Comprehensive Approaches and Effective Treatments to Relieve Lower Back Pain
Discover comprehensive strategies and treatments to effectively alleviate lower back pain. From identifying common causes and diagnosis methods to safe exercises and lifestyle tips, this detailed guide empowers you to manage and prevent lower back discomfort, ensuring improved mobility and quality of life.
In-Depth Strategies and Therapeutic Options for Alleviating Lower Back Discomfort
Lower back pain is a common health issue that affects a significant portion of the population at some point in their lives. Whether it manifests as a persistent dull ache or an intense, sharp shooting pain that radiates into the legs, lower back discomfort can considerably impact daily life and overall well-being. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and management options is essential for effective relief and prevention.
Lower back pain may arise suddenly, often following activities like heavy lifting, sports injuries, or awkward movements, or it could develop gradually due to poor posture or chronic conditions. Recognizing early warning signs and seeking appropriate treatment can prevent escalation and promote quicker recovery.
Common Causes of Lower Back Discomfort
Identifying the root causes of lower back pain is crucial for targeted treatment. Persistent discomfort should always prompt consultation with healthcare professionals, especially if accompanied by alarming symptoms like unexplained weight loss, neurological deficits, or signs of infection. Often, lower back pain results from muscle strains, ligament sprains, or herniated discs that put pressure on nerves, leading to radiating pain from the hips down to the legs.
Repetitive movements such as lifting heavy objects improperly, frequent pulling motions, or sustaining poor posture during prolonged sitting can all contribute significantly to lower back issues. Overexertion during physical activity, excessive weight gain, and sedentary lifestyles are also risk factors that increase vulnerability. Individuals lacking adequate core strength or doing insufficient back exercises may experience recurring discomfort.
Furthermore, some chronic health conditions like fibromyalgia, spinal stenosis, or inflammatory diseases such as ankylosing spondylitis can cause persistent lower back pain that requires specialized management. Proper diagnosis involves understanding the specific cause to craft an effective treatment plan.
Diagnosing lower back pain typically involves imaging techniques such as X-ray, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or computed tomography (CT) scans. A thorough physical exam, assessment of symptom progression, medical history review, and sometimes nerve conduction studies help pinpoint the underlying issue. Once diagnosed, treatment strategies may include medications, physical therapy, or in some cases, surgical intervention.
Mild to moderate pain can often be relieved with over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen. Topical gels and creams also provide targeted relief. However, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional before using medications or pursuing specific treatments, especially if symptoms persist or worsen.
Back Strengthening and Supportive Exercises for Pain Relief
Remaining inactive or avoiding movement can exacerbate back pain by weakening supporting muscles. Therefore, engaging in appropriate exercises designed to strengthen the back, core, and leg muscles is vital for both recovery and prevention. Always seek medical advice before commencing any new exercise routine to prevent further injury.
While certain exercises like toe touches or full sit-ups might strain the back, safer alternatives include hamstring stretches, pelvic tilts, wall sits, partial crunches, and bridging exercises. For instance, the wall sit involves standing about 12 inches from a wall, sliding down until your knees are bent at a 90-degree angle, pressing your back flat against the wall, holding for approximately 10 seconds, then slowly rising back up. Perform this 10 to 12 times to build endurance.
Additional beneficial exercises include knee-to-chest stretches to relieve lower back tension, pelvic tilts to strengthen abdominal muscles, and press-up back extensions. To perform a bridge, lie on your back with knees bent, feet flat on the ground, then lift your hips upwards, hold briefly, and gently lower yourself back down. These exercises improve mobility and support the spine’s stability.
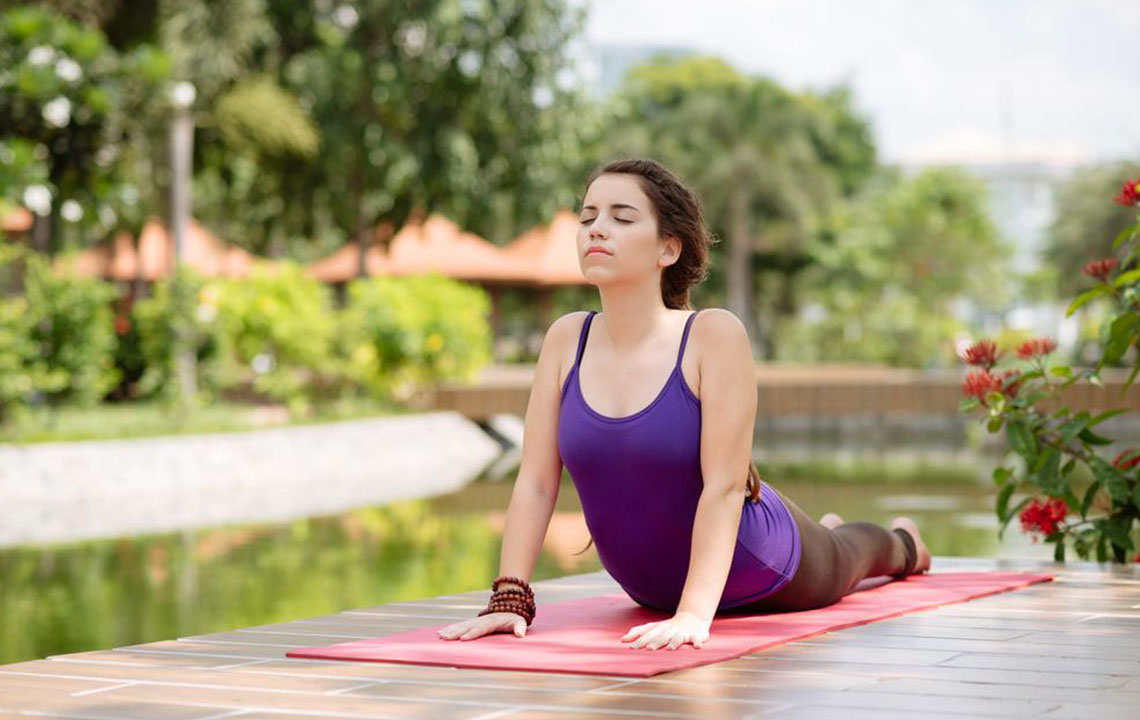
During episodes of acute pain, avoid heavy lifting and opt for gentle, low-impact activities such as swimming, walking, or cycling. Incorporating Pilates and yoga can also enhance flexibility, strengthen supporting muscles, and reduce discomfort.
In addition to exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, and using ergonomic furniture can further aid in pain management and prevention. Regular stretching routines, staying active, and addressing mental health aspects—such as managing stress—can contribute significantly to overall back health.
By understanding the causes of lower back pain, employing effective exercise routines, and seeking timely medical intervention when necessary, individuals can achieve significant relief and reduce the risk of future episodes. Remember, persistent or severe pain warrants professional evaluation to tailor an appropriate treatment plan that addresses your specific needs and promotes long-term spinal health.