Comprehensive Guide to the Top 5 Hospital Bed Types Ideal for Home Use
This comprehensive guide explores the top 5 hospital bed types suitable for home use, emphasizing features, benefits, and limitations. From manual to bariatric beds, it helps homeowners and caregivers select the best options for safety, comfort, and affordability, enhancing quality of life for individuals with special health needs or mobility limitations.

In-Depth Overview of the Top 5 Hospital Bed Varieties Perfect for Home Environments
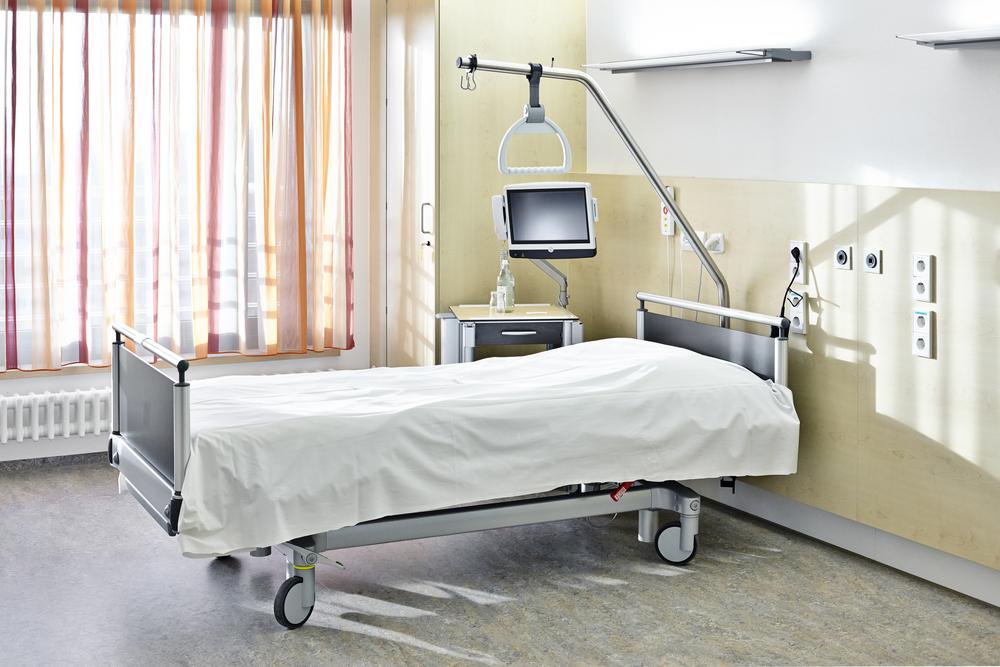
For individuals requiring extended bed rest or those with specific health needs, choosing the right hospital bed for home use can greatly enhance comfort, safety, and convenience. These specialized beds are designed to provide better support and ease of movement, making caregiving and daily routines more manageable. With advancements in medical bed technology, there are now multiple types geared towards different user needs, safety considerations, and budget constraints. This extensive guide explores the five most popular hospital bed options suitable for home settings, highlighting their unique features, advantages, and potential drawbacks.
Manual Hospital Beds: The traditional choice, these beds operate via hand cranks that adjust the head and foot sections. Known for their simplicity, they are a reliable option for budget-conscious users who prefer minimal technological dependence.

Advantages: Manual hospital beds are typically more affordable and easier to maintain. They do not rely on electricity, reducing the risk of technical failures, making them suitable for areas with unstable power supplies. The straightforward design also means durability and less need for repairs over time.
Disadvantages: Adjusting positions requires physical effort, which may be taxing for elderly users or those with limited strength. Frequent adjustments can lead to fatigue, especially if the user needs multiple position changes daily.
Semi-Electric Hospital Beds: Combining manual and electric functionalities, these beds simplify adjustments with motor-assisted movement while still requiring some manual input, such as adjusting the bed height.
Advantages: Semi-electric beds strike a good balance between cost and convenience. They promote easier positioning through remote controls and motor assistance, leading to less physical strain. Their affordability compares favorably with full-electric models, making them accessible to a broader audience.
Disadvantages: While head and foot adjustments are electrical, the manual effort needed to alter bed height remains, which could be a challenge for users with significant mobility issues.
Full-Electric Hospital Beds: Designed for maximum ease, all adjustments—height, head, foot—are controlled electronically via remote control devices, offering ultimate user comfort and convenience.
Advantages: The key benefit is effortless operation—users and caregivers can easily modify bed positions without physical effort, making them ideal for individuals with severe mobility limitations or caregivers who need to frequently change bed settings. These beds enhance independence and reduce caregiver fatigue.
Disadvantages: The advanced features come with a higher price tag. Additionally, electric components may require more maintenance and could be susceptible to technical issues or power outages.
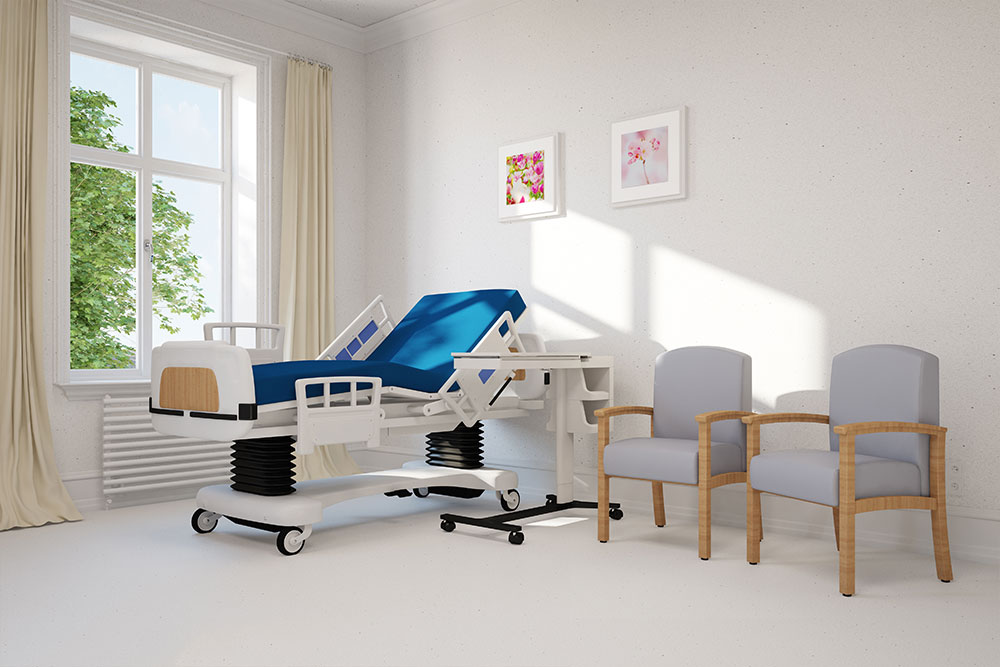
Hi-Low Hospital Beds: Specially engineered to feature an ultra-low profile, these beds are ideal for patients at risk of falls, especially when the deck height is close to the floor, typically around seven inches.
Advantages: Safety is paramount with the auto-rise feature that allows caregivers to elevate or lower the bed for easier patient transfers or to prevent falls. The low height minimizes injury risk if a patient slips or falls, adding an extra layer of protection.
Disadvantages: These specialized beds tend to be more costly than standard electric beds, but their safety benefits often justify the investment, especially in fall-prone individuals.
Bariatric Hospital Beds: These robust beds are built to accommodate patients with higher body weights, offering wider frames and reinforced support structures. They are suitable for medical or home use where patient weight exceeds standard limits.
Advantages: Bariatric beds provide superior durability and support, with frames that can support weights ranging from 350 to 1000 pounds. They are designed to prevent damage, ensure safety, and improve comfort for heavier individuals.
Disadvantages: Due to their reinforced construction and larger size, bariatric beds are generally more expensive and require more space, which can be a consideration for smaller homes.
Choosing the appropriate hospital bed depends on various factors, including the user's mobility, safety needs, medical conditions, and financial considerations. While manual options may suit those on a budget, electric or specialized beds offer increased convenience and safety features that can significantly improve quality of life. Proper assessment and consultation with healthcare professionals are essential in making the right choice for home use, ensuring safety, comfort, and practical support for individuals with diverse health requirements.