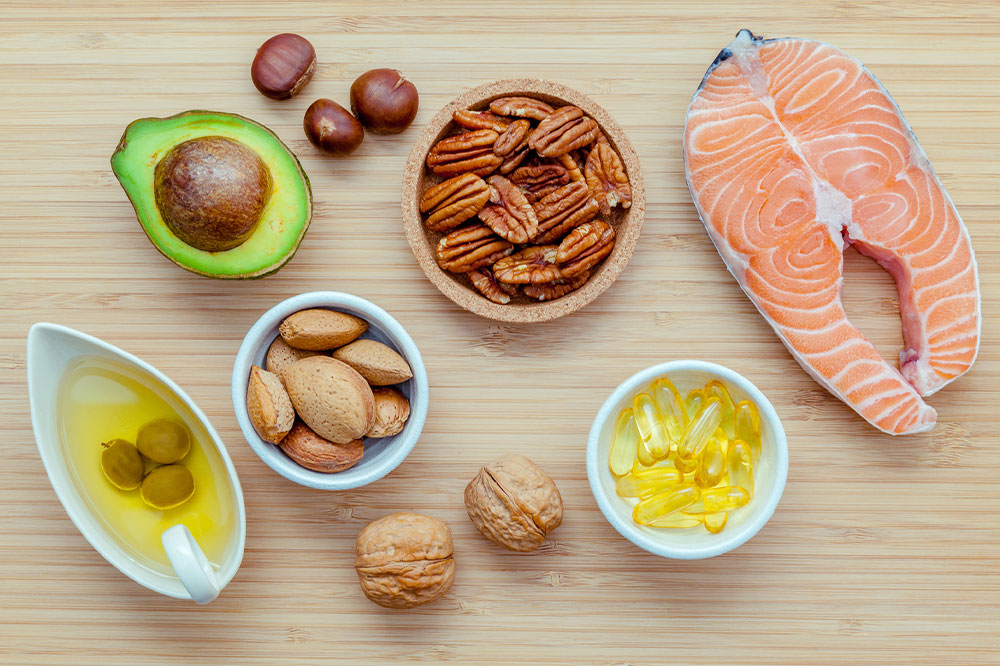
Consuming nuts such as almonds, walnuts, and peanuts in moderation (about two ounces per day) can provide invaluable benefits for heart health. Nuts are rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which help lower LDL cholesterol while maintaining or slightly raising HDL levels. They also provide essential nutrients like vitamin E, magnesium, and plant sterols that protect against oxidative damage and improve artery function. Incorporating nuts as a snack or adding them to cereals and salads can be a delicious way to support cholesterol management.
Healthy Fats and Vegetable Oils:
Choosing heart-healthy fats is critical for managing cholesterol. Instead of saturated fats found in butter and lard, opt for oils rich in monounsaturated fats such as olive oil, or plant-based oils like sunflower, canola, and avocado oil. These oils can be used for cooking or salad dressings, helping to reduce LDL cholesterol levels while providing essential fatty acids. Limiting the use of processed and fried foods, which are often high in trans fats, also plays an important role in maintaining healthy lipid profiles.
Legumes and Plant-Based Proteins:
Legumes like beans, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent sources of soluble fiber and plant-based protein. They help lower LDL cholesterol and have additional benefits such as stabilizing blood sugar levels and promoting satiety. Including legumes in soups, salads, or as meat substitutes can improve diet quality and contribute effectively to cholesterol management.
Soy Products:
Soy-based foods such as tofu, tempeh, soy milk, and edamame contain isoflavones and high-quality protein sources that have been shown to significantly lower LDL cholesterol. Consuming around 20 grams of soy protein daily can lead to a reduction of up to 6% in LDL levels, especially when combined with other healthy dietary choices. These foods can be integrated into daily meals as alternatives to meat or dairy products, providing variety and nutritional value.
Lifestyle Tips and Monitoring for Effective Cholesterol Control
Beyond dietary changes, maintaining an active lifestyle is essential for managing cholesterol. Regular aerobic exercises such as walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming can help boost HDL levels and reduce LDL cholesterol. Combining physical activity with dietary modifications yields the most effective results in lowering cardiovascular risk factors.
Additionally, routine cholesterol testing allows individuals to monitor their progress and adjust their dietary and lifestyle choices accordingly. Healthcare professionals can help interpret cholesterol profiles and recommend personalized nutrition plans that include more fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and lean proteins, further enhancing heart health.
Incorporating stress management techniques, limiting alcohol intake, and avoiding smoking are also integral components of a holistic approach to managing cholesterol levels and ensuring long-term cardiovascular health.
In conclusion, adopting a heart-healthy diet rich in soluble fibers, healthy fats, nuts, seeds, and plant-based proteins forms the foundation of managing elevated cholesterol levels. Combined with regular physical activity and routine health monitoring, these strategies can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease and improve overall well-being. Prioritize these dietary modifications today for a healthier heart and a longer, more vibrant life.





