Comprehensive Guide to Effective Medications for Cold and Flu Relief
This detailed guide explores effective medications and remedies for managing cold and flu symptoms. It covers symptom distinctions, over-the-counter and prescription options, and supportive care strategies for swift recovery. Understanding treatment options empowers you to choose the best approach for relief and health management during cold and flu episodes.

Comprehensive Guide to Effective Medications for Cold and Flu Relief
Colds and influenza are among the most common respiratory illnesses worldwide, affecting millions of people each year. While these illnesses are often considered minor, their impact on daily life can be substantial, causing discomfort and disrupting routines at home, work, and school. Proper understanding of the symptoms, available medications, and supportive care options is crucial for effective management and swift recovery. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the various medications and remedies to help you combat cold and flu symptoms efficiently and safely. Whether you prefer over-the-counter solutions or prescription treatments, knowing your options ensures you can make informed decisions for optimal health outcomes.
Distinguishing Between Cold and Flu Symptoms
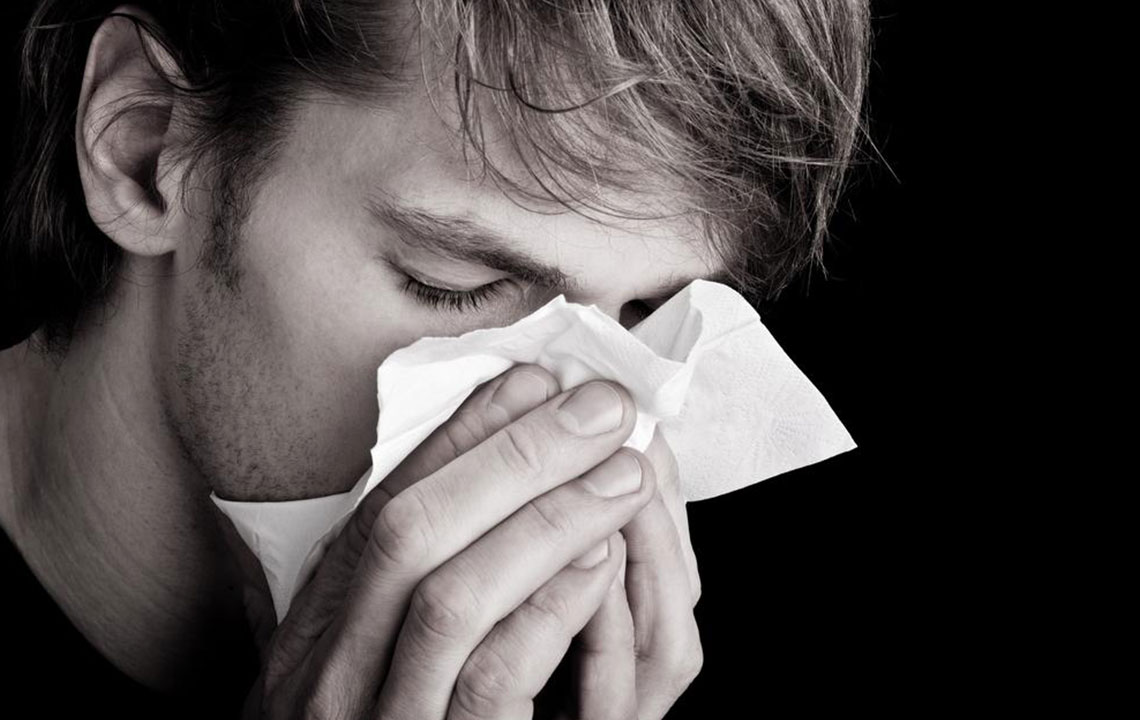
Understanding the key differences between cold and flu symptoms helps determine the severity and appropriate treatment. The common cold usually presents with mild symptoms such as sore throat, sneezing, nasal congestion, cough, and a slight rise in temperature. Cold symptoms tend to appear gradually and are less intense. In contrast, the flu manifests more suddenly with high fever, severe body aches, headaches, chills, and fatigue. Sometimes, flu can cause nausea or gastrointestinal upset. The severity of symptoms varies among individuals, and persistent or worsening symptoms warrant medical consultation to rule out complications or secondary infections.
Available Treatment Options for Cold and Flu
Managing cold and flu symptoms involves a combination of medications and supportive care. The choice of treatment depends on the specific symptoms, their severity, and individual health considerations. Over-the-counter (OTC) medicines are often sufficient for mild cases, while prescription medications may be necessary for severe or complicated cases. Here is an extensive overview of the most common medications and remedies to effectively relieve symptoms:
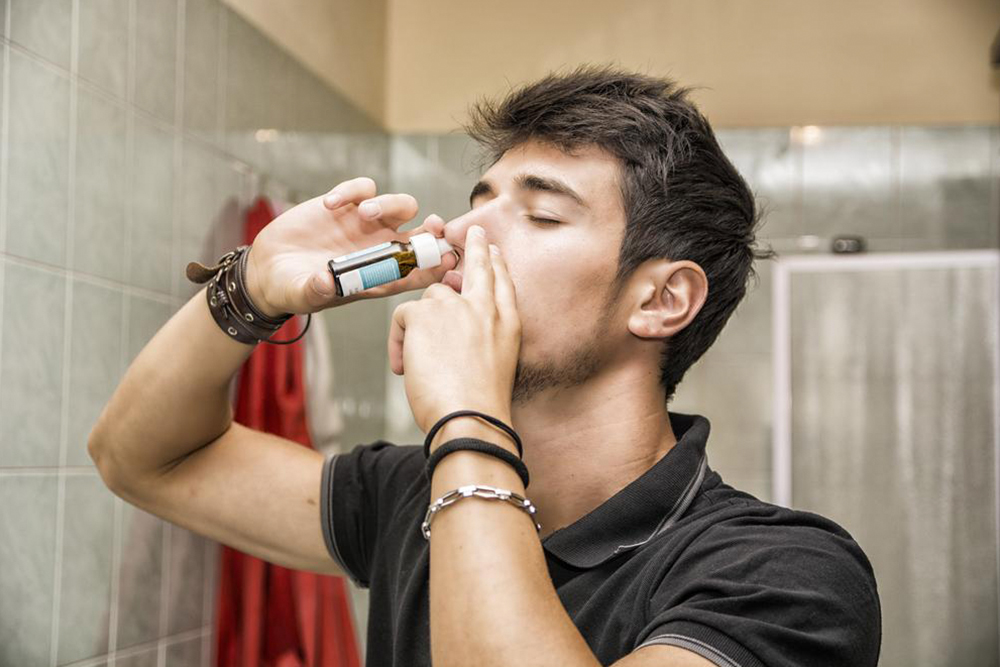
Decongestants: These medications are designed to reduce nasal swelling and ease breathing difficulties caused by congestion. They work by constricting blood vessels in the nasal passages, which diminishes swelling and fluid buildup. Decongestants are available in various forms, including oral tablets, nasal sprays, and drops. Popular OTC options include pseudoephedrine and phenylephrine, but it’s important to consult your healthcare provider before use, especially if you have underlying health issues such as hypertension, heart disease, or diabetes. Overuse of decongestant sprays can cause rebound congestion, so use them as directed.
Antihistamines: These are primarily used to combat allergy symptoms like sneezing, runny nose, and watery eyes, but they can also be helpful if allergies contribute to your cold-like symptoms. Antihistamines can be sedating or non-sedating, depending on the formulation. Examples include diphenhydramine, loratadine, and cetirizine. While effective, antihistamines may cause side effects such as dry mouth, drowsiness, or dizziness. OTC and prescription variants are available based on severity and individual response.
Fever reducers and pain relievers: For high fever, muscle aches, headaches, and sore throat, medications like acetaminophen (paracetamol) and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen are highly effective. These drugs help lower fever, reduce inflammation, and alleviate pain. It’s vital to follow dosage instructions carefully to prevent overdose or adverse effects, especially in children, the elderly, or those on other medications. Always consult your healthcare provider if symptoms persist beyond a few days or worsen.
Cough remedies: Cough management involves various formulations, including suppressants and expectorants. Cough suppressants, such as dextromethorphan, help diminish the urge to cough, providing relief, especially during rest or sleep. Expectorants like guaifenesin facilitate mucus elimination from the respiratory tract, making coughing more productive. Additionally, topical ointments such as menthol or eucalyptus-based chest rubs provide soothing effects and are applied directly to the chest or throat for local relief.
Combination therapies: Many OTC products contain a blend of ingredients aimed at relieving multiple symptoms simultaneously, such as a cough suppressant with a pain reliever or a decongestant combined with an antihistamine. These combination medicines can be convenient but should be used judiciously to avoid overmedication or unwanted side effects. Always check ingredient labels and consult your healthcare provider if unsure about their compatibility with existing medications.
While medications are central to managing cold and flu symptoms, supportive care is equally important. Rest allows your body to recover faster. Staying well-hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids—water, herbal teas, broths—helps loosen mucus and replace fluids lost due to fever. Inhalation of vapors, such as steam from hot water or humidifiers, can soothe nasal passages and reduce congestion. Warm baths can ease body aches and promote relaxation. Vitamin C supplementation or consumption of antioxidant-rich foods may support immune function. Applying hot compresses to sinuses or inflamed areas can reduce pain, while saline gargles provide relief for sore throats.
In summary, choosing the right medications and care strategies for cold and flu symptoms involves understanding your specific condition, severity, and underlying health status. Always seek medical advice if symptoms are severe, persistent beyond a week, or accompanied by warning signs such as difficulty breathing, chest pain, or neurological symptoms. Proper medication usage, combined with supportive measures, can significantly shorten illness duration and enhance comfort during recovery.