Comprehensive Guide to Effectively Managing Plantar Fasciitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Strategies
This comprehensive guide explores causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and effective treatments for plantar fasciitis. It emphasizes preventive measures like supportive footwear, stretching, and lifestyle modifications to manage heel pain and improve foot health. Ideal for those experiencing persistent heel discomfort, the article provides insights to aid early diagnosis and successful recovery, ensuring mobility and comfort in daily life.
In-Depth Overview of Plantar Fasciitis and How to Manage It Effectively
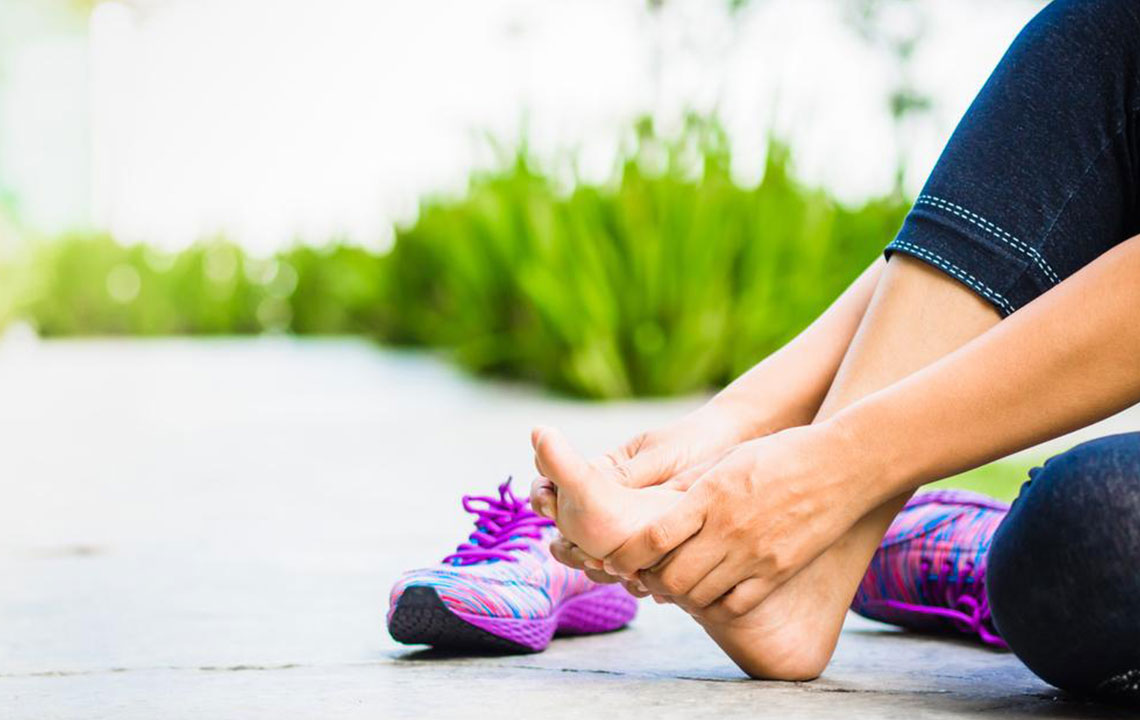
Foot pain is a common issue that many overlook or dismiss as minor discomfort, yet in many cases, it can be a serious sign of underlying conditions such as plantar fasciitis. This chronic condition involves inflammation of the plantar fascia, the thick band of tissue that runs along the bottom of your foot, connecting your heel bone to your toes. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for plantar fasciitis is essential for anyone experiencing persistent foot pain, especially athletes, active individuals, or those who spend a lot of time on their feet.
Plantar fasciitis develops due to excessive stress and strain on the plantar fascia, leading to tissue tears, inflammation, and pain. Common causes include repetitive impact activities like running or jumping, improper footwear, foot mechanics issues such as flat feet or high arches, and factors like obesity or sudden weight gain that increase load on the heel. Additionally, occupations involving prolonged standing or walking can contribute to the development of this condition. Recognizing early symptoms and triggers can help prevent worsening of the condition and facilitate effective management.
Identifying Symptoms of Plantar Fasciitis
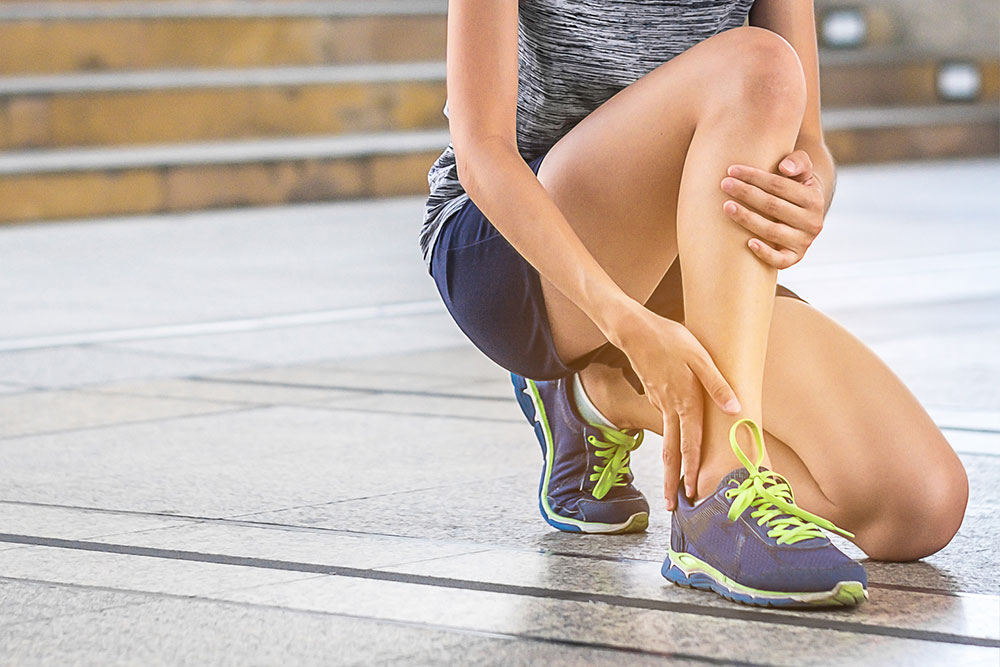
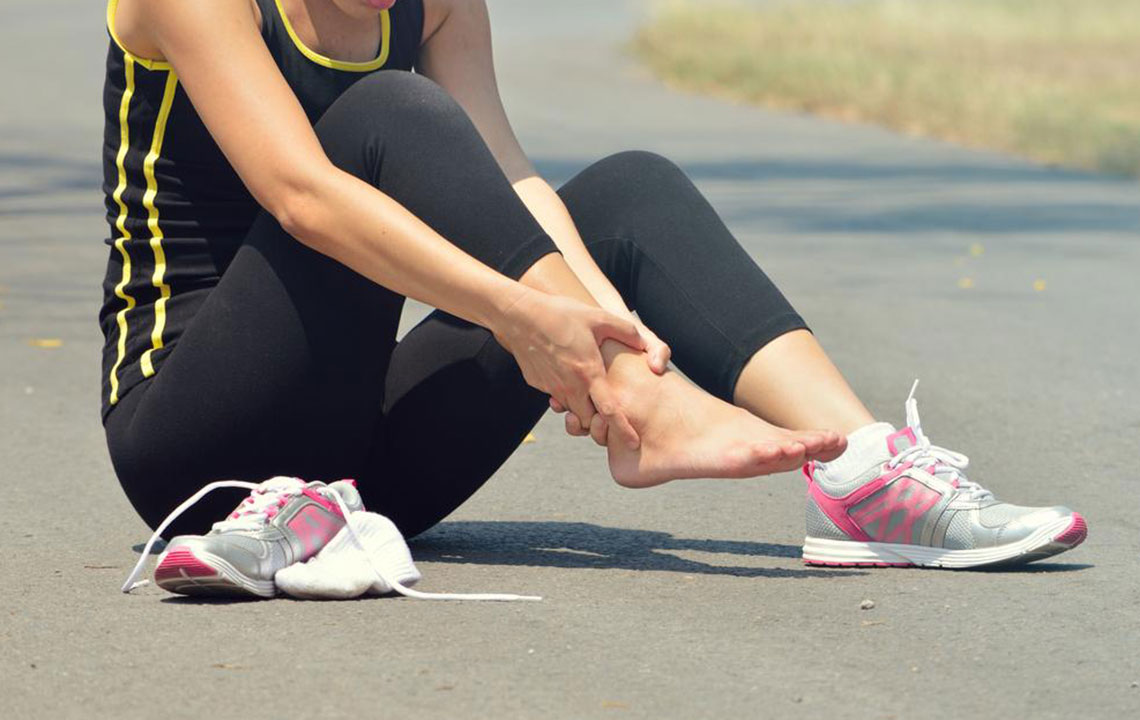
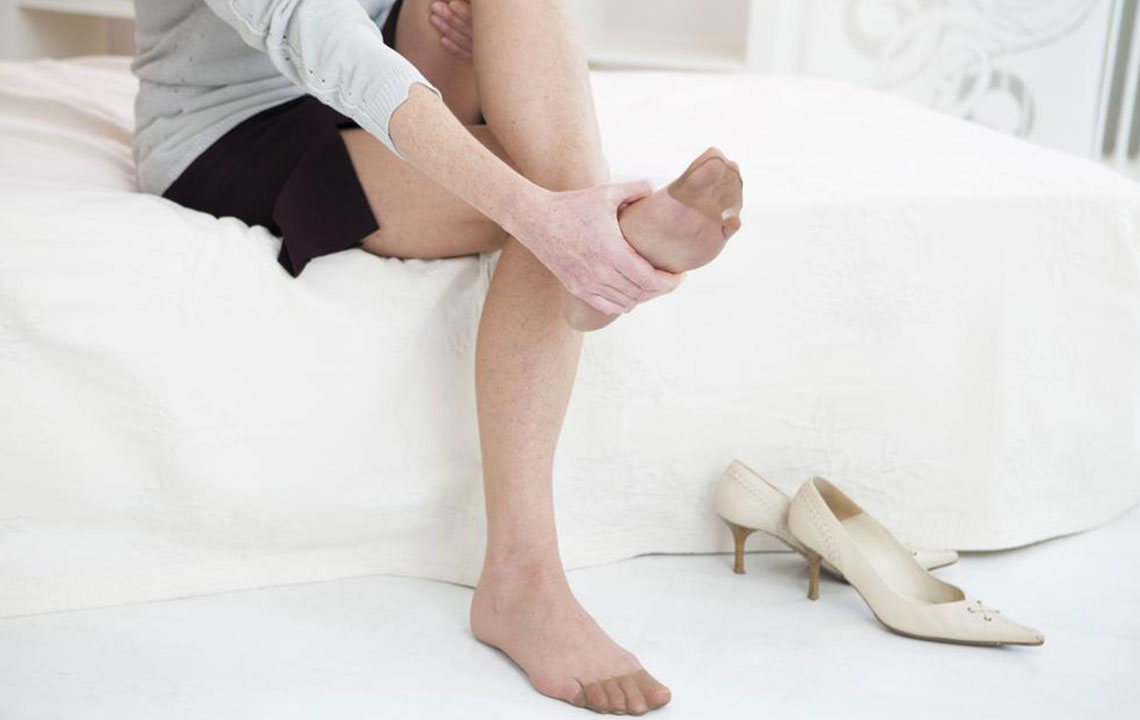
The hallmark symptom of plantar fasciitis is pain in the heel, usually described as a sharp or stabbing sensation that is most intense with the first steps after waking up or after periods of rest. As the day progresses or after extended activity, the pain may diminish temporarily but often returns after prolonged standing or activity. Some individuals may also notice swelling or tenderness along the bottom of the foot, particularly near the heel. If left untreated, the pain can become persistent and debilitating, affecting daily activities and overall mobility.
Diagnosing Plantar Fasciitis
Accurate diagnosis involves a combination of self-assessment and professional evaluation. Typically, sufferers experience increased pain after rest, especially in the morning. A healthcare professional will conduct a physical examination, applying gentle pressure to the heel and arch to identify tender points. They may observe your gait and foot arches, and in some cases, order imaging tests such as X-rays to rule out calcaneal spurs or other underlying issues. Proper diagnosis is crucial as it guides appropriate treatment strategies and rules out other conditions that might mimic plantar fasciitis symptoms.
Effective Treatment Options for Plantar Fasciitis
Managing plantar fasciitis effectively often involves a multi-faceted approach aimed at reducing inflammation, alleviating pain, and preventing recurrence. Non-surgical treatments are the first line of defense and include rest, ice application, stretching exercises, and anti-inflammatory medications. Physical therapy may be recommended to strengthen the foot and calf muscles, improve flexibility, and correct biomechanical abnormalities. Wearing supportive footwear plays a vital role in relief; shoes with proper arch support and cushioned insoles help distribute pressure evenly across the foot, reducing stress on the plantar fascia.
Custom orthotic inserts or over-the-counter heel cushions can provide additional targeted support. These inserts help absorb shock, alleviate tension, and promote proper foot alignment. In some cases, clinicians may suggest night splints that keep the fascia stretched overnight, easing morning pain. When conservative treatments fail, other options like corticosteroid injections, extracorporeal shockwave therapy, or, in rare cases, surgery may be considered. Most importantly, lifestyle modifications such as weight management and avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms can significantly improve outcomes.
Preventing Plantar Fasciitis and Maintaining Foot Health
Prevention is key when it comes to plantar fasciitis. Wearing properly fitted footwear with ample arch support and cushioning helps minimize strain. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces undue pressure on the heels and plantar fascia. Incorporating regular stretching and strengthening routines, especially for calf muscles and foot arches, can enhance foot stability and resilience. Athletes should avoid sudden increases in activity intensity or duration and always warm up adequately before engaging in vigorous exercise.
Understanding your foot mechanics through gait analysis can also help identify potential issues early. Custom orthotics tailored to your foot structure can prevent abnormal stress distribution. Proper rest periods and avoiding prolonged standing or walking can reduce the risk of developing plantar fasciitis. Early intervention at the first signs of discomfort ensures a quicker recovery and prevents the need for invasive procedures later on.
In conclusion, plantar fasciitis is a common but manageable cause of heel pain. Recognizing the symptoms early, diagnosing accurately, and adopting appropriate treatment strategies can significantly reduce discomfort and restore normal foot function. Whether through supportive footwear, targeted exercises, or medical intervention when necessary, most individuals can successfully overcome this condition and return to pain-free activity. Staying proactive with foot health is essential for maintaining mobility and overall well-being.





