Effective Nutritional Strategies for Managing Epilepsy
This comprehensive guide explores the vital role of diet in managing epilepsy. It covers key foods like fruits, vegetables, proteins, and healthy fats, and details effective dietary plans such as ketogenic and low glycemic index diets. Proper nutrition can help reduce seizure frequency and improve overall neurological health, making it an important aspect of epilepsy management. Patients should work closely with healthcare professionals to tailor nutrition strategies suited to their individual needs, ensuring better quality of life and day-to-day functioning.

Comprehensive Dietary Approaches and Nutrient-Rich Foods for Epilepsy Control
Epilepsy is a complex neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures caused by abnormal electrical activity in the brain. This condition affects millions worldwide, and managing it often requires a multifaceted approach combining medication, lifestyle adjustments, and specialized diets. Recent scientific research highlights the significant role of nutrition in controlling seizure frequency and severity. This article delves into various dietary strategies and specific foods that can be integrated into daily routines to enhance neurological health and potentially reduce epileptic episodes.
Emphasizing Fruits and Vegetables for Antioxidant Support
One of the fundamental aspects of epilepsy management through diet involves increasing antioxidant intake. A deficiency in antioxidants has been linked to heightened seizure susceptibility, as oxidative stress can exacerbate neural instability. Including a wide variety of colorful fruits and vegetables ensures a rich supply of antioxidants such as vitamins C and E, flavonoids, and carotenoids. These nutrients support nerve regeneration, reduce inflammation, and neutralize free radicals, thus fostering a healthier neural environment. Experts recommend consuming at least five servings of fruits and vegetables each day. Focus on dark leafy greens like spinach, kale, and broccoli, known for their high antioxidant content. Incorporate low-sugar fruits such as berries—blueberries, strawberries, and blackberries—for their potent antioxidant properties without the added risk of blood sugar spikes.
Nutrient-Dense Vegetables and Their Role in Seizure Control
Including half of each meal as vegetables can significantly contribute to overall health. Non-starchy vegetables such as mushrooms, zucchini, celery, cauliflower, and peppers are excellent choices. These vegetables are low in carbohydrates but high in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. When following ketogenic or low-carb diets, these foods are particularly beneficial, as they provide essential nutrients without disrupting ketosis. A diet rich in these vegetables helps stabilize blood sugar levels, reduce inflammation, and support neurological functions vital in epilepsy management.
Incorporate a colorful array of vegetables into each meal, focusing on options like mushrooms, zucchini, and celery. These vegetables are not only nutrient-dense but also low in carbohydrates, making them ideal for ketogenic and low-glycemic diets aimed at controlling epileptic seizures. Prioritize fresh, organic produce whenever possible to maximize nutrient retention and reduce exposure to pesticides. Combining these vegetables with healthy fats enhances absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, further supporting brain health and neural stability.
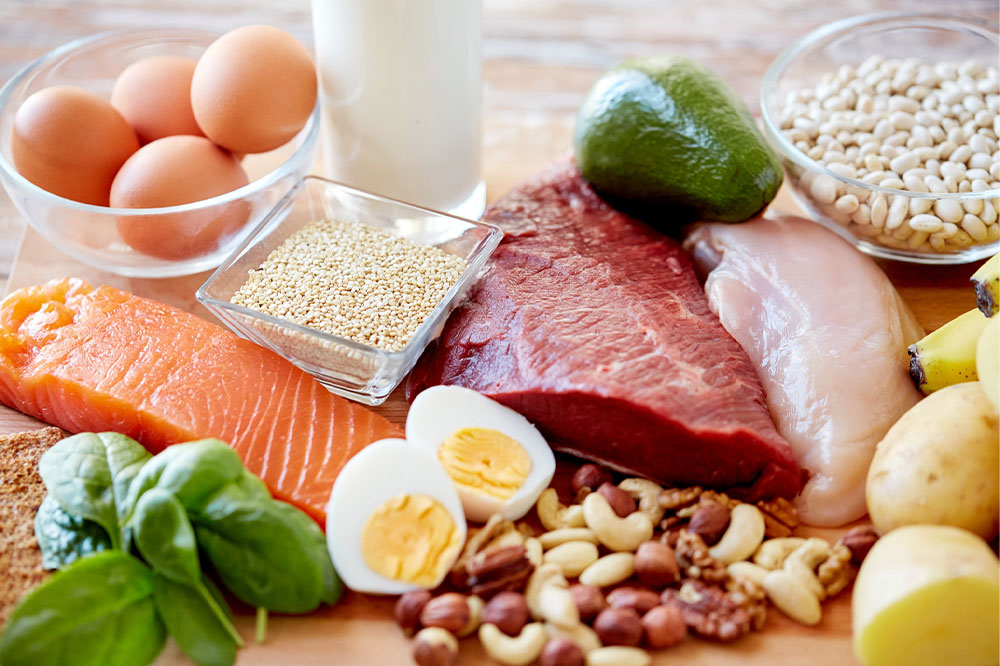
Protein-Rich Foods and Seafood for Neural Support
High-quality protein sources are essential components of an anti-epileptic diet, especially within ketogenic and modified Atkins plans. Proteins from poultry, fish, shellfish, and eggs provide amino acids necessary for neurotransmitter synthesis and neural repair. Fish, particularly fatty varieties such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties and support cognitive function. Choosing pasture-raised or wild-caught options ensures a higher nutrient profile, including better omega-3 and mineral content. For those who prefer red meats, lamb presents a high-fat alternative that complements a ketogenic approach.
Importance of Healthy Fats and Cooking Oils
Fats play a crucial role in maintaining optimal brain function. Incorporating healthy, plant-based oils like extra virgin olive oil and canola oil into cooking routines can improve brain lipid composition, enhance cell signaling, and support neurological health. These oils are rich in monounsaturated fats, which are known for their anti-inflammatory effects. Additionally, medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), found in MCT oil supplements, are rapidly absorbed and converted into ketones, providing an alternative energy source for brain cells, especially in ketogenic diets aimed at seizure reduction.
Dietary modifications should also include a conscious effort to limit sugar and processed foods, as excessive intake can trigger epileptic episodes. Simple sugars, candies, baked goods, sodas, and foods high in refined carbohydrates can cause rapid blood sugar fluctuations and increase neural excitability. Instead, focus on whole, unprocessed foods and natural sweeteners like stevia or erythritol if needed. Maintaining a balanced intake of fats, proteins, and complex carbs helps stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce seizure risks.
Various dietary plans have proven effective for managing epilepsy, each with its own specific guidelines and applications. These include:
Ketogenic Diet: A high-fat, adequate-protein, and very low-carbohydrate regimen designed to induce ketosis, a metabolic state where fat is used as the primary energy source, which has shown to significantly decrease seizure frequency.
MCT Diet: Similar to the ketogenic diet but utilizing medium-chain triglycerides derived from coconut oil and other sources, making it easier for some individuals to stay in ketosis while consuming more carbs and proteins.
Modified Atkins: A less restrictive diet that emphasizes increased protein intake and a more flexible carbohydrate allowance compared to traditional keto, making it more sustainable while still maintaining seizure control potential.
Low Glycemic Index Diet: Focuses on foods that have a minimal impact on blood sugar spikes, helping to maintain stable glucose levels and reduce neural excitability without strict carbohydrate restrictions.
Overall, tailored nutritional strategies play an essential role in the holistic management of epilepsy. Consultation with healthcare professionals or dietitians is crucial to designing an appropriate plan that complements medication and individual health needs. Incorporating nutrient-dense foods, prioritizing healthy fats, reducing sugar intake, and choosing suitable dietary approaches can empower individuals with epilepsy to improve their quality of life and potentially reduce the frequency and severity of seizures.