Comprehensive Overview of Health Risks Caused by Staphylococcus Bacteria
This comprehensive article explores the various health risks associated with Staphylococcus bacteria, including skin infections, toxic shock syndrome, food poisoning, bloodstream infections, and joint infections. It emphasizes early detection, prevention strategies, and the importance of medical treatment to prevent serious complications. Understanding these risks is essential for maintaining good health and safeguarding against staph infections, which can impact overall well-being if left untreated.
Comprehensive Overview of Health Risks Caused by Staphylococcus Bacteria
Staphylococcus bacteria, commonly known as staph, are a significant cause of various infections that affect individuals across different age groups and health conditions. These bacteria are versatile pathogens capable of causing a wide spectrum of health problems ranging from minor skin issues to life-threatening systemic infections. Even healthy individuals can be susceptible, especially when hygiene practices are inadequate or when underlying health conditions weaken the immune system. Understanding the various health risks associated with staph bacteria is crucial for early detection, prevention, and effective treatment.
Through this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different types of infections caused by staph bacteria, including skin-related ailments, toxic shock syndrome, food poisoning, bloodstream infections, and joint infections. We will discuss how these infections manifest, their symptoms, and the importance of timely medical intervention to prevent severe complications.
Maintaining good hygiene practices, being aware of risk factors, and seeking prompt medical care are essential steps in minimizing the impact of staph infections. Let’s delve into each of these health risks and understand their implications in detail.
Exploring the Various Health Issues Linked to Staphylococcus Infections
Staph bacteria are notorious for their ability to infect different parts of the body, leading to a variety of health complications. These range from skin and soft tissue infections to serious systemic conditions that can threaten life if not diagnosed and treated promptly.
Understanding these health risks is vital for anyone to recognize early signs of infection and seek appropriate medical attention. This knowledge also underscores the importance of maintaining hygiene, practicing safe behaviors, and managing pre-existing conditions that might increase susceptibility to infections.
Key Types of Health Problems Caused by Staphylococcus Bacteria
Staph infections can be categorized based on the site of infection and severity. Below, we will discuss the primary health problems associated with staphylococcus bacteria, detailing their causes, symptoms, and potential complications.
Skin-Related Infections
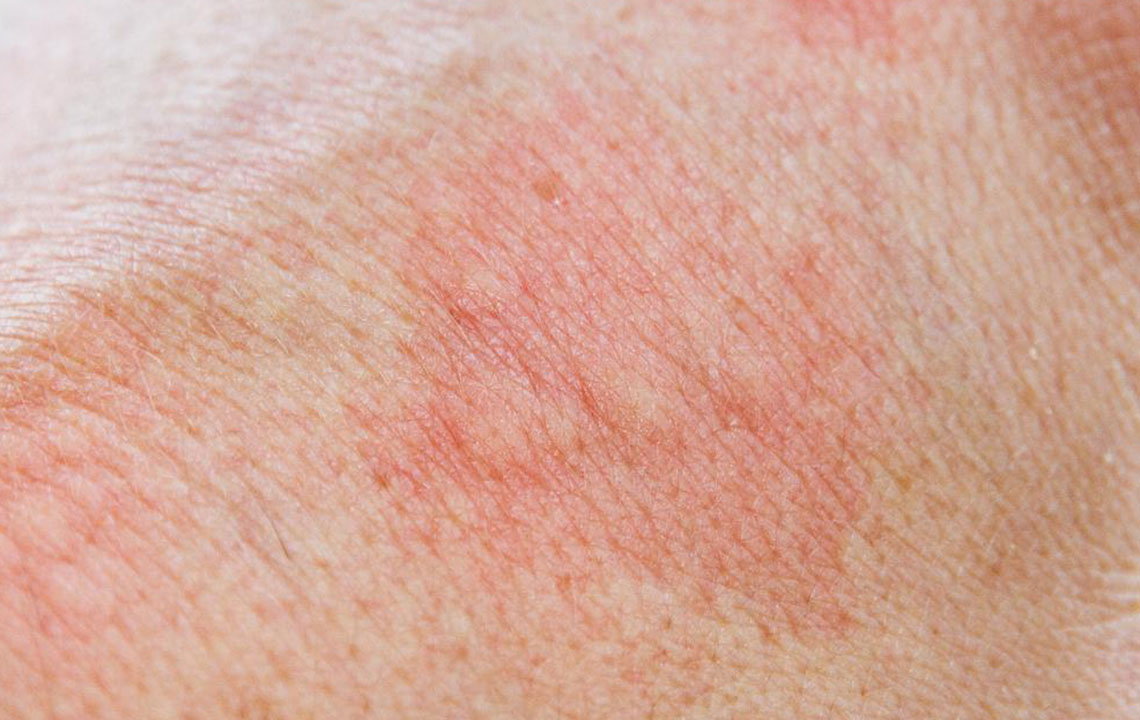
One of the most common manifestations of staph bacteria is skin infections, which can appear almost anywhere on the body. Your skin acts as a barrier against external pathogens, but when compromised, it becomes an entry point for bacteria leading to various dermatological issues.
These infections can range from minor irritations to severe skin conditions that require medical intervention. Here’s an in-depth look at the most common skin-related staph infections:
Boils - Boils are large, painful, pus-filled lumps that develop around hair follicles or oil glands. They are often redness, swelling, and tender to touch. These are typically caused by Staphylococcus aureus and require drainage and antibiotics for treatment.
Impetigo - This contagious skin infection manifests as red sores that quickly develop into crusted, oozing blisters. It’s common among children and can spread easily through contact.
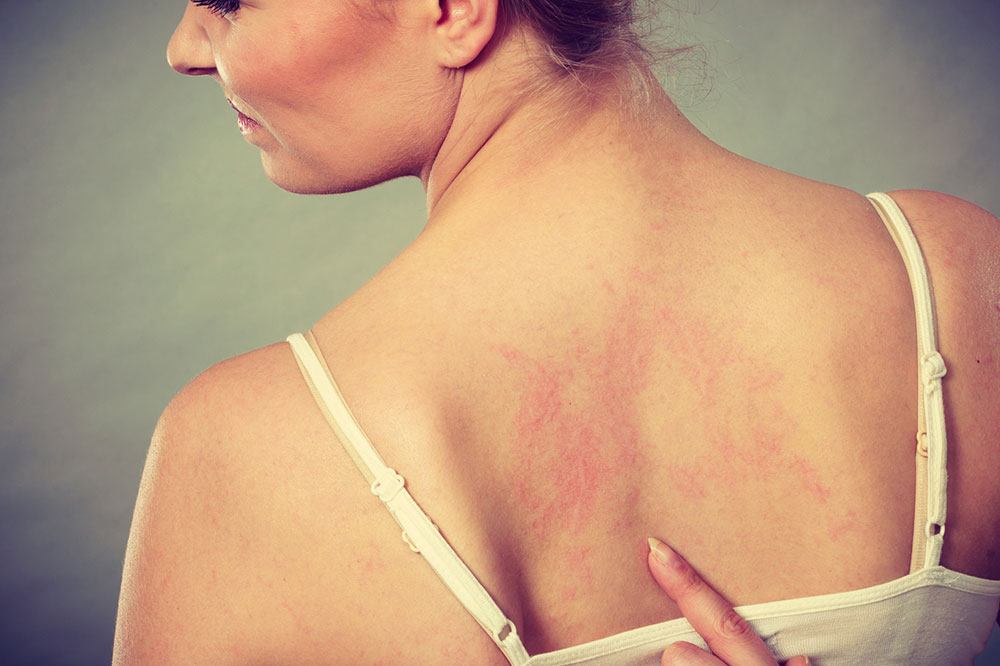
Cellulitis - A deeper infection of the skin and underlying tissues, cellulitis presents with redness, swelling, tenderness, and warmth. If untreated, it can lead to more serious systemic infections.
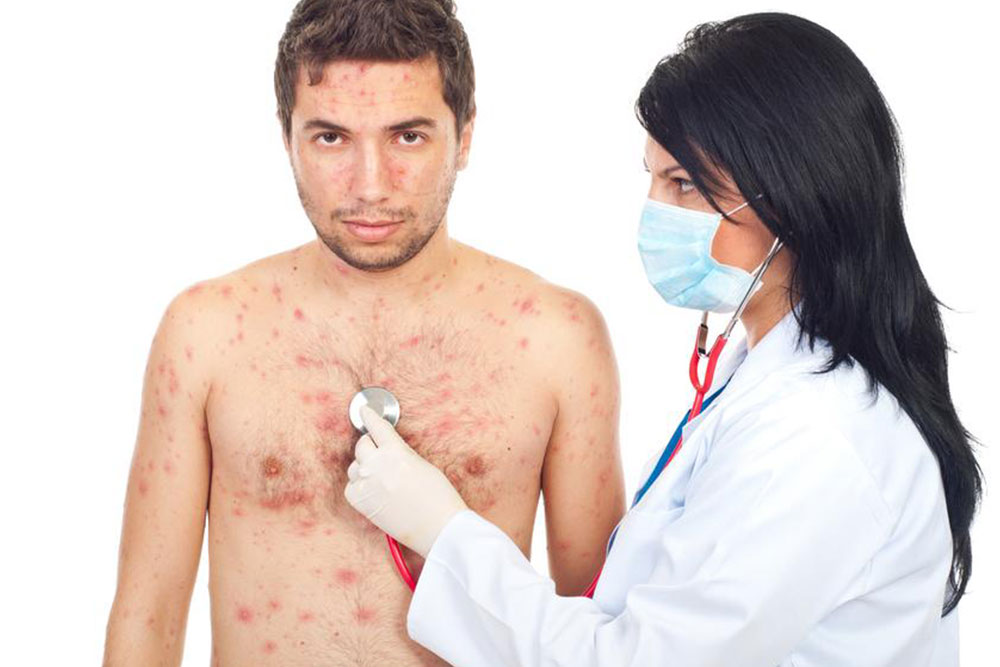
Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome - Primarily affecting infants and young children, this severe condition results from toxins produced by staph bacteria, leading to widespread redness, blistering, and peeling of the skin. It requires immediate medical attention to prevent complications.
Other Critical Health Conditions Related to Staph Infections
Beyond skin issues, staph bacteria can cause a range of serious health conditions, including:
Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS): A potentially life-threatening condition linked to prolonged tampon use, infected surgical wounds, or cuts. Symptoms include high fever, sudden drop in blood pressure, rash, muscle aches, confusion, nausea, and vomiting. Immediate medical hospitalization and antibiotic therapy are critical for recovery.
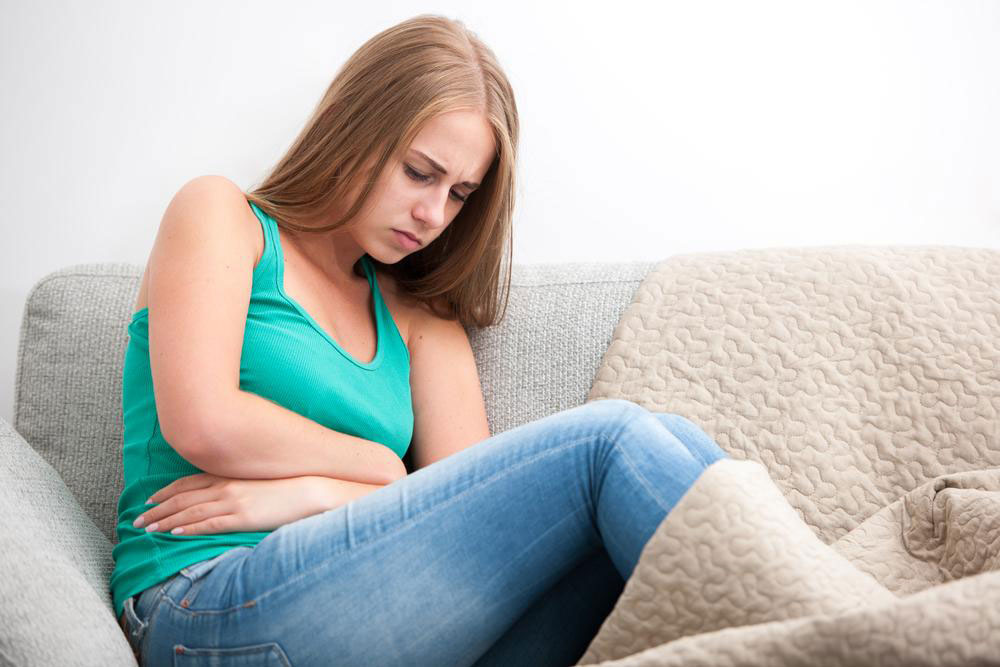
Food Poisoning: Staphylococcus bacteria are common culprits behind food poisoning incidents. Contaminated food, especially dairy, meats, and salads, can result in rapid onset of symptoms like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dehydration, and abdominal cramps. Proper food handling and storage are essential to prevent outbreaks.
Bloodstream Infections (Bacteremia): When staph bacteria invade the bloodstream, it can cause bacteremia, leading to symptoms such as fever, chills, low blood pressure, and systemic inflammation. If untreated, it can progress to sepsis, a life-threatening condition that damages organs.
Septic Arthritis: Infection of the joints such as knees, hips, shoulders, or fingers, caused by bacteria entering the joint space. This results in severe joint pain, swelling, redness, and stiffness. Prompt diagnosis and antibiotic treatment are vital to prevent joint damage.
Recognizing early symptoms and seeking immediate medical care can prevent the progression of these infections into more severe or systemic diseases. Medical professionals may recommend antibiotics, drainage procedures, or supportive care based on the type and severity of the infection.
In sum, staphylococcus bacteria pose a significant health threat due to their ability to cause diverse infections. Awareness, good hygiene, and early intervention are the best defenses to combat these potentially dangerous pathogens.