Comprehensive Guide to Kidney Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, and Early Detection Strategies
This detailed guide explores the causes, risk factors, and early symptoms of kidney cancer, emphasizing the importance of early detection for effective treatment. It provides valuable insights for individuals to understand their risks and recognize warning signs, encouraging timely medical consultation to improve health outcomes and survival chances.
Understanding the Root Causes and Recognizing the Signs of Kidney Cancer
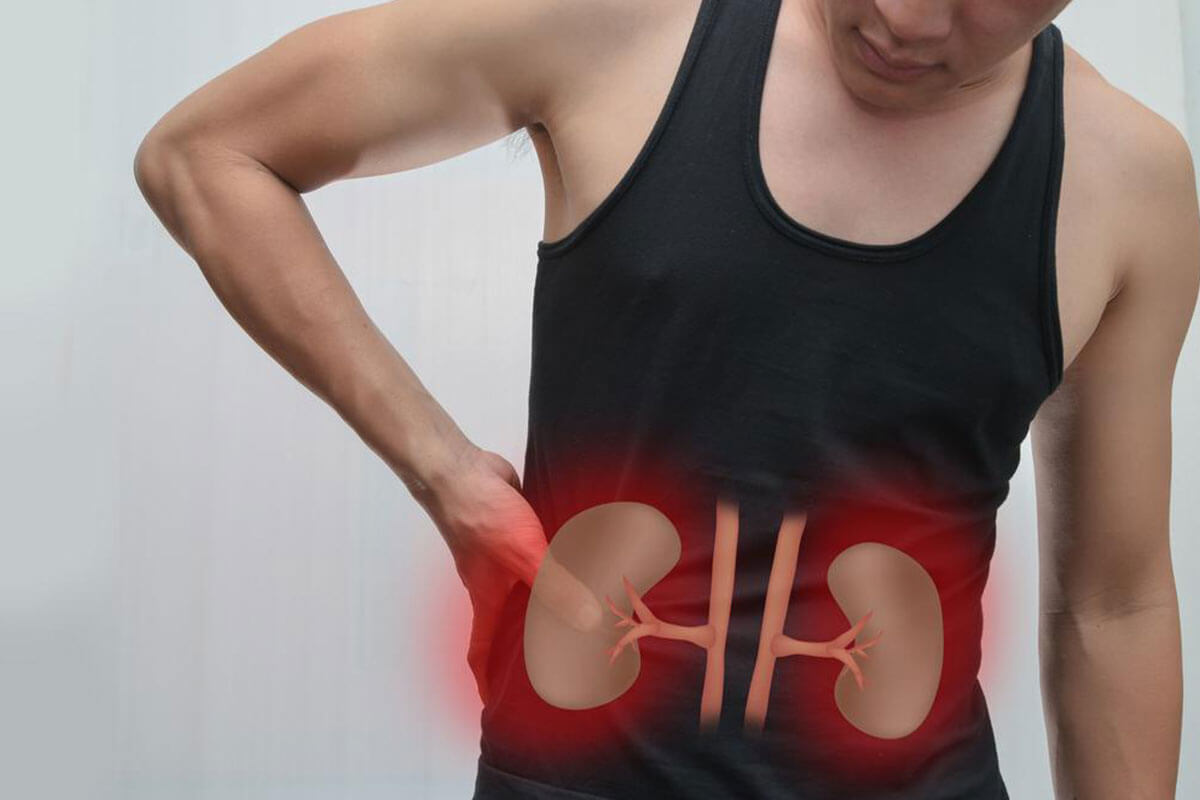
Kidney cancer, also known as renal cell carcinoma, is a form of malignant tumor that originates within the kidney tissues. It occurs when abnormal cells in the kidney grow uncontrollably, forming masses that can invade surrounding tissues and potentially metastasize to other parts of the body. Early identification of kidney cancer is essential for effective treatment, which significantly improves survival rates and quality of life. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the key causes, risk factors, and symptoms associated with kidney cancer to aid early detection and prompt medical intervention.
Causes and Risk Factors Contributing to Kidney Cancer Development
Understanding what causes kidney cancer is crucial for identifying at-risk individuals and implementing preventive measures. The development of kidney tumors involves complex genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. While some causes may be beyond control, many risk factors can be managed or mitigated through lifestyle changes and medical supervision.
Major Causes of Kidney Cancer
Although the precise cause of kidney cancer remains unclear, research points to several factors that increase susceptibility. These include genetic predispositions, lifestyle habits, and environmental exposures that can damage kidney tissues over time, leading to malignant transformations.
Key Risk Factors for Kidney Cancer
Several specific risk factors have been identified as significantly increasing the likelihood of developing kidney cancer. Awareness of these factors can lead to earlier screening and intervention, potentially saving lives through timely diagnosis.
Smoking: Tobacco use remains the most prominent preventable risk factor. Chemicals in cigarettes can damage the DNA within kidney cells, leading to mutations that eventually cause cancer. Smokers are markedly more vulnerable, making smoking cessation a critical step in reducing risk.
Gender: Men are statistically more prone to developing kidney cancer than women, possibly due to hormonal differences or lifestyle variations. Understanding this disparity can help tailor screening efforts towards higher-risk groups.
Obesity and Excess Weight: Being overweight or obese influences hormonal levels, which can promote abnormal cell growth in the kidneys. The accumulation of fat around the abdominal area also puts extra pressure on the kidneys and liver, exacerbating overall health risks.
Medication Use: Prolonged use of certain over-the-counter drugs, especially pain relievers like NSAIDs, has been linked to kidney damage over time, potentially increasing the risk for malignancies.
Previous Kidney Disease: Individuals with a history of kidney-related conditions, such as chronic kidney disease or renal cysts, face a greater chance of developing kidney cancer due to ongoing cellular stress and inflammation.
Genetic Factors: Family history plays a role, with inherited genetic mutations increasing the likelihood of early tumor development. Conditions like Von Hippel-Lindau disease are known genetic contributors to kidney cancer.
High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Hypertension is a common condition associated with damage to blood vessels, including those in the kidneys, increasing the risk for tumor formation.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Kidney Cancer
Early detection of kidney cancer significantly influences treatment outcomes. While some individuals may remain asymptomatic in the initial stages, others exhibit warning signs that should prompt medical evaluation. Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to timely diagnosis and improved prognosis.
Blood in the Urine (Hematuria): One of the most common and noticeable symptoms is hematuria, characterized by blood appearing in the urine. The blood may be visible to the naked eye or detectable only via laboratory tests, signaling possible damage or tumors within the kidney.
Pain in the Back or Flank: Persistent pain located in the back or flank region, particularly on one side, can be indicative of an underlying kidney abnormality. This discomfort may be dull or aching and does not resolve with typical pain relievers.
Unexplained Weight Loss: Significant weight loss without any change in diet or exercise routines often points to an underlying health concern, such as tumor growth, that disrupts normal metabolic processes.
Fatigue and Weakness: Persistent tiredness, despite adequate rest, can be a sign of systemic effects from cancer, including anemia or metabolic changes associated with tumor activity.
Fever of Unknown Origin: Long-lasting or recurrent fever not linked to infections may be symptomatic of an inflammatory response triggered by tumor activity within the kidney.
Anemia: Reduced red blood cell counts, resulting in pallor and weakness, might be a consequence of internal bleeding or marrow suppression due to cancer invasion.
Preventive Measures and When to Seek Medical Advice
While some risk factors like genetics and age are beyond control, lifestyle modifications play a vital role in reducing the chances of developing kidney cancer. Avoiding tobacco, maintaining a healthy weight, controlling blood pressure, and limiting the use of nephrotoxic medications are practical steps to lower risk.
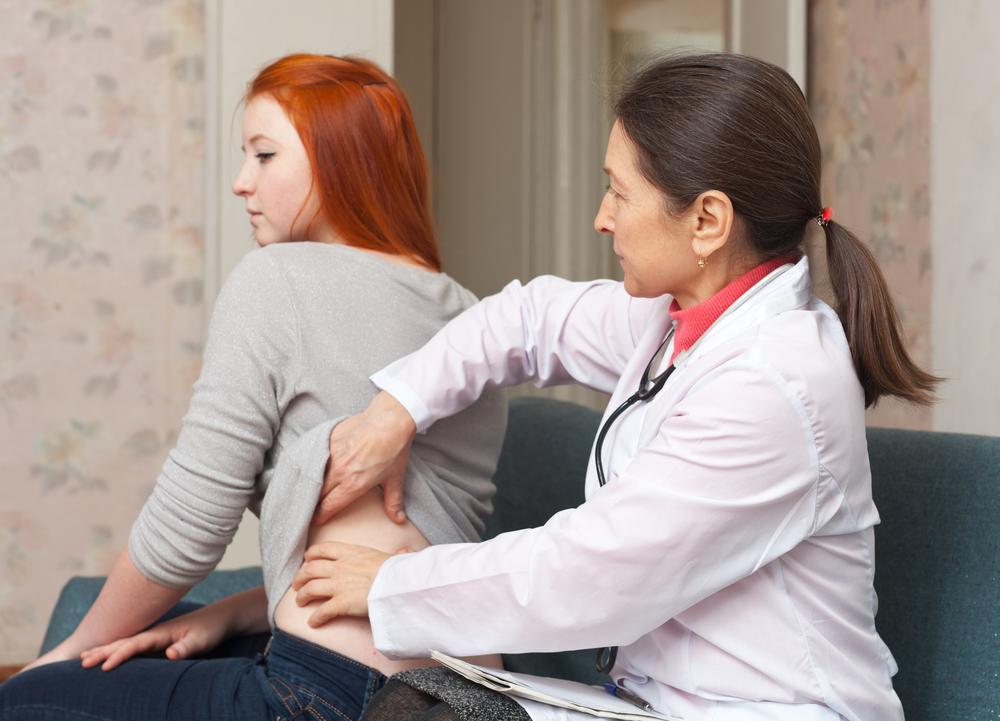
If you experience symptoms such as blood in your urine, persistent back pain, unexplained weight loss, or fatigue, it is imperative to consult a healthcare professional promptly. Early diagnosis typically involves imaging tests such as ultrasounds, CT scans, or MRI scans, along with laboratory analyses. Regular check-ups and screenings are crucial for individuals with higher risk profiles, ensuring that potential issues are caught at the earliest stages for more successful treatment outcomes.
Conclusion: Staying Vigilant Against Kidney Cancer
Kidney cancer remains a significant health concern worldwide, primarily due to its often subtle early symptoms. Understanding the causes and recognizing the signs are the first lines of defense in effective management. By adopting healthier lifestyles, avoiding known risk factors, and seeking medical attention when symptoms appear, individuals can improve their chances of early detection and successful treatment. Continued research and awareness campaigns are essential in the fight against kidney cancer, helping save lives through education and preventive health strategies.