Effective Strategies for Managing Gout Discomfort and Preventing Flare-Ups
This comprehensive guide provides effective strategies for managing gout discomfort, including medication options, lifestyle modifications, dietary advice, and early warning signs. It emphasizes proactive prevention and long-term control to improve quality of life for individuals suffering from gout. The article explores the causes of gout, symptom recognition, and practical steps to reduce flare-ups, offering valuable insights for patients seeking relief and prevention of this painful condition.
Comprehensive Approaches to Alleviating Gout Pain and Preventing Future Attacks
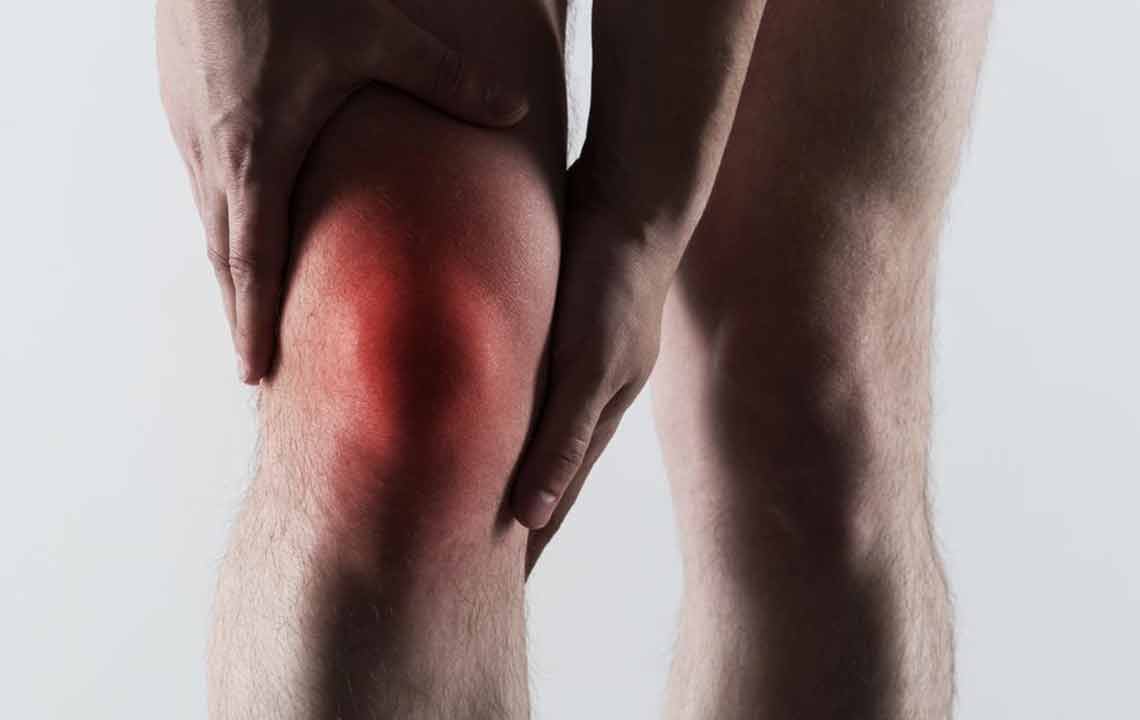
Gout, a form of inflammatory arthritis, can profoundly affect daily activities and overall quality of life. Characterized by sudden and intense joint pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness, gout occurs when excess uric acid crystallizes and deposits in the joints. Understanding how to effectively manage gout is essential for those affected, not only to ease pain during flare-ups but also to prevent future episodes. This detailed guide explores the root causes of gout, early warning signs, and comprehensive strategies—including medical treatments and lifestyle modifications—to effectively control this painful condition.
Understanding Gout Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
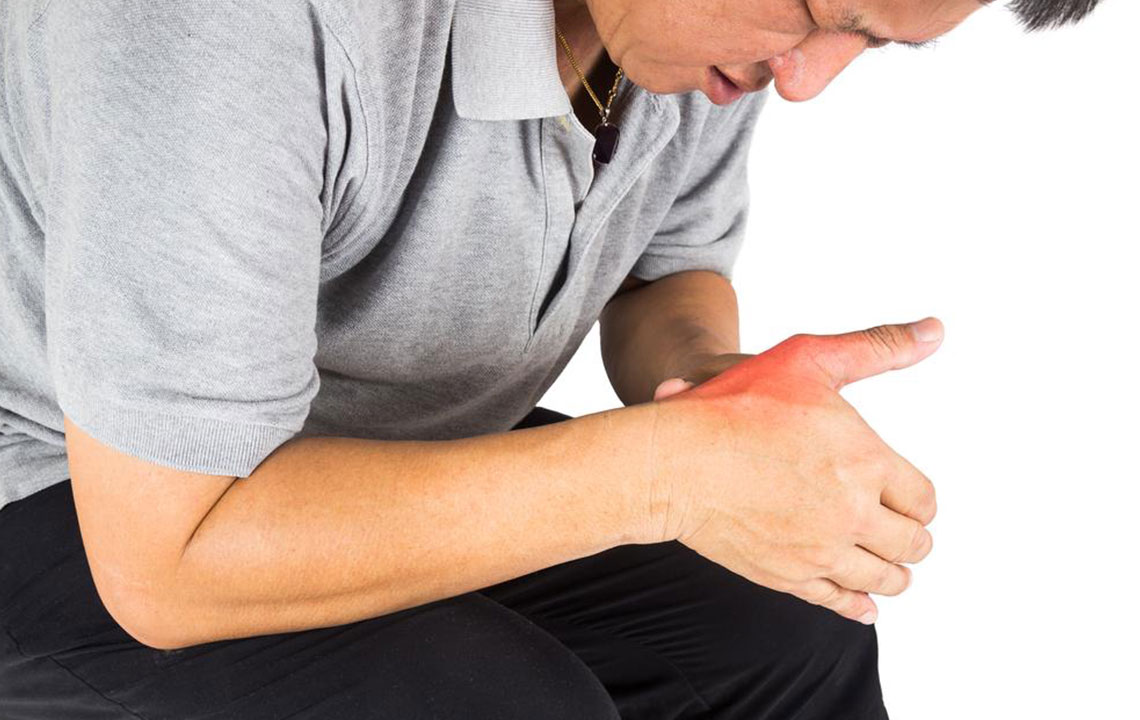
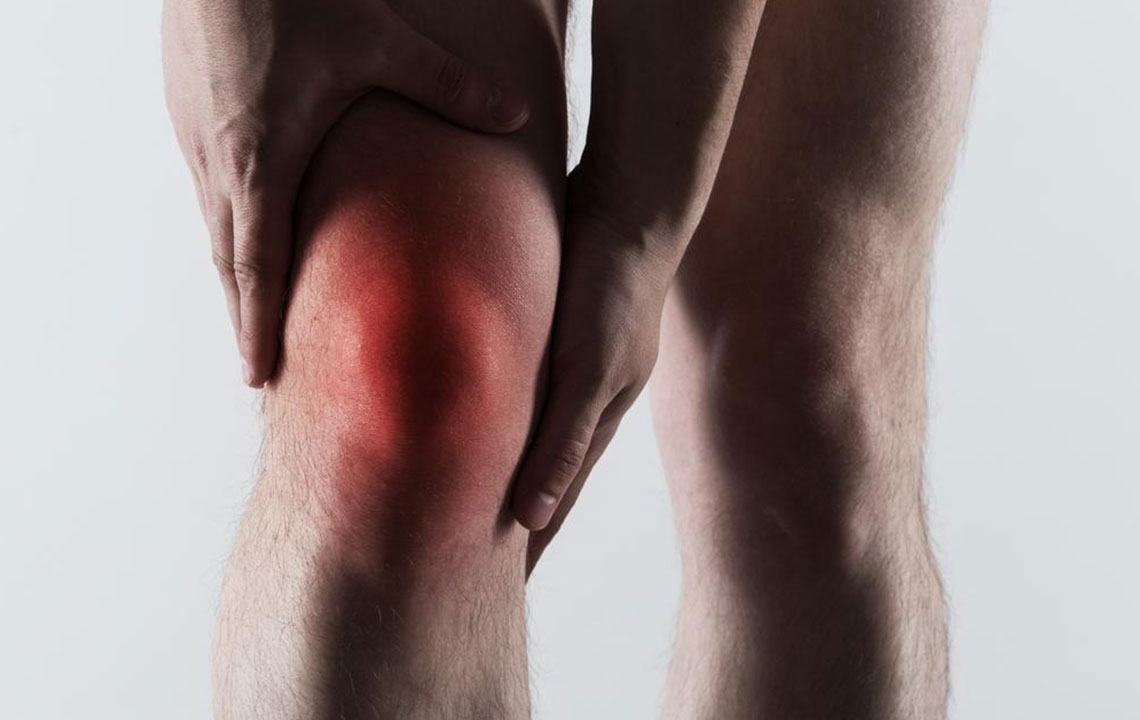
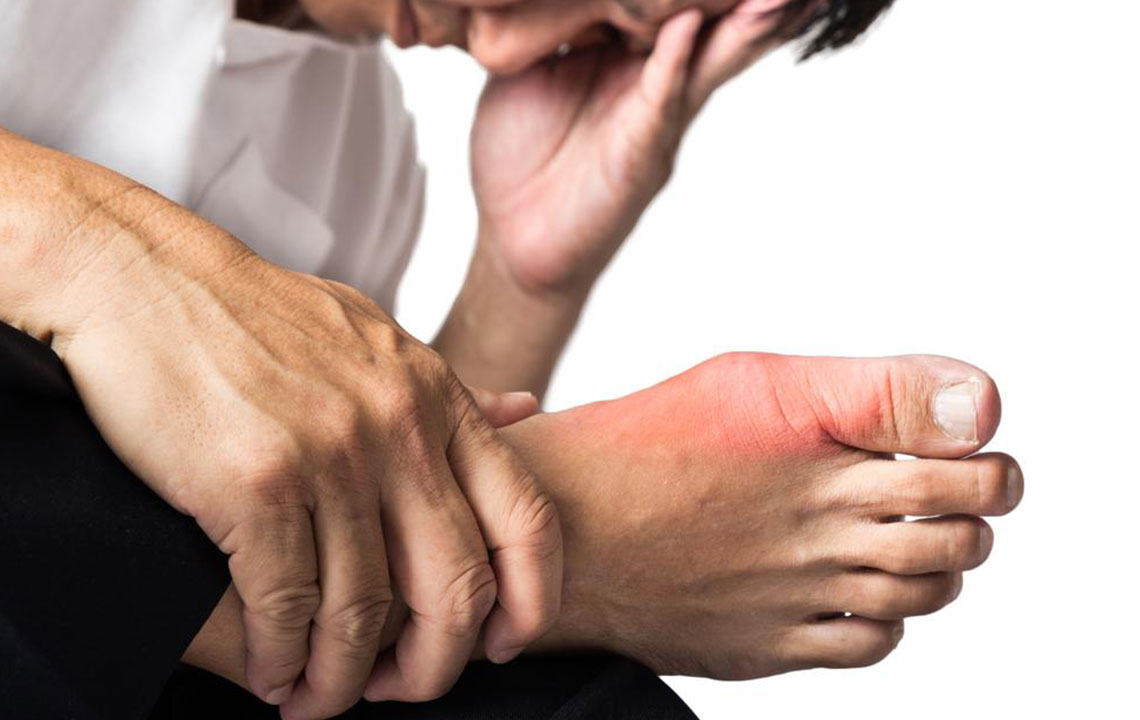
Gout symptoms can appear suddenly, often without warning. Early signs may include a burning sensation, stiffness, or tingling in the affected joint, sometimes hours before the intense pain sets in. Nighttime attacks are particularly common, with the joints becoming so sensitive that even light touch or bed sheets can trigger pain. Recognizing these initial symptoms allows individuals to seek prompt treatment, potentially reducing the severity and duration of flare-ups. Besides pain, symptoms include visible swelling, warmth, redness, and increased sensitivity in the affected area, typically the big toe, ankles, knees, or fingers.
Understanding the Causes and Risk Factors of Gout
Gout develops primarily due to elevated levels of uric acid in the bloodstream, known as hyperuricemia. When uric acid surpasses its solubility limit, it forms sharp crystals that deposit in the joints, triggering inflammation and intense pain. Several factors contribute to uric acid buildup, including genetics, dietary choices, obesity, certain medications, stress, and lifestyle habits such as excessive alcohol consumption. Men are generally more susceptible to gout, especially between ages 30-50, but women can also develop gout after menopause. Recognizing these risk factors enables better prevention strategies.
Effective Prevention Strategies for Gout Management
Maintaining a proactive lifestyle is key to preventing gout attacks. Dietary modifications play a significant role; reducing intake of red meats, organ meats, sugary foods, and beverages rich in fructose helps lower uric acid levels. Instead, focus on consuming fruits, vegetables, low-fat dairy, and whole grains. Regular physical activity and maintaining a healthy weight help decrease the risk of hyperuricemia. Hydration is crucial—drink plenty of water daily to facilitate uric acid excretion. Limiting alcohol intake, especially beer and spirits, is vital because alcohol interferes with uric acid clearance.
Medical Treatment Options for Gout
During acute gout attacks, anti-inflammatory medications such as NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and colchicine are prescribed to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. These treatments should be used under medical supervision to ensure safety and effectiveness. For long-term control, healthcare providers may recommend medications like Allopurinol, Febuxostat, or Pegloticase, which lower uric acid levels and prevent crystal formation. Regular monitoring of uric acid levels and kidney function is essential during medication therapy. Patients should consult healthcare professionals to create a personalized management plan, considering their overall health and comorbidities.
Lifestyle Modifications for Long-Term Gout Control
Aside from medical treatments, adopting healthy lifestyle habits is crucial for minimizing gout episodes. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in antioxidant-packed foods like berries, cherries, and leafy greens can reduce inflammation. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, such as meditation or yoga, helps prevent stress-induced flare-ups. Staying physically active not only aids weight management but also supports overall joint health. Avoiding trigger foods and drinks, quitting smoking, and ensuring adequate sleep are additional steps to improve quality of life. Consistency in these practices significantly enhances the effectiveness of medical therapies and reduces the frequency of gout attacks.
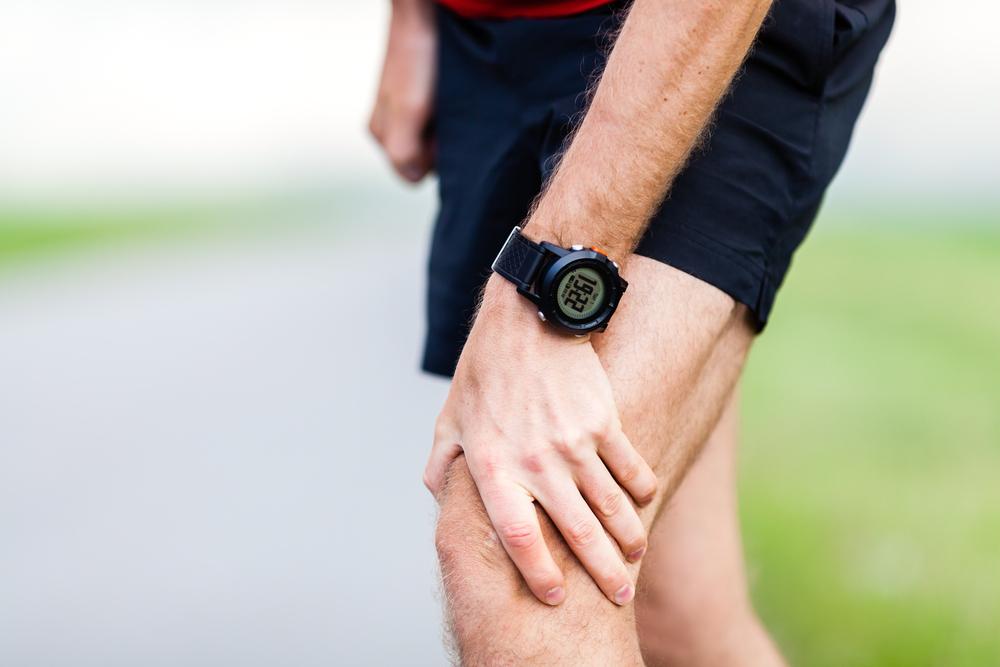
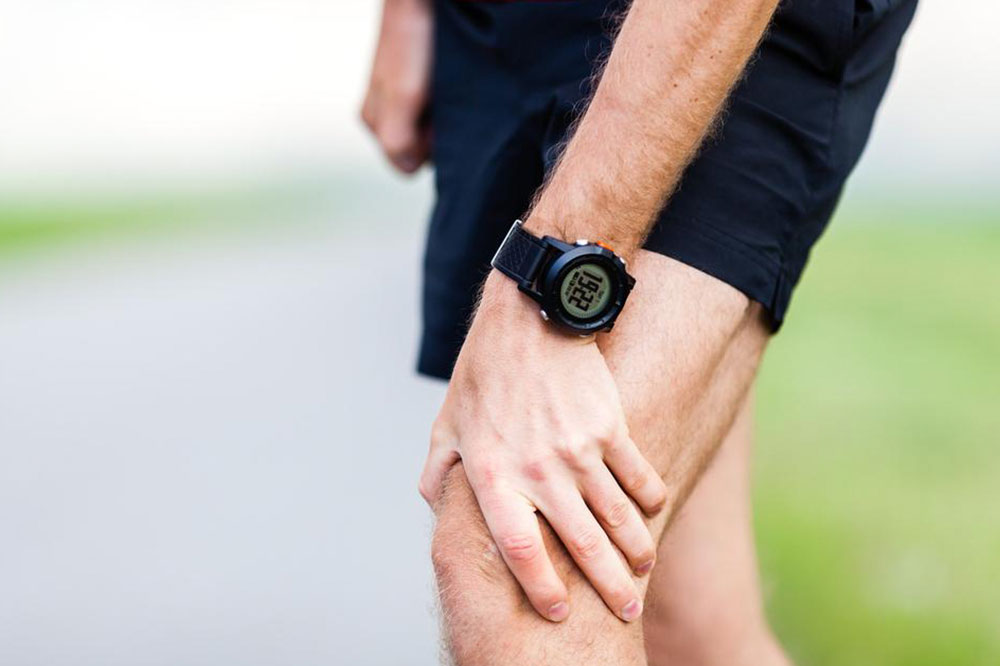
Immediate Actions During a Gout Attack
When experiencing a gout flare-up, immediate measures can help reduce pain and inflammation. Resting the affected joint, elevating it, and applying ice packs can provide relief. Stay well-hydrated and avoid foods or drinks that may worsen symptoms. Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications may be used, but only as recommended by a healthcare provider. If pain persists or worsens, seek medical attention promptly to prevent complications. Early intervention not only alleviates discomfort but also minimizes joint damage and the risk of recurrent attacks.
In conclusion, managing gout requires a comprehensive approach, combining medical treatment with lifestyle modifications. Recognizing early symptoms and understanding risk factors empower individuals to take proactive steps in prevention. Long-term management strategies—such as dietary changes, medication adherence, hydration, and stress reduction—are essential for controlling symptoms and enhancing quality of life. With proper care and lifestyle adjustments, those affected by gout can significantly reduce flare-ups and enjoy a more comfortable, pain-free life.