Comprehensive Guide to Detecting and Managing Childhood Allergies
This comprehensive guide explores the key signs of childhood allergies, including respiratory, skin, digestive, and eye symptoms. Recognizing these early indicators enables timely intervention to prevent severe reactions and improve children's quality of life. The article provides detailed insights for parents and caregivers, emphasizing the importance of vigilance and prompt medical attention for allergy management in children, along with strategies to identify triggers and reduce exposure. Empowering caregivers with knowledge is crucial for safeguarding children's health and well-being.
Essential Child Allergy Symptoms and How to Recognize Them
Allergic reactions among children are relatively common occurrences across various age groups, ranging from infants to teenagers. While many children experience mild symptoms, allergies can sometimes compromise the immune system, making children more susceptible to additional infections and health complications. Early detection of allergy signs is critical, as it enables timely intervention, which can significantly enhance a child's quality of life and prevent more severe reactions in the future.
At its core, an allergy represents an abnormal immune system response to substances that are generally harmless to most people. These substances, known as allergens, can include pollen, dust mites, pet dander, certain foods, insect stings, or airborne pollutants. When a child’s immune system perceives an allergen as a threat, it produces specific antibodies called Immunoglobulin E (IgE). These antibodies trigger the release of chemicals such as histamine, which cause the various allergy symptoms. The severity of these reactions can vary from mild discomfort to life-threatening emergencies.
Airborne allergens are among the leading causes of allergies in children. These allergens often lead to conditions like allergic rhinitis, commonly known as hay fever. In the United States alone, approximately 10% of children show symptoms indicative of allergic rhinitis. Recognizing the early signs of allergy in children is crucial to prevent complications such as asthma development, persistent discomfort, and reduced quality of life. A vigilant approach to monitoring symptoms can help parents and caregivers act swiftly and seek appropriate medical advice.
Breathing Difficulties and Respiratory Symptoms
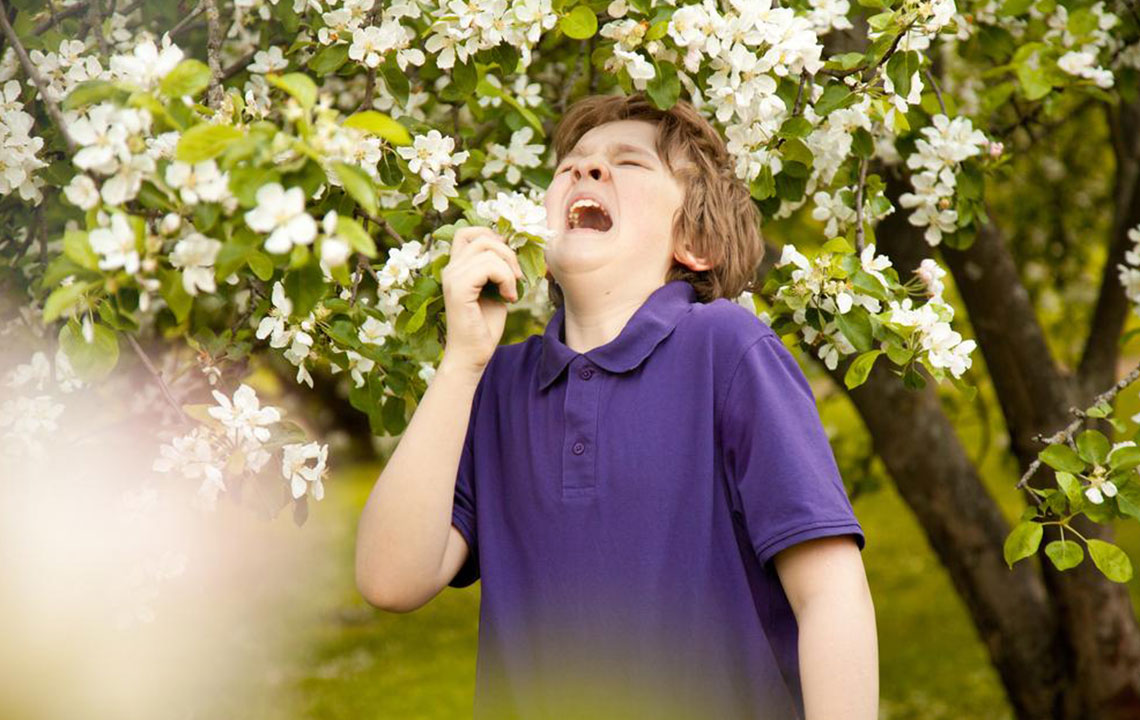
Difficulty in breathing is one of the most prominent and concerning allergy symptoms in children. This often presents as persistent coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, or shortness of breath. Respiratory allergies frequently relate to allergic asthma, a common condition among young children. Asthma episodes can be triggered by exposure to dust mites, pollen, mold, or pet dander, leading to airway inflammation. Recognizing early signs of respiratory distress allows for prompt management and can prevent full-blown asthma attacks.
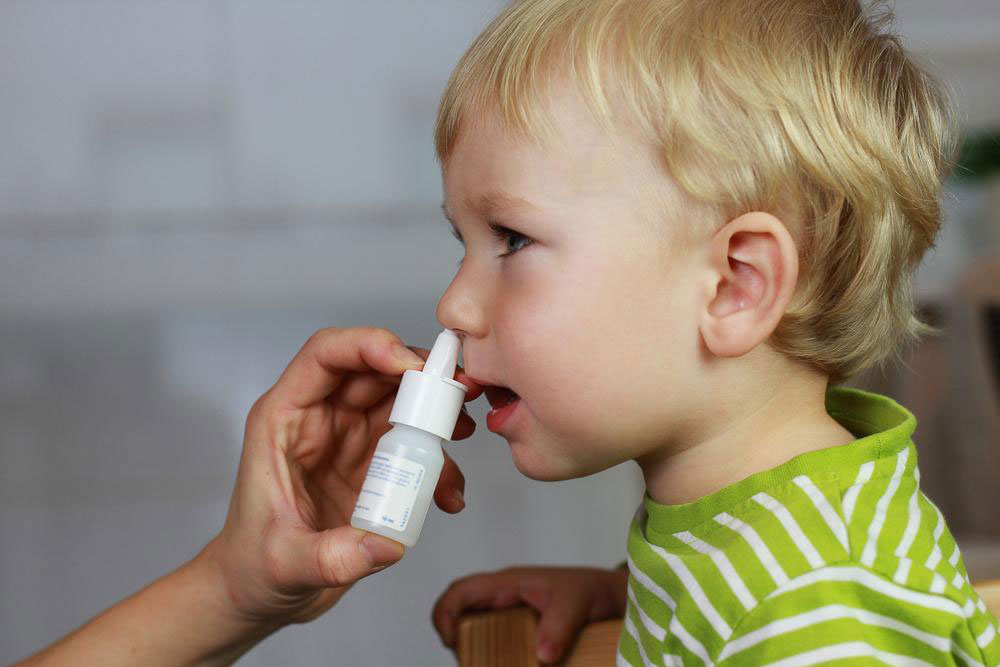
Nasal Congestion and Runny Nose
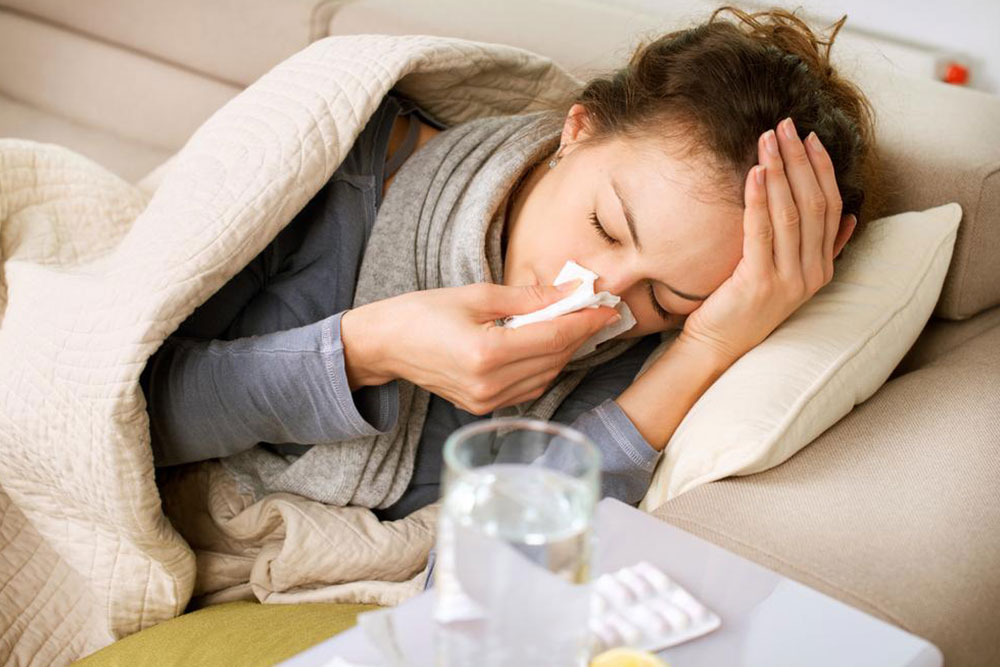
Nasal blockage caused by allergens entering the nasal passages results in mucus buildup, leading to nasal congestion. This often causes a postnasal drip, which can irritate the throat and cause discomfort. Children may frequently blow their noses or complain of a stuffy nose. If untreated, persistent nasal congestion can lead to secondary infections like sinusitis or worsen allergy symptoms over time.
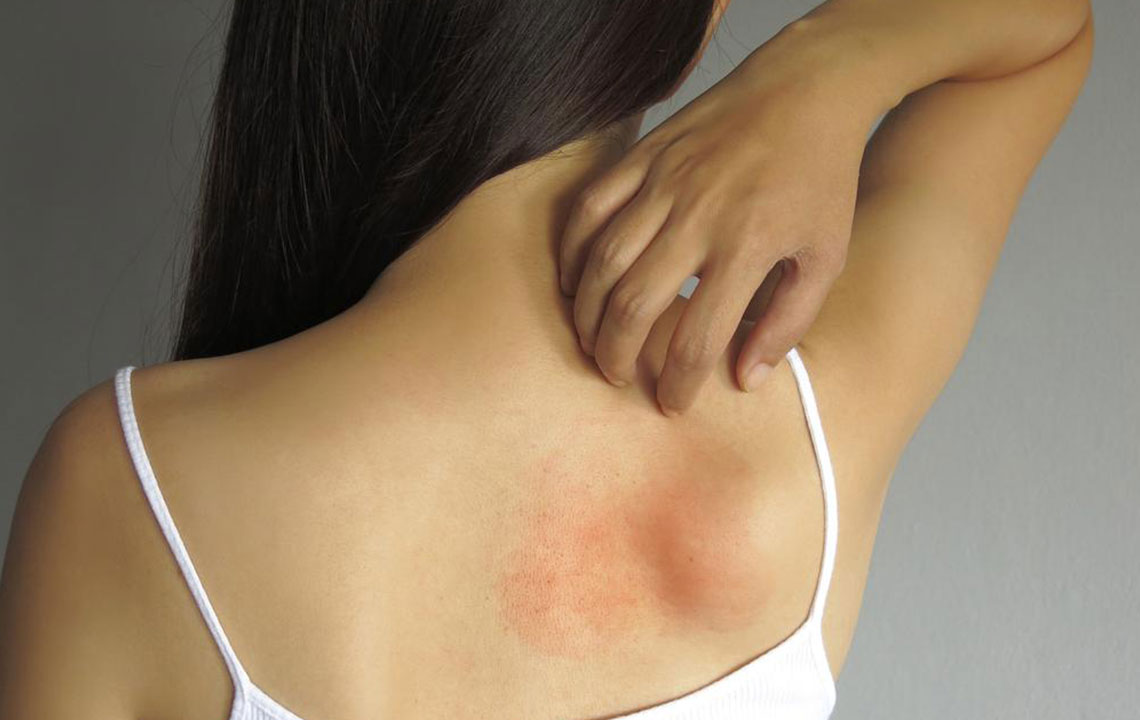
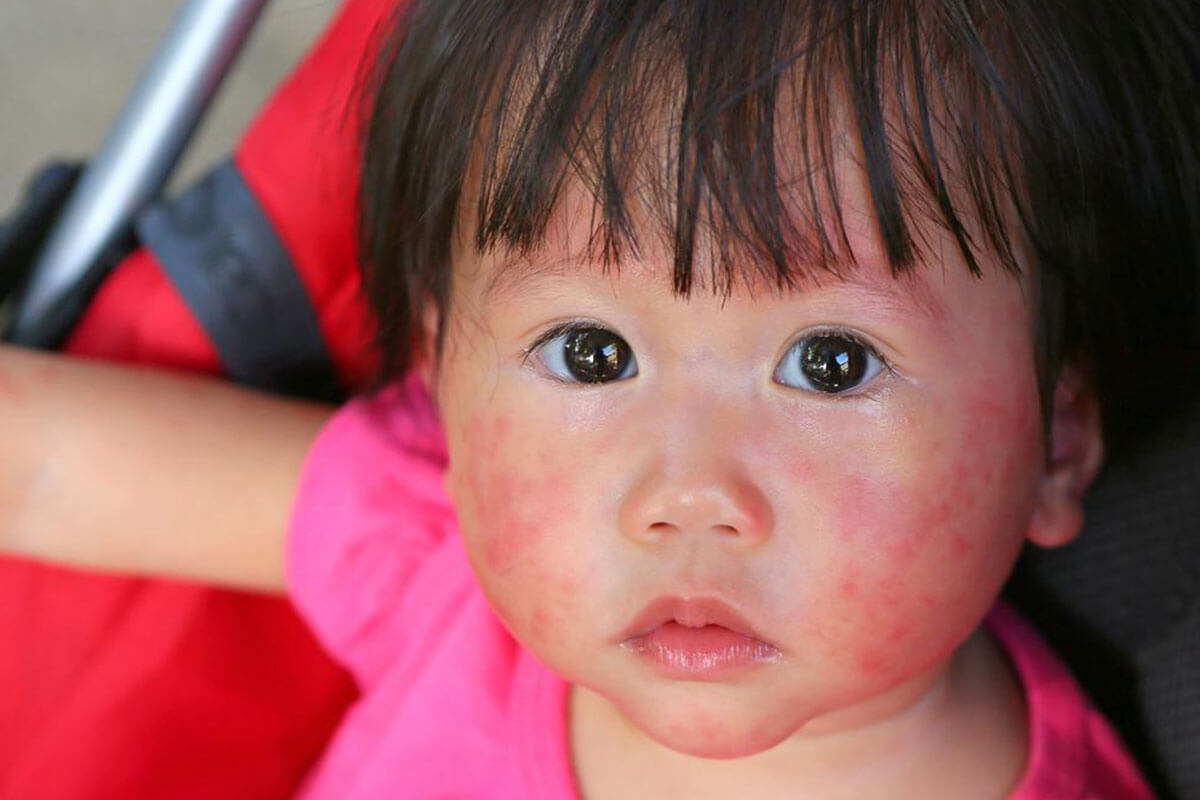
Skin Reactions and Dermatitis
Skin symptoms are among the most visible indicators of allergies in children. Allergens can irritate or inflame skin cells, leading to redness, dryness, itching, or rashes. Conditions such as eczema and contact dermatitis are common allergic skin reactions. Swelling called angioedema may also occur, which involves deeper layers of the skin and can be quite painful or uncomfortable. Monitoring skin changes and allergies triggers is essential for managing these reactions effectively.
Persistent Cough and Respiratory Signs
Nighttime coughing that persists without explanation is often a subtle yet significant warning sign of allergies. This cough can be mistaken for a common cold but tends to worsen if allergies are left untreated. It indicates ongoing inflammation or irritation in the respiratory pathways, especially in children with allergic asthma.
Digestive Problems and Food Allergies
Allergic reactions can also affect the gastrointestinal system. Symptoms like stomach pain, vomiting, diarrhea, or constipation may indicate food allergies or intolerances. If these digestive symptoms persist, they can lead to nutritional deficiencies or growth concerns. Particularly with food allergies, identifying and eliminating trigger foods is vital to maintaining overall health and nutrition.
Itchy, Watery, or Red Eyes
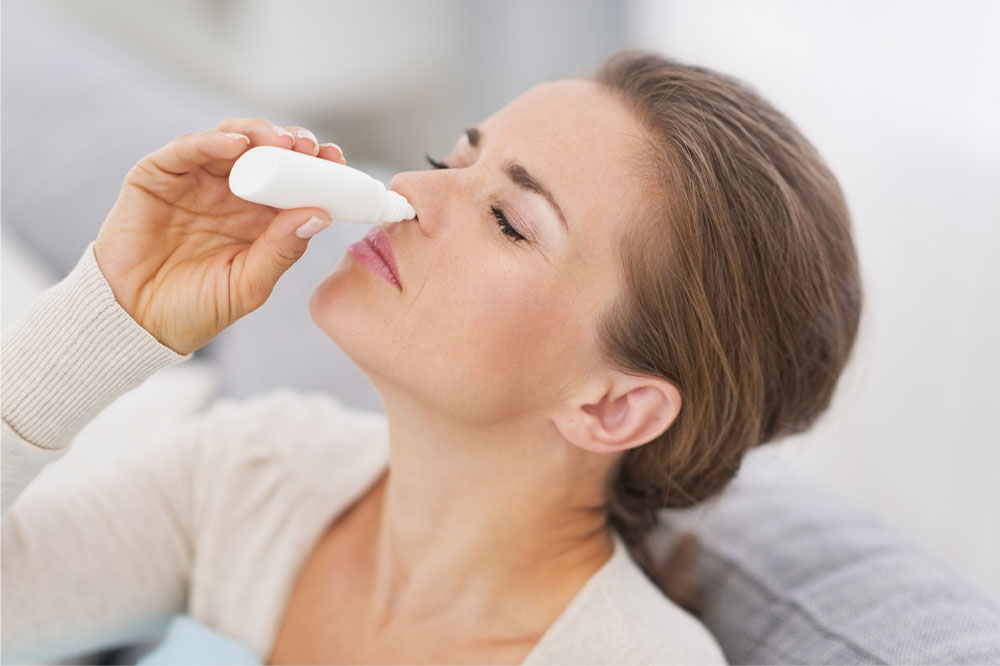
Allergens such as pollen or pet dander are common culprits causing eye irritation. Children with allergies often exhibit symptoms like red, itchy, watery eyes, swelling of eyelids, or a burning sensation. Some over-the-counter eye drops may worsen irritation if used improperly; hence, identifying triggers and avoiding them is a more effective approach. Allergic conjunctivitis can significantly impair vision and comfort if not managed appropriately.
All these symptoms vary depending on the child's age, sensitivity levels, and environmental exposures. Some children may only have mild localized reactions, while others experience multiple symptoms across different parts of their body. Additionally, in rare but serious cases, allergies can lead to anaphylaxis — a severe reaction that can be life-threatening if immediate care isn’t provided. Therefore, caregivers should be vigilant, stay informed about symptoms, and seek medical advice promptly to prevent emergencies.
Children often cannot articulate their symptoms clearly, making adult observation and proactive management essential for early detection and effective treatment of allergies. Regular check-ups, environmental control measures, and allergy testing can help identify specific triggers and reduce the risk of severe reactions. Proper education about allergy management empowers parents and caregivers to provide safer environments for children and improve their overall health outcomes.