Comprehensive Guide to Managing Postherpetic Neuralgia Effectively and Safely
Postherpetic neuralgia is a persistent nerve pain caused by shingles, affecting mainly older adults. This comprehensive guide explores various treatment options including medications, self-care tips, physical therapies, and mind-body practices. Combining these strategies can effectively reduce pain, improve quality of life, and provide long-term relief. Personalized management plans, supervised by healthcare professionals, are essential to achieving the best outcomes. Whether through medication, lifestyle adjustments, or alternative therapies like acupuncture and exercise, patients can regain comfort and confidence in managing this challenging condition.

Comprehensive Guide to Managing Postherpetic Neuralgia Effectively and Safely
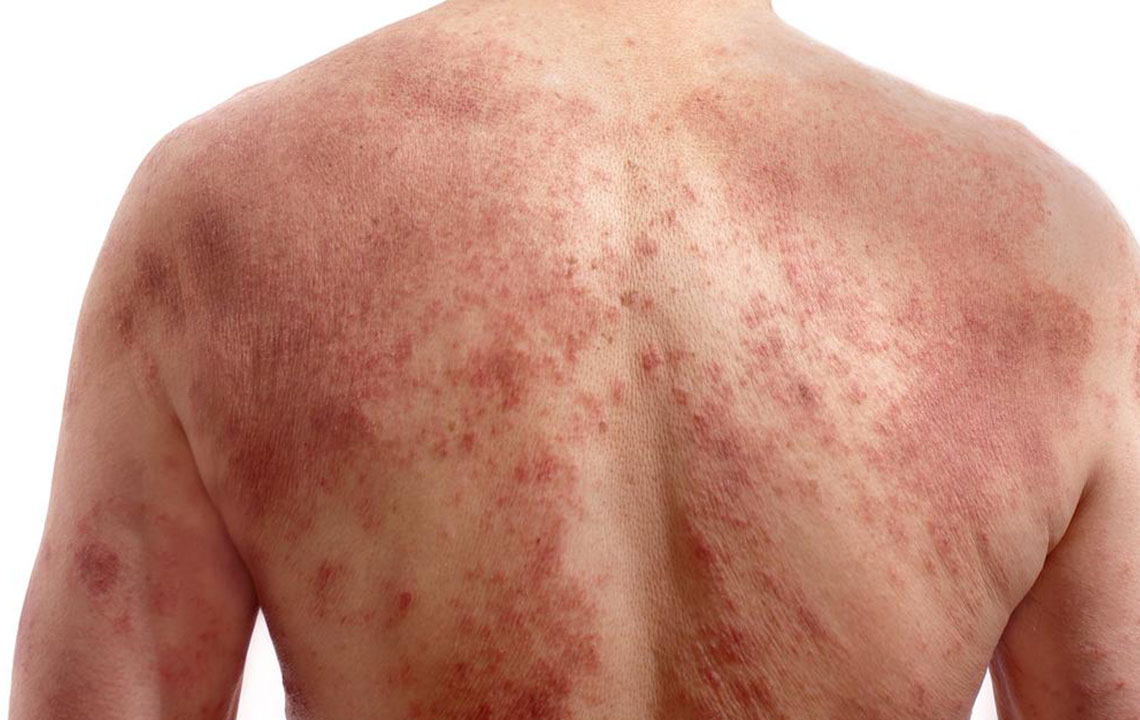
Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) is a chronic nerve pain condition that commonly occurs after an episode of shingles, caused by the reactivation of the herpes zoster virus. This condition manifests as persistent burning, stabbing, or aching sensations that can significantly impair quality of life. As shingles lesions heal, nerve fibers damaged by the virus often continue to send pain signals, leading to prolonged discomfort that can last for months or even over a year. Although more prevalent in older adults, particularly those over 60 years of age, PHN affects individuals of various ages and health backgrounds. Effectively managing this condition requires a holistic approach because, at present, there is no definitive cure or single medication that completely eradicates the symptoms. Instead, a combination of medical treatments, physical therapies, and lifestyle modifications can significantly reduce pain intensity and improve overall well-being.
Understanding the complexities of PHN and adopting an integrated treatment strategy can help patients regain control over their lives and reduce the burden of chronic pain.
Medication Strategies for PHN Relief While there is no universal cure for postherpetic neuralgia, various medications can provide meaningful pain relief and improve patients’ quality of life. It’s important to recognize that medications are often part of a broader treatment plan and may require adjustments based on individual responses. Here are some of the most common drug options used for managing PHN:
Over-the-counter pain relievers such as paracetamol (acetaminophen) or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) might be used initially for mild discomfort. However, these are often insufficient for severe neuropathic pain. In such cases, stronger prescription medications are necessary.
Antidepressants - Medications like duloxetine (Cymbalta) and amitriptyline are frequently prescribed because they target nerve signaling pathways involved in pain perception. These drugs can be highly effective in reducing neuralgia symptoms, although they are typically started at low doses to minimize side effects such as drowsiness, dry mouth, constipation, and weight gain. The therapeutic effects may take several weeks to become fully apparent.
Anticonvulsants — Drugs originally developed to treat epilepsy such as pregabalin (Lyrica) and gabapentin (Neurontin) are highly effective in calming overactive nerve activity responsible for pain. They help decrease pain sensitivity and improve comfort. Common side effects include swelling in extremities, dizziness, and mental fog, which usually subside with dosage adjustments.
Opioids — In cases where other therapies fail to provide adequate relief, opioids like tramadol and morphine may be considered under strict medical supervision. Due to potential dependencies, cognitive impairment risks, and emotional side effects, opioids are prescribed cautiously and for short-term use only.
Topical agents — Lidocaine patches deliver numbing medication directly to affected areas, providing localized pain relief without systemic side effects. Capsaicin cream, derived from hot chili peppers, works by depleting substance P, a neurotransmitter involved in transmitting pain signals, leading to a gradual decrease in pain over time.
Effective medication management often involves careful monitoring and combination therapy tailored to the patient's specific needs and tolerance levels.
Self-care and Preventive Measures to Ease Symptoms Incorporating simple lifestyle modifications can significantly lessen the severity and duration of neuralgic pain episodes:
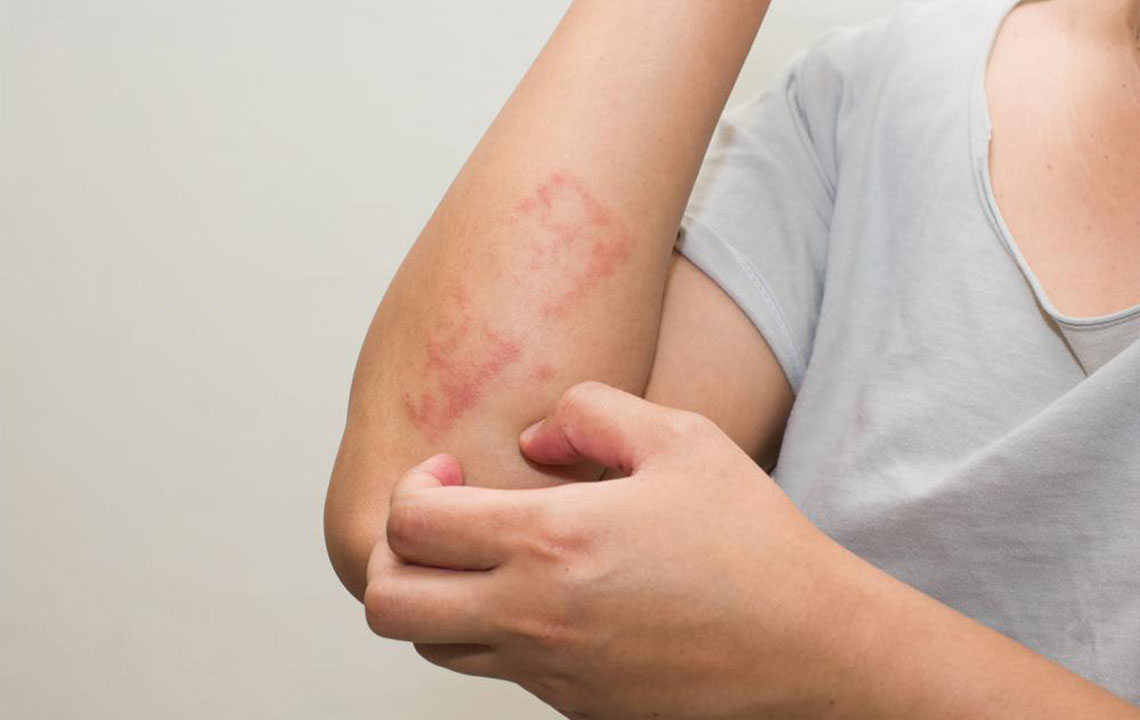
Protect affected skin by covering sensitive areas with soft dressings or cling film to prevent irritation from clothing or external elements.
Wear loose, breathable, and natural fabrics like cotton or silk, avoiding tight, rough, or coarse textiles that can aggravate skin hypersensitivity.
Apply cold packs with caution on painful regions to numb discomfort. Always check for adverse reactions and avoid prolonged application to prevent skin damage.
Physical and Mind-Body Approaches in Managing PHN
Engaging in gentle physical activities, as well as practicing alternative therapies, can play a vital role in managing postherpetic neuralgia. These approaches help not only in reducing pain but also in enhancing mental health and overall resilience:Exercise — Incorporating low-impact exercises such as yoga, tai chi, or stretching routines can strengthen muscles, improve circulation, and reduce stress, which may, in turn, diminish neuralgic pain. Consulting with healthcare or physical therapy professionals ensures exercises are safe and appropriately tailored to individual capabilities.
Acupuncture — This traditional Chinese medicine technique involves inserting fine needles at specific points on the body to unblock energy pathways (“qi”). Many patients report significant relief from nerve pain through acupuncture, with minimal side effects. It is often used in conjunction with other therapies.
In addition to physical activities, relaxation techniques including deep breathing exercises, meditation, and mindfulness have demonstrated beneficial effects in reducing pain perception and emotional stress associated with PHN. Regular practice of these mind-body approaches can lead to lasting improvements in symptoms and enhance quality of life.
In conclusion, managing postherpetic neuralgia requires a multi-faceted approach involving medication, self-care, physical therapy, and mind-body strategies. Patients are encouraged to work closely with healthcare providers to develop personalized treatment plans that address their specific needs. With proper management, individuals suffering from PHN can experience significant pain relief and regain control over their daily lives.