Comprehensive Guide to Effective Ear Infection Treatment and Management
This detailed guide explores effective strategies for diagnosing, managing, and preventing ear infections. It covers symptoms, types, natural remedies, and medical treatments, emphasizing early detection and personalized care to ensure swift recovery, especially in children and vulnerable adults. Emphasizing prevention and responsible antibiotic use, the article aims to help readers understand how to handle ear infections effectively and reduce the risk of complications.
Effective Strategies for Managing and Treating Ear Infections
Ear infections are a common health concern that can significantly impact quality of life, especially during certain seasons or in specific populations. They often occur during rainy seasons and are more prevalent in children, though adults can experience them as well. Recognizing the symptoms early and understanding the appropriate treatment options can help prevent complications and promote faster recovery. This comprehensive guide explores the causes, symptoms, prevention, and effective treatment methods for ear infections.
Understanding Ear Infections: Causes and Types
Ear infections, medically known as otitis media or otitis externa depending on their location, are caused by bacterial, viral, or fungal agents. Environmental factors such as humidity, high temperatures exceeding 38°C, and water exposure during swimming can increase the risk. Allergy-related inflammation and skin conditions like eczema can also contribute to outer ear infections.
Primarily, ear infections are classified into two main types:
Inner Ear Infections (Otitis Interna): More common in children, often triggered by respiratory viruses such as cold and flu viruses. They involve inflammation of the ear canal and eustachian tubes connecting the middle ear to the throat, leading to pain and balance issues.
Outer Ear Infections (Otitis Externa or Swimmer's Ear): More prevalent among adults aged 45-75, caused by irritants like prolonged water exposure, injuries, or skin conditions such as eczema. These infections impact the external auditory canal and can interfere with the eustachian tube function.
Understanding these distinctions helps tailor treatment strategies effectively.
Recognizing Symptoms of Ear Infections
Early detection of ear infections is crucial for effective treatment. Symptoms can vary depending on age and infection type:
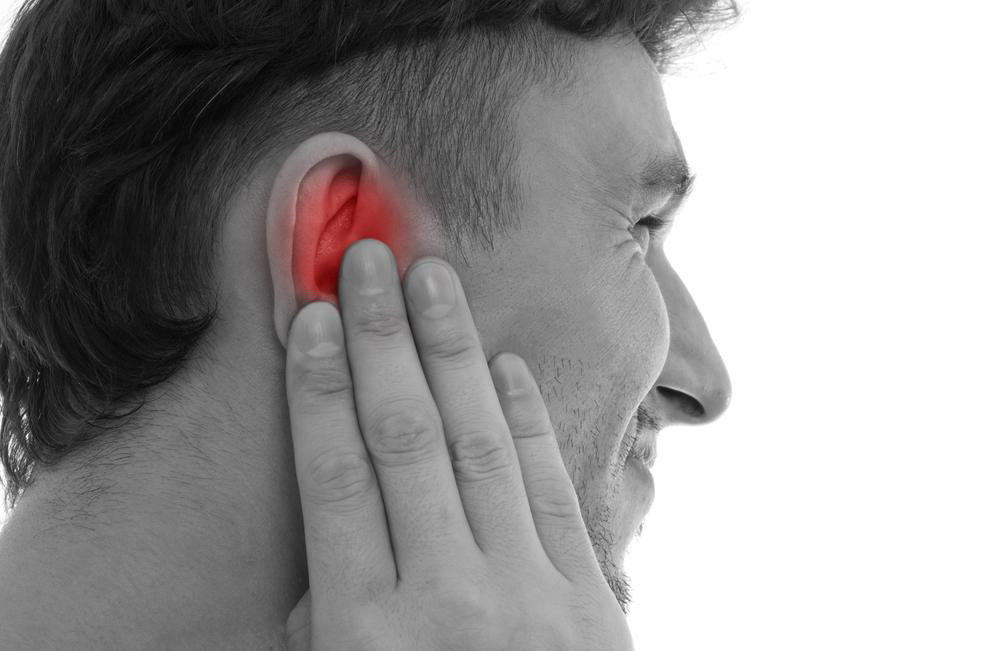
Ear pain or discomfort
Fullness or pressure sensation in the ear
Hearing difficulties or muffled sounds
Discharge from the ear, often yellow or fluid-like
Reduced energy and malaise
Skin peeling around the ear in outer infections
In infants and young children, symptoms may include:
Fussiness and irritability
Restlessness and difficulty sleeping
Loss of appetite
Rubbing or tugging at the ears
Balance issues or dizziness
Monitoring these signs can prompt timely medical intervention, reducing risks of complication.
Diagnosis and Differentiation
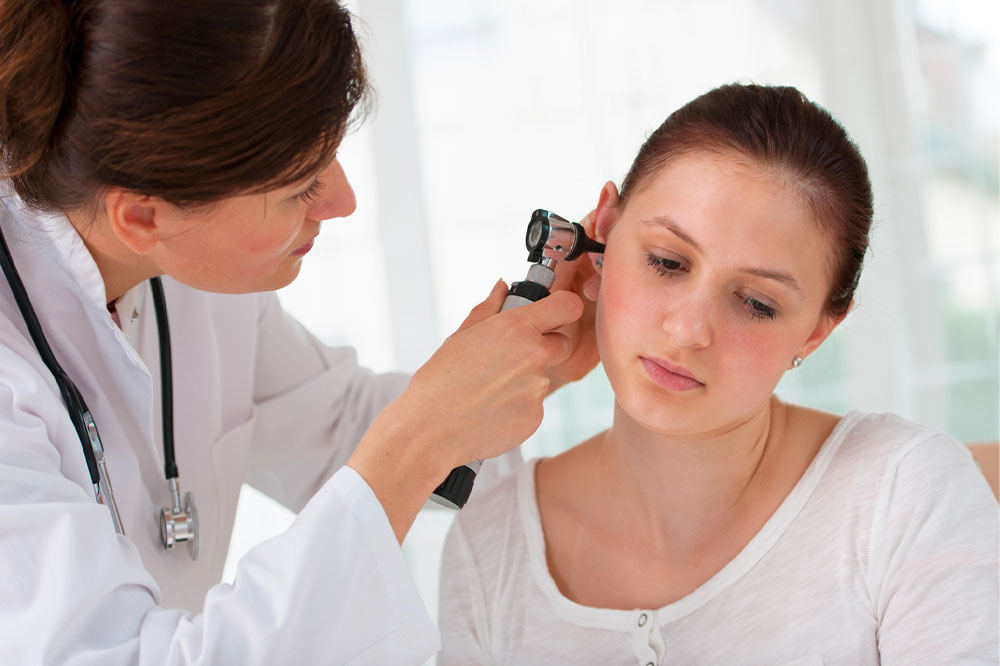
Physicians diagnose ear infections through physical examinations, looking at the ear canal, eardrum, and surrounding tissues. They may use otoscopes to visualize the ear structures and determine the infection's location and severity. Differentiating between inner and outer ear infections helps determine the best course of treatment.
Inner ear infections impact the eustachian tube and middle ear, often associated with respiratory infections, while outer ear infections typically involve skin issues or water-related irritants.
Effective Treatment Approaches for Ear Infections
While many ear infections resolve spontaneously within 2-3 days, appropriate management can alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. Treatment strategies include:
Pain Management: Over-the-counter analgesics such as paracetamol or ibuprofen are effective. Avoid aspirin in children under six due to Reye's syndrome risk.
Application of Warm or Cold Compresses: Using a clean, soft cloth with warmth or cold can provide soothing relief.
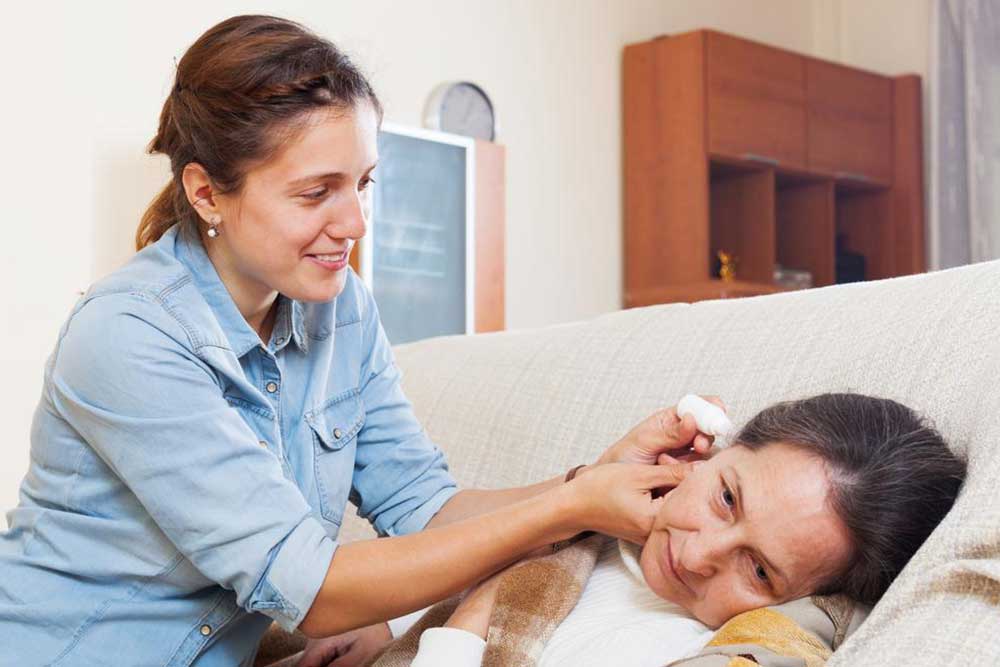
Maintaining Ear Hygiene: Gently clean any ear discharge with cotton wool, avoiding inserting objects into the ear canal.
Monitoring and Antibiotic Use: Since many ear infections are viral, physicians often recommend a watchful waiting approach for 72 hours. Antibiotics are reserved for bacterial infections or if symptoms worsen or persist beyond this period. Overuse of antibiotics can disrupt gut health and promote resistant bacteria.
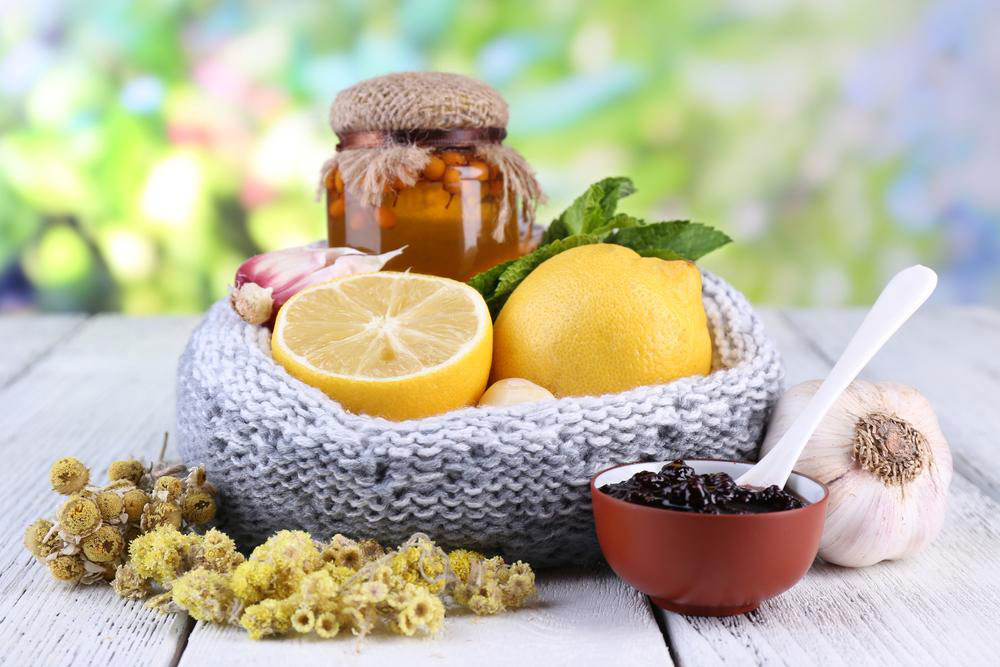
Natural Remedies and Home Care Tips
In addition to medical interventions, natural remedies can support recovery and symptom relief:
Garlic Oil: Due to its antiviral and antimicrobial properties, warm a few drops of garlic-infused oil and carefully apply into the affected ear daily.
Tea Tree Oil: Known for its antiseptic qualities, dilute a few drops in coconut or olive oil and apply around the ear, avoiding direct entry into the canal.
Addressing Food Allergies: Eliminating potential food allergies such as dairy, nuts, or gluten can reduce inflammatory responses that contribute to ear infections.
Eating certain foods can bolster immunity and help prevent future infections:
Hydrating Fluids: Drinking plenty of water aids mucus clearance.
Vitamin C-Rich Foods: Citrus fruits, broccoli, guava, and strawberries strengthen immune defenses.
Foods to avoid include:
Allergen-prone foods like gluten, nuts, and dairy (if allergic)
Sugar, which impairs immune function
Processed foods with artificial additives and preservatives
Prevention Tips for Ear Infections
Preventative measures are crucial to reduce the risk of ear infections:
Keep ears dry, especially during swimming or bathing
Avoid inserting objects into the ears
Practice good hygiene, especially after water exposure
Manage allergies effectively
Maintain a healthy diet to support immune health
Regular check-ups and prompt medical attention at the onset of symptoms can help limit infection severity and recurrence. If symptoms worsen or do not improve within 72 hours, consult a healthcare professional promptly.