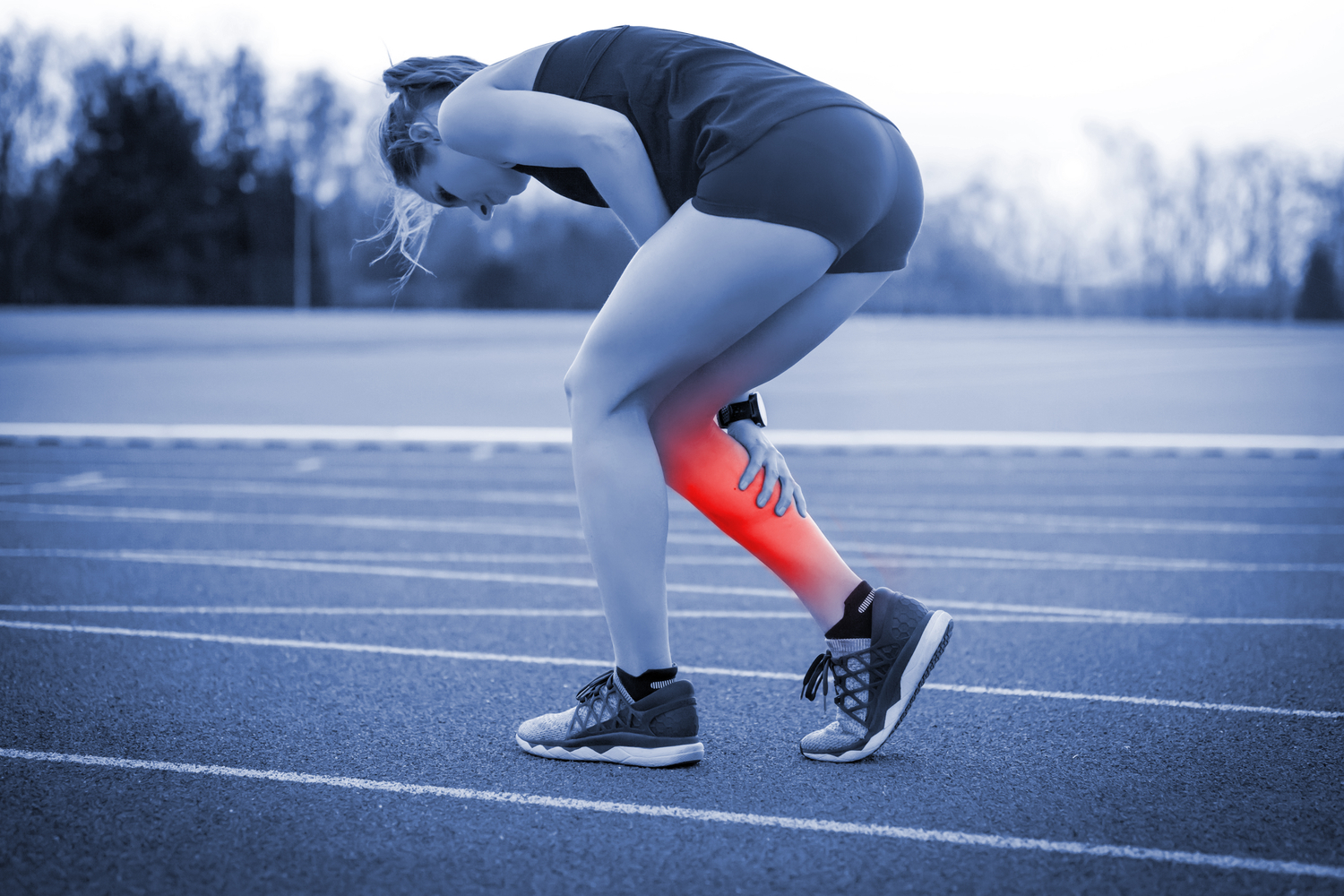
Complete Guide to Understanding and Preventing Leg Cramps for Better Mobility
This comprehensive guide explores the causes, risks, and effective prevention methods for leg cramps. Covering lifestyle tips, dietary recommendations, and relief techniques, it aims to help individuals reduce the frequency and severity of muscle spasms. Whether due to dehydration, mineral deficiencies, or aging, understanding how to prevent and manage cramps can improve mobility and comfort. The article emphasizes the importance of proper nutrition, hydration, and posture, along with consulting healthcare providers for persistent issues, ensuring a holistic approach to muscle health. Ideal for anyone seeking relief from leg cramps and improved muscle function.
Comprehensive Overview of Leg Cramps: Causes, Prevention, and Relief Strategies
Leg cramps are sudden, involuntary contractions or spasms of muscles in the thighs, calves, or feet that can cause intense pain and discomfort. These cramps can strike unexpectedly, often during nighttime sleep or after physical activity, disrupting rest and daily activities. Understanding the underlying causes and implementing effective prevention techniques can significantly improve comfort and mobility. This detailed guide explores the causes, risk factors, remedies, and preventive measures related to leg cramps, providing valuable insights for individuals experiencing these painful episodes.
What Are Leg Cramps?
Leg cramps are involuntary contractions of muscles that occur suddenly and can last from a few seconds to several minutes. They are commonly experienced in the calves but can also affect the thighs and feet. Although generally benign, frequent or severe cramps can interfere with daily life and sleep quality. Recognizing the symptoms and triggers of leg cramps is essential for developing effective prevention and relief strategies.
Common Causes of Leg Cramps
Poor blood circulation: Reduced blood flow to the muscles can cause cramps. Factors such as prolonged sitting or standing, sedentary lifestyle, and certain health conditions impair circulation, leading to muscle fatigue and spasms.
Nerve compression: Conditions such as spinal nerve pressure or nerve impingements can induce muscle spasms in the legs. Maintaining proper posture and avoiding prolonged compression on nerves can help prevent this.
Mineral imbalances: Deficiencies in essential minerals such as magnesium, calcium, and potassium disrupt normal muscle function and increase cramp risk. These minerals are vital for nerve transmission and muscle contraction regulation.
Dehydration: Loss of body fluids due to intense exercise, hot weather, or insufficient fluid intake depletes electrolytes and impairs muscle function, often leading to cramps.
Pregnancy and hormonal changes: During pregnancy, increased mineral and fluid demands make women more susceptible to cramps. Hormonal fluctuations can also influence muscle excitability.
Age-related muscle degeneration: As people age, muscle mass and strength decline, increasing vulnerability to cramps. Aging also affects nerve and blood vessel health, further elevating risk.
Underlying medical conditions: Conditions such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, and liver diseases can contribute to muscle cramps. Certain medications, including diuretics and statins, may deplete electrolyte levels or affect nerve function, leading to cramps.
Several factors heighten the likelihood of experiencing leg cramps. Age-related changes cause muscles to weaken and lose elasticity, making cramps more frequent. Dehydration from vigorous activity or exposure to high temperatures exacerbates the risk, as water and electrolytes are critical for muscle function. Pregnant women are especially vulnerable due to increased mineral and fluid needs, which can lead to deficiencies. Chronic health issues such as diabetes, thyroid problems, and liver diseases also increase susceptibility, along with certain medications that interfere with electrolyte balance or nerve signaling.
Understanding these causes helps in tailoring effective prevention strategies. Simple lifestyle modifications, such as staying well-hydrated, engaging in regular stretching, and maintaining proper posture, can dramatically reduce the occurrence of cramps.
Relief and Management of Leg Cramps
When a cramp strikes, immediate relief can be achieved through gentle stretching and massage of the affected muscle. For example, if experiencing calf cramps, straightening the leg and pulling the toes upward towards the shin can help relax the muscle. Applying heat through a heating pad or warm towel can promote muscle relaxation, while cold packs can reduce inflammation and pain.
Maintaining hydration before, during, and after activities is crucial. Drinking water enriched with electrolytes can replenish lost minerals and prevent future cramps. Proper sleep posture, such as elevating the legs and avoiding prolonged pressure on muscles, can also be beneficial.
Preventive measures include regularly stretching the calves, thighs, and feet, especially before exercise or bed. Gentle massaging muscles after activity supports circulation and reduces stiffness. Lifestyle approaches such as quitting smoking, managing weight, and avoiding excessive alcohol intake further promote vascular health and reduce cramp frequency.
Dietary Supplements for Preventing Leg Cramps
Supplementing with key minerals may support muscle health, but should always be done under medical guidance. These nutrients include:
Calcium: Essential for strong bones and proper muscle contractions. Rich sources are dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods.
Magnesium: Facilitates muscle relaxation and nerve function. Food sources include nuts, seeds, dark chocolate, and green vegetables.
Potassium: Balances electrolytes and promotes healthy nerve signaling in muscles. Found abundantly in bananas, potatoes, spinach, and citrus fruits.
Optimal mineral intake supports day-to-day muscle function and reduces cramps. However, excessive supplementation can cause adverse effects such as gastrointestinal discomfort or cardiac issues, emphasizing the importance of consulting healthcare providers before starting any supplement regimen.
Incorporating a balanced diet rich in these nutrients, alongside a healthy lifestyle, greatly reduces the likelihood of leg cramps and supports overall musculoskeletal health. It’s also vital to address underlying health issues with your healthcare provider to manage chronic conditions effectively.
Final thoughts emphasize that proactive lifestyle modifications, balanced nutrition, and proper hydration are key to preventing leg cramps. Regular exercise, including stretching routines, can improve muscle flexibility and resilience. Consulting healthcare professionals for persistent or severe cramps ensures personalized treatment and nutritional guidance, ultimately enhancing quality of life and mobility.