Comprehensive Guide to Emphysema: Recognizing Symptoms, Causes, and Effective Management Strategies
This comprehensive guide explores emphysema, detailing its symptoms, causes, and management strategies. It emphasizes early detection, lifestyle adjustments, medications, and surgical options to improve patient outcomes. Effective prevention and treatment can significantly enhance quality of life for individuals living with this chronic lung condition.

Comprehensive Guide to Emphysema: Recognizing Symptoms, Causes, and Effective Management Strategies
Emphysema is a serious chronic respiratory condition that primarily impacts the lungs' alveoli, which are tiny air sacs responsible for oxygen exchange. Over time, damage to these alveoli reduces lung capacity and hampers breathing efficiency, leading to persistent shortness of breath, chronic cough, wheezing, and fatigue. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms early, and knowing the available treatment options are crucial for improving quality of life for those affected. This comprehensive guide delves into everything you need to know about emphysema, including risk factors, prevention tips, and management strategies to help control this debilitating disease.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Emphysema
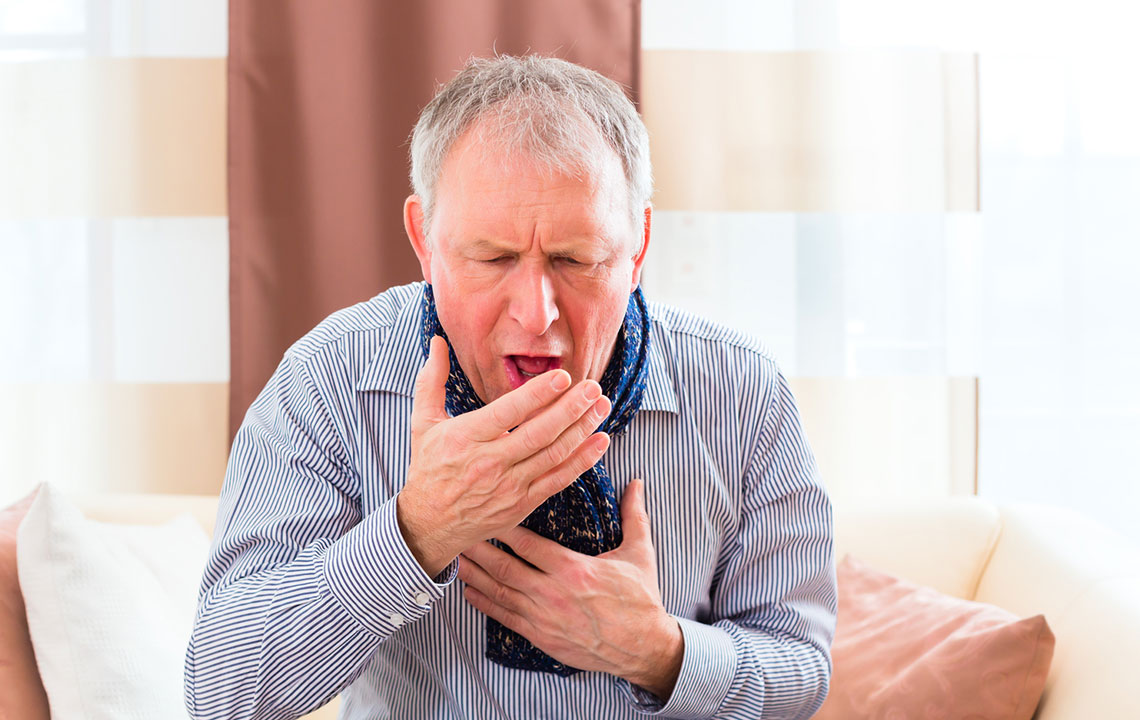
Early detection of emphysema hinges on awareness of its characteristic symptoms. Individuals may experience shortness of breath during exertion or even at rest as the disease progresses. Chronic cough, often accompanied by sputum production, becomes a persistent issue. Wheezing—an abnormal whistling sound during breathing—is also common. As lung function declines, sufferers may experience fatigue, chest tightness, and a reduced ability to perform daily activities. Recognizing these warning signs promptly can lead to earlier diagnosis and intervention, which is vital for managing the disease effectively.
Understanding the Causes and Risk Factors of Emphysema
The primary cause of emphysema involves the deterioration of the elastic fibers within the lungs, which leads to loss of lung elasticity and airflow obstruction. This damage is often caused by prolonged exposure to inhaled irritants and harmful substances. Cigarette smoking remains the most significant risk factor, accounting for the majority of cases worldwide. However, long-term exposure to occupational pollutants such as asbestos, chemical fumes, and dust also plays a substantial role. Environmental pollution, including vehicle exhaust and indoor fumes from cooking or heating, can exacerbate the risk.
Other contributing factors include repeated respiratory infections, genetic predispositions such as alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, and a history of viral lung infections like influenza or pneumonia, which can accelerate tissue damage. Lifestyle choices and environmental conditions greatly influence the likelihood of developing emphysema. Minimal exposure to tobacco smoke, pollutants, and irritants can substantially reduce risk. Moreover, maintenance of overall lung health through proper diet, regular exercise, and avoiding environmental toxins can act as protective measures.
Effective Management and Treatment Options for Emphysema
While emphysema is a progressive disease with no known cure, there are various strategies to alleviate symptoms, slow progression, and improve quality of life. The cornerstone of management involves lifestyle modifications, medications, and, in certain cases, surgical interventions.
Lifestyle Modifications and Preventive Measures
Ceasing smoking is the most impactful step in managing emphysema. Quitting smoking can prevent further lung damage and significantly improve prognosis. Additionally, reducing exposure to air pollutants, dust, fumes, and indoor irritants is vital—using air purifiers, ensuring proper ventilation, and avoiding strong fragrances or incense can make a meaningful difference.
Engaging in regular, moderate physical activity supports lung capacity and overall health. Activities such as walking, swimming, cycling, and gentle aerobic exercises are recommended after consulting healthcare providers. Maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding respiratory infections through vaccination and hygiene practices also form part of effective management.
Medications and Pulmonary Rehabilitation
Pharmacological treatment often includes bronchodilators, corticosteroids, and combination inhalers aimed at reducing airway inflammation and relaxing bronchial muscles. These medications help improve airflow, alleviate symptoms, and prevent exacerbations. Pulmonary rehabilitation programs—comprehensive interventions that combine exercise training, education, and behavioral changes—are highly beneficial. Such programs enhance endurance, reduce breathlessness, and improve mental health by addressing the emotional impacts of living with a chronic disease.
Advanced Treatments and Surgical Options
In severe cases unresponsive to medication and lifestyle interventions, surgical procedures such as lung volume reduction surgery (LVRS) or lung transplantation may be considered. LVRS involves removing damaged lung tissue to allow healthier regions to expand and function more effectively. For eligible patients with extensive lung destruction, lung transplants can replace the diseased lungs with healthy donor organs. Post-operative care includes careful monitoring and ongoing medication to prevent rejection and infection.
Emerging and Natural Supportive Therapies
Complementary approaches—such as breathing techniques including diaphragmatic and pursed-lip breathing—can help improve oxygenation and reduce dyspnea. Practicing yoga, meditation, and mindfulness may support mental well-being. Nutritional support, particularly ensuring adequate vitamin D levels through safe sun exposure or supplementation, may also help reduce airway inflammation and promote lung tissue repair.
Keeping indoor environments free of cigarette smoke, pet dander, fumes, and dust, along with using high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters, contributes significantly to symptom management. Proper hydration and balanced nutrition further support immune function and overall health.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis and Professional Care
Early detection is key to managing emphysema effectively. Individuals experiencing persistent respiratory symptoms should seek medical evaluation promptly. Pulmonologists can perform lung function tests, imaging studies, and other assessments to confirm diagnosis. Timely intervention, adherence to prescribed therapies, and lifestyle changes can delay disease progression and enhance quality of life.
Living with emphysema requires ongoing medical care, but with appropriate strategies, many individuals maintain active, fulfilling lives. Education about environmental controls, medication adherence, and healthy habits empowers patients to take control of their health and minimize the disease's impact.
In conclusion, while emphysema poses significant challenges, understanding its causes, symptoms, and management options can lead to better outcomes. Proactive measures, medical treatment, and lifestyle modifications are essential components of comprehensive care for those affected by this chronic lung disease.