Comprehensive Guide to Detecting Early Signs of Type 2 Diabetes
Learn how to identify the early symptoms of Type 2 diabetes with this detailed guide. Understanding signs like persistent thirst, constant hunger, frequent urination, and slow wound healing can help in early detection and effective management of the disease. This comprehensive article discusses risk factors, the importance of regular screenings, and lifestyle tips to prevent serious complications associated with diabetes.

Comprehensive Guide to Detecting Early Signs of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a widespread chronic condition that affects millions worldwide. Unlike conditions that can be fully cured, diabetes is generally considered a lifelong illness, often described as a deficiency rather than a disease because it cannot be completely eradicated once it develops. Managing this condition primarily focuses on lifestyle modifications, including maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and following prescribed medications. Recognizing the early symptoms of Type 2 diabetes is vital for early intervention, which can significantly reduce the risk of severe complications such as cardiovascular diseases, vision loss, nerve damage, kidney failure, and compromised immune function.
Understanding the early warning signs can empower individuals to seek medical advice promptly. Many early symptoms can be subtle and easy to overlook, which is why awareness is crucial. This comprehensive guide will explore the most common and early indicators of Type 2 diabetes, providing valuable information for early detection and prevention.
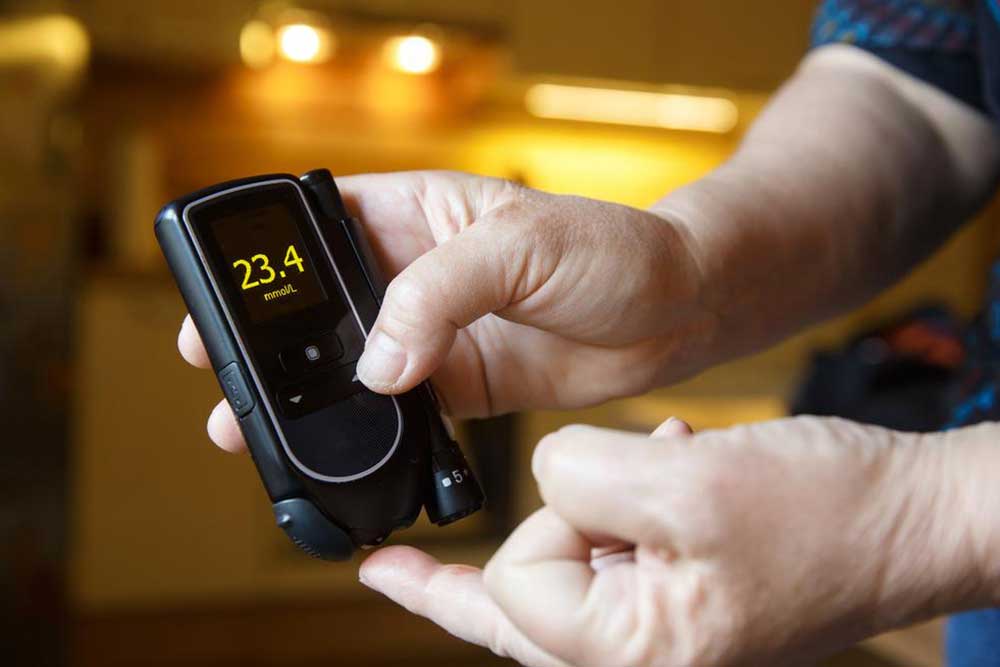
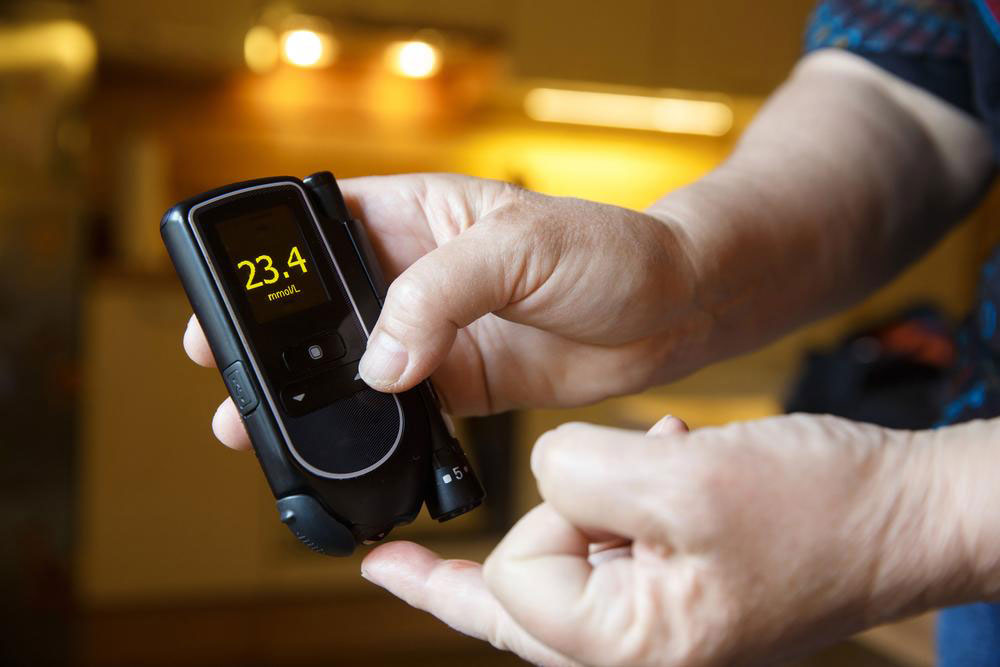
Persistent Thirst: Experiencing excessive dryness or constant feeling of thirst even after drinking adequate amounts of water is a common early sign. When blood sugar levels are high, the kidneys work harder to remove excess glucose, leading to dehydration and increased thirst.
Unrelenting Hunger: Feeling hungry frequently, even after consuming meals, can be an indication of how the body's insulin response is compromised. The body struggles to process glucose effectively, prompting increased hunger signals as it attempts to supply energy.
Frequent Urination: An increase in urination, especially waking up multiple times during the night or urinating more than usual during the day, is a typical symptom. Elevated blood sugar levels cause the kidneys to produce more urine to eliminate excess glucose, which leads to dehydration and further thirst.
Unusual Fatigue: Persistent tiredness and low energy levels that do not improve with rest or sleep can suggest that the body's cells are not getting enough energy due to impaired glucose metabolism.
Slow Wound Healing: Cuts, bruises, or sores that take significantly longer to heal than usual are a warning sign. High blood sugar can impair circulation and immune response, delaying the healing process.
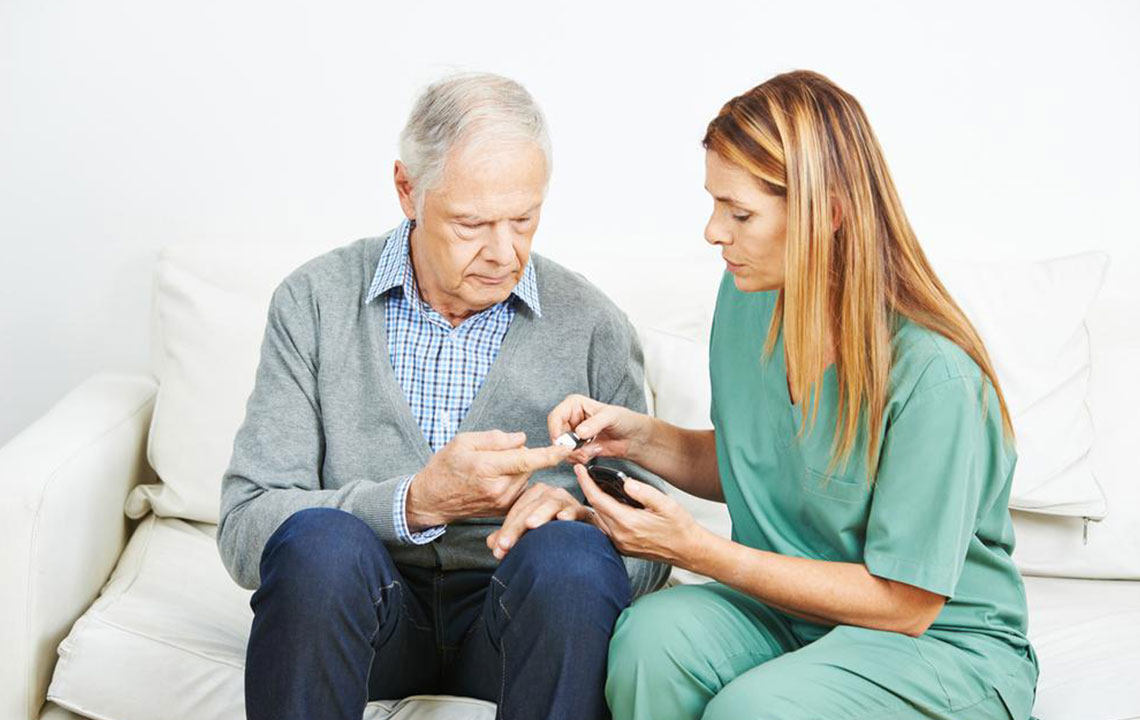
Family History of Diabetes: A strong family history increases the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. Individuals with such a background should be vigilant and regularly monitor their blood sugar levels to catch early signs.
It is important to highlight that nearly one-third of individuals with Type 2 diabetes remain unaware of their condition. This silent progression underscores the need for routine health screenings, especially for those with risk factors like obesity, sedentary lifestyle, or a family history.
Early detection and lifestyle changes are the keys to controlling and managing Type 2 diabetes effectively. Regular checkups, blood sugar testing, and awareness of symptoms can help prevent the progression of the disease and reduce serious health complications.