In-Depth Strategies for Preventing and Managing Tick-borne Diseases
This comprehensive guide covers the identification, treatment, and prevention of tick-borne diseases. Learn effective removal techniques, recognize symptoms early, and adopt preventive measures to protect yourself from these tiny but significant health threats. Staying vigilant and prepared can significantly reduce the risk of serious illnesses caused by ticks, especially in outdoor environments. Whether you're hiking, camping, or simply enjoying nature, understanding how to prevent tick bites is crucial for maintaining good health and avoiding potential complications.
Comprehensive Approaches to Prevent and Treat Tick-related Illnesses
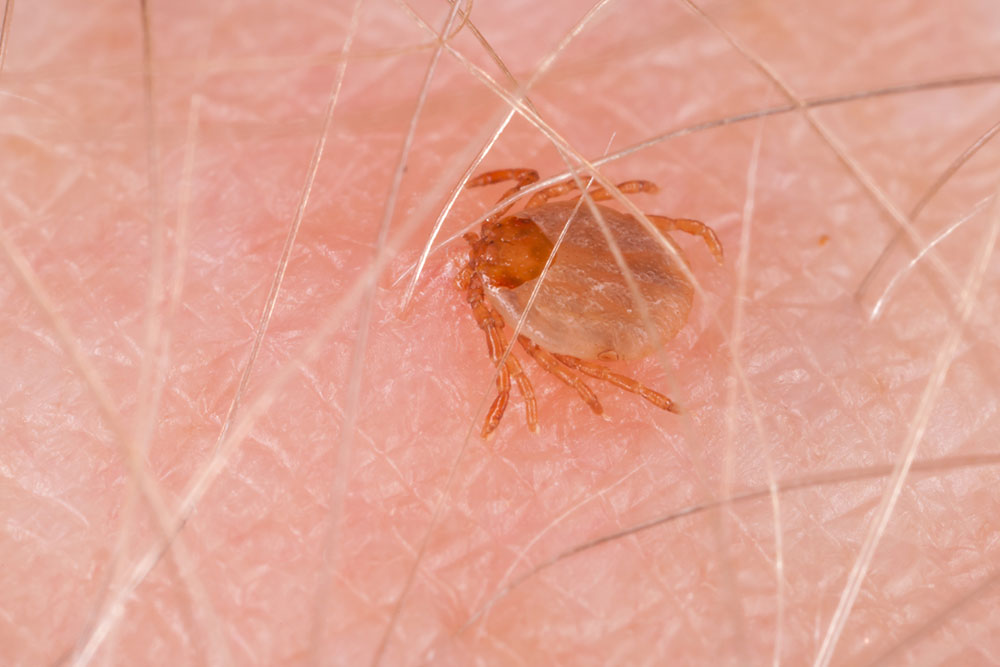
Ticks are tiny arachnids that present a significant health risk to humans due to their capacity to transmit a variety of infectious diseases. These small parasites, often less than 3 millimeters when unfed, latch onto human skin to feed on blood. During feeding, ticks release saliva containing toxins and pathogens that can cause serious illnesses. Diseases such as Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, Ehrlichiosis, Babesiosis, Tularemia, and Colorado tick fever have all been associated with tick bites. Recognizing the importance of timely intervention and effective prevention methods is crucial in minimizing health risks associated with these vectors.
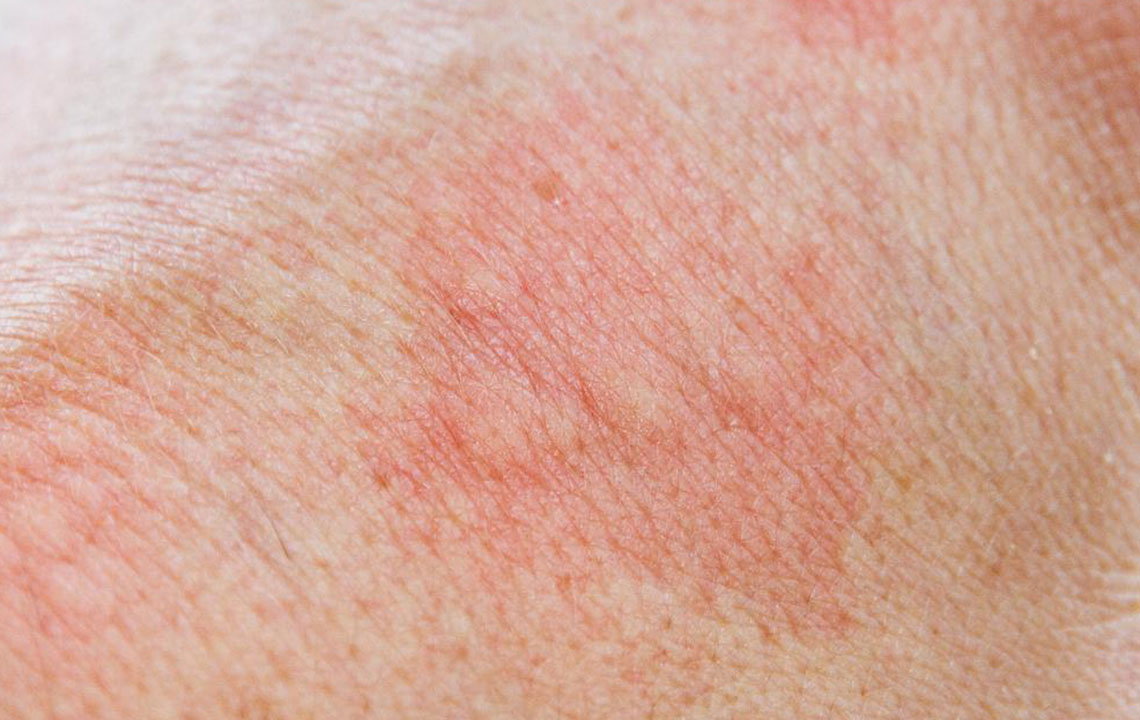
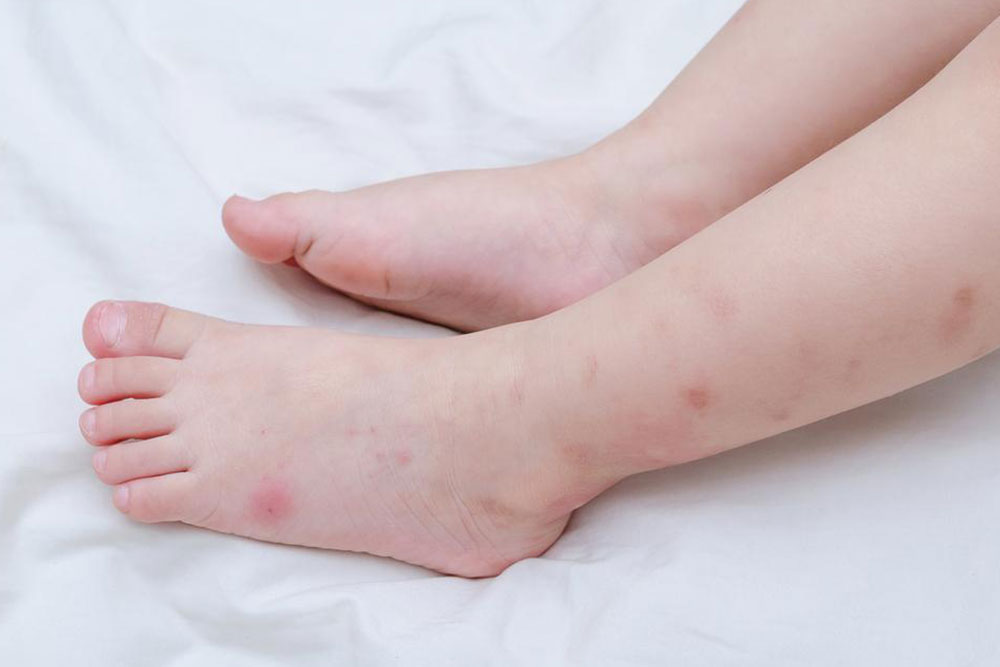
Because of their diminutive size, many individuals are unaware they have been bitten until symptoms develop. These symptoms can include rashes, fever, fatigue, or flu-like conditions that may appear days or even weeks after exposure. It's important to remain vigilant during outdoor activities in endemic areas, especially in wooded, grassy, or brush-covered regions where ticks thrive.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Tick-borne Diseases
Fever, chills, and headache
Muscle and joint aches
Numbness or tingling sensations
Palpitations or irregular heartbeat
Weakness, paralysis, or neurological issues
Neck stiffness and severe fatigue
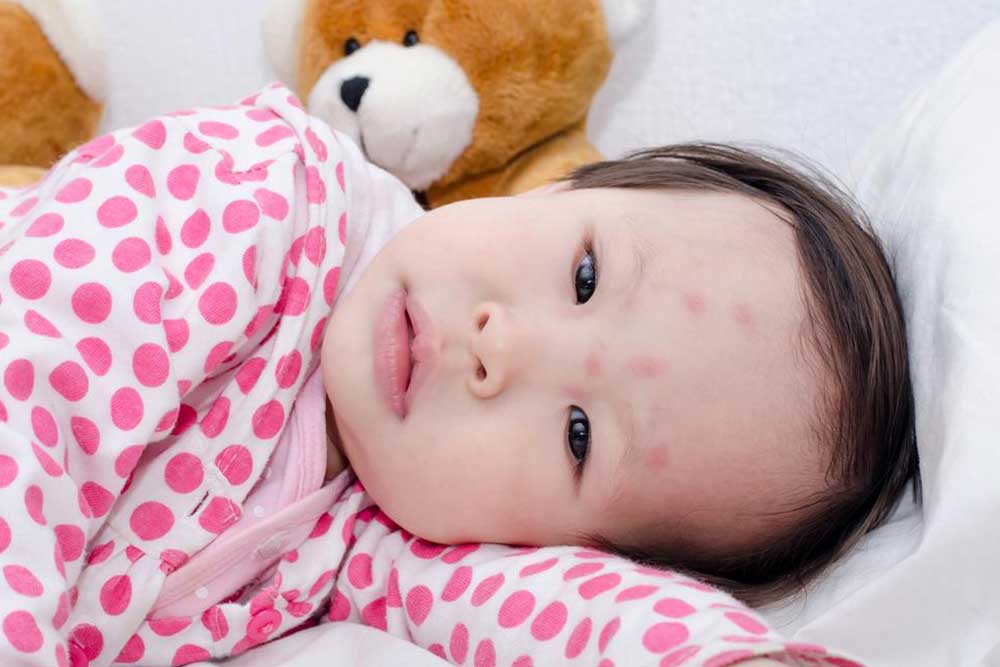
Rashes that vary depending on the disease, such as the characteristic erythema migrans in Lyme disease
Nausea, vomiting, or gastrointestinal discomfort
Swollen lymph nodes
Breathing difficulties or chest pain
If you experience these symptoms, especially after a known tick exposure, seek immediate medical attention. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are vital in preventing complications.
If parts of the tick are embedded, particularly the mouthparts or head, consult healthcare professionals for removal and testing.
Individuals with compromised immune systems, pregnant women, or children should seek medical advice after a tick bite, even if no symptoms are present.
Proper Techniques for Tick Removal and Post-Bite Care
Immediately examine your body for ticks after outdoor activities, paying close attention to hidden areas.
Use fine-tipped tweezers or specialized tick removal tools to grasp the tick as close to the skin's surface as possible.
Pull upward with steady, even pressure without twisting or squeezing, which could cause mouthparts to remain embedded.
Ensure the entire tick, including mouthparts, is removed. If any parts remain, seek medical attention for proper extraction.
Avoid handling ticks with bare hands; wear gloves or use tools to minimize infection risk.
Do not use harmful substances like nail polish, hot matches, or petroleum jelly on the tick, as these can trigger regurgitation of infectious fluids.
Place the removed tick in a sealed container or alcohol—this can aid identification and provide evidence if needed.
Immediately clean the bite area with soap and warm water, then disinfect thoroughly with alcohol or iodine scrub.
Monitor your health for symptoms over the following weeks. Follow your healthcare provider's advice, which may include antibiotics or other treatments.
Even if symptoms subside, it's recommended to undergo medical evaluation to rule out infection.
Early detection and removal of ticks are crucial steps for reducing the risk of disease transmission. Awareness and prompt action can significantly decrease health complications associated with tick bites.
Effective Prevention Measures to Avoid Tick Bites
Dress appropriately by wearing long-sleeved shirts and full-length pants when venturing into grassy, wooded, or bushy areas.
Choose pathways and trails that are cleared of tall grass and brush to reduce exposure.
Apply proven tick repellents containing at least 20% DEET on skin and clothing to deter ticks.
Perform thorough body checks after outdoor activities, paying special attention to commonly affected areas like behind ears, underarms, knees, and between toes.
Shower promptly after returning indoors to wash away unattached ticks and reduce your risk.
Inspect gear, clothing, and pets for ticks before entering and after outdoor excursions.
Remove and wash clothing separately in hot water after outdoor activities.
Consider using permethrin-treated clothing or gear for added protection.
Stay informed about local tick populations and disease prevalence in your area.
Since most ticks need to feed for over 24 hours before transmitting diseases, early detection and removal are essential in preventing infections. Applying these preventive strategies consistently can help safeguard you and your loved ones from tick-borne illnesses.