Comprehensive Guide to Staphylococcus Infections: Prevention and Treatment Strategies
This comprehensive guide provides insights into staphylococcus aureus bacteria, detailing how infections occur, common symptoms, and effective prevention and treatment strategies. Learn how to keep yourself safe from these common bacterial infections through proper hygiene, early detection, and medical care. The article emphasizes the importance of personal cleanliness and environmental hygiene to prevent the spread of staph bacteria, offering practical tips for reducing infection risks in everyday life. Ideal for those seeking to understand and prevent staph infections effectively.

Comprehensive Guide to Staphylococcus Infections: Prevention and Treatment Strategies
Staphylococcus aureus, commonly known as staph bacteria, is a type of bacteria that naturally exists on the skin surface in a dormant or inactive state in most healthy individuals. These bacteria can become active and cause infections when the body's defenses are compromised or when hygiene practices are inadequate. Understanding how staph bacteria operate, how infections occur, and what steps can be taken to prevent them is essential for maintaining optimal health and avoiding serious complications.
Staph bacteria are part of the normal flora that reside harmlessly on the skin and in the nasal passages of many people. However, they can turn pathogenic when they infiltrate the skin through cuts, wounds, or abrasions, or when immune defenses are weakened. This can result in a variety of infections, ranging from superficial skin issues to severe systemic conditions. These infections are commonly seen in settings where hygiene may be compromised, such as beauty salons, gyms, hospitals, or communal environments.
One of the key factors contributing to the spread of staph infections is poor hygiene. Regular handwashing, maintaining cleanliness of the skin, and disinfecting shared surfaces are critical in curbing the transmission of bacteria. Particular attention should be paid to often touch areas and vulnerable spots on the body, such as the feet, underarms, and areas where skin may be broken or sore. Bacteria tend to thrive in warm, moist environments, making these areas especially prone to infection if hygiene is not properly maintained.
Walking barefoot on unclean surfaces or neglecting foot hygiene can easily lead to infections, including fungal infections and bacterial colonization, which can develop into more serious conditions like boils, impetigo, or cellulitis. Ensuring floors are clean, wearing socks and shoes in public spaces, and avoiding direct contact with contaminated surfaces are effective preventive practices. Additionally, wearing properly fitted and clean clothing, particularly socks and shoes, creates a protective barrier against bacterial invasion.
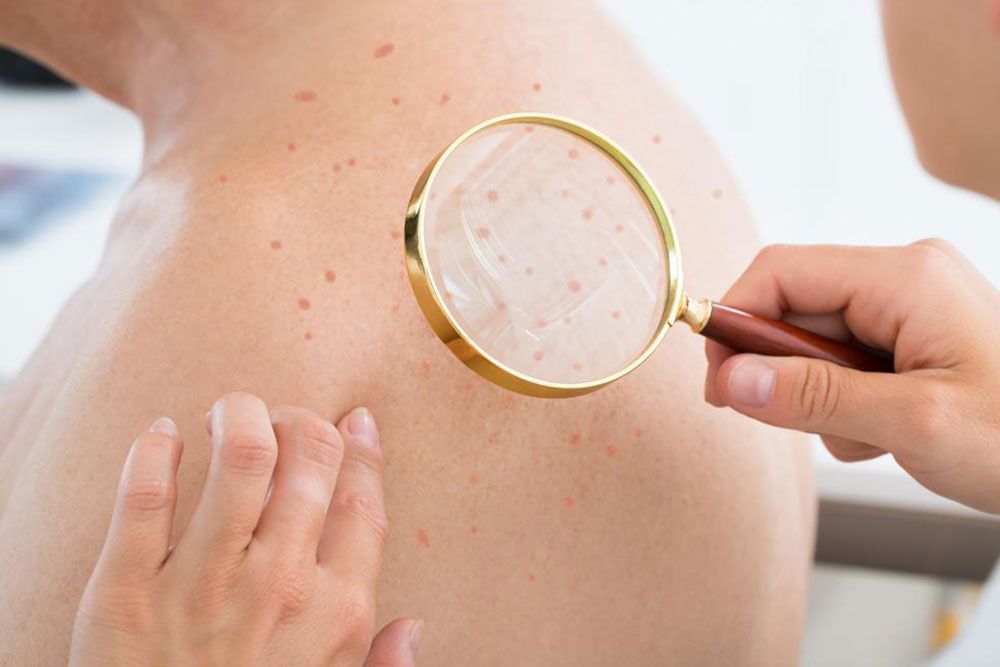
Recognizing the symptoms of staph infections early is vital for prompt treatment. Common signs include the appearance of painful boils, red lumps, or pus-filled lesions, which may be accompanied by swelling, warmth, and sometimes fever. Infections such as impetigo, characterized by honey-colored crusted sores, or cellulitis, which presents as spreading redness and swelling, require immediate attention from healthcare providers.
Treatment for staph infections typically involves targeted antibiotics prescribed by a healthcare professional. These may include cephalosporins, vancomycin, or other antibiotics based on the severity and location of the infection. For localized abscesses or boils, draining the infected area might be necessary to promote healing and reduce bacterial load. Proper wound care and hygiene are essential components of managing the infection effectively.
Prevention is always preferable to treatment. Enhancing the immune system through a balanced diet, regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management is crucial in reducing susceptibility. Maintaining rigorous personal hygiene, such as frequent handwashing with soap and water, disinfecting surfaces regularly, and avoiding sharing personal items, significantly decrease the risk of infection.
Healthcare professionals recommend additional measures to prevent recurrent infections, including staying up to date with vaccinations, especially if you are prone to skin infections, and monitoring for early signs of infection so that treatment can be initiated promptly. In community settings, implementing strict hygiene protocols and educating individuals about infection control can drastically reduce the transmission of staph bacteria.
In conclusion, understanding the nature of staphylococcus aureus bacteria and adopting comprehensive hygiene and preventive practices are essential steps toward avoiding both superficial and invasive staph infections. Timely recognition of symptoms and adherence to medical advice ensure effective management and recovery. By staying vigilant and committed to personal and environmental cleanliness, you can safeguard yourself and others from the risks associated with these common yet potentially serious bacterial infections.