Comprehensive Guide to Effectively Managing Foot Neuropathy and Enhancing Nerve Health
Foot neuropathy is a complex nerve disorder affecting many, primarily caused by diabetes and other health issues. Early diagnosis, comprehensive treatment including medications, lifestyle changes, and foot care are crucial. This detailed guide explains causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and effective management strategies to help sufferers control pain, slow progression, and improve their quality of life.

Comprehensive Strategies for Managing Foot Neuropathy and Promoting Nerve Recovery
Foot neuropathy, a condition characterized by abnormal nerve function in the lower extremities, affects countless individuals worldwide. Those suffering from this ailment often report sensations such as tingling, burning, numbness, or a combination of these, which can significantly impair mobility and overall quality of life. This neurological disorder is predominantly linked to nerve damage, a process that results from various underlying causes, with diabetes mellitus being the most common.
Early recognition and prompt management of foot neuropathy are crucial in preventing irreversible nerve damage and improving patient outcomes. Although complete prevention may be challenging, advances in medical science and integrated treatment approaches have made it possible to manage symptoms effectively, slow disease progression, and improve patient quality of life. This comprehensive guide explores the causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and effective management strategies for foot neuropathy, aiming to empower sufferers and healthcare providers with valuable information.
Understanding the intricacies of foot neuropathy involves appreciating how nerve impairment manifests within the nervous system. Nerves in our legs and feet relay critical sensory information to the brain. When these nerves are damaged, abnormal signals are sent, leading to sensations such as burning, tingling, and numbness. The complexity of this disorder is underscored by the fact that it can involve a single nerve (mononeuropathy) or multiple nerves simultaneously (polyneuropathy). Effective management strategies need to address both the symptoms and the root causes to prevent further nerve injury.
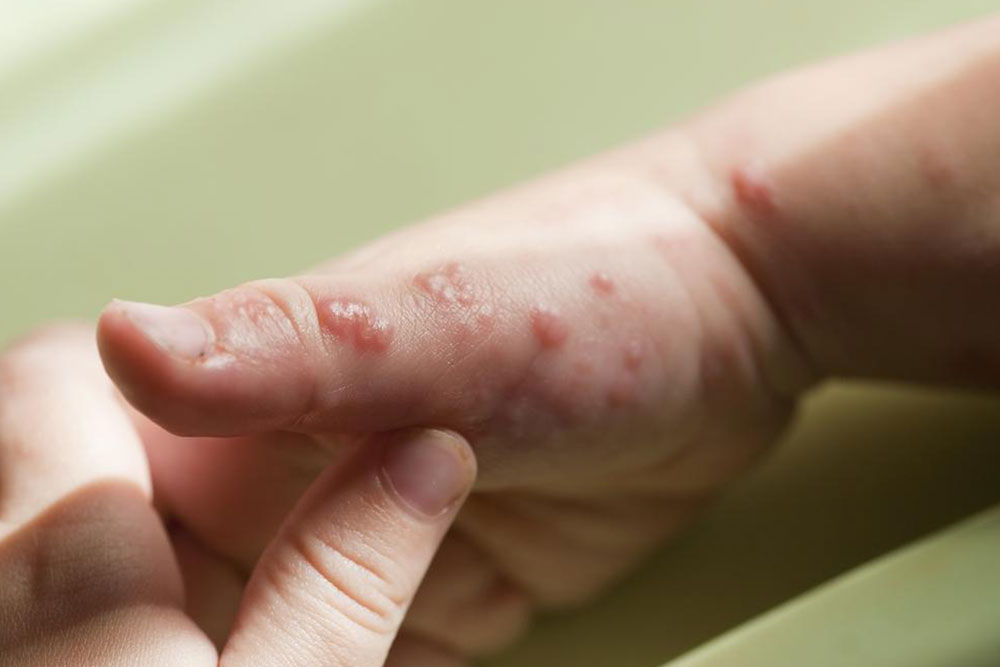
The primary goal in treating foot neuropathy is to halt or slow nerve damage while alleviating pain and discomfort. Commonly, patients experience burning sensations in their feet, often caused by nerves misfiring and sending false or exaggerated signals to the brain. These miscommunications can result in a range of symptoms, including muscle twitching, skin changes, hair and nail alterations, and coordination problems. Recognizing these signs early allows for timely interventions that can greatly improve outcomes.
Understanding the Causes of Neuropathy
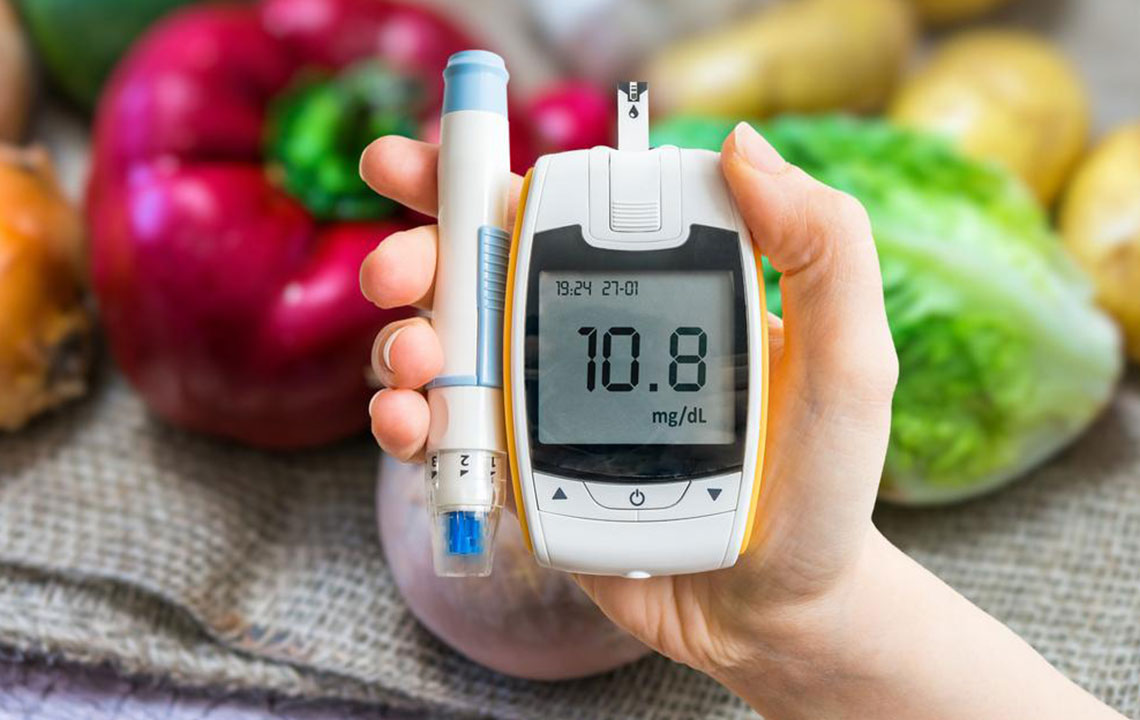
Although diabetes remains the leading cause of neuropathy, numerous other health conditions and environmental factors contribute to this disorder. Recognizing these causes can help in developing tailored treatment plans. Some of the notable causes include:
Chronic kidney disease (uremia), which leads to toxin build-up affecting nerve health
Vitamin deficiencies, notably B12, B6, and folate, essential for nerve regeneration and function
Thyroid disorders such as hypothyroidism, reducing metabolic support to nerves
Excessive alcohol consumption, which damages nerves directly
Infections like Lyme disease and HIV that induce nerve inflammation
Genetic disorders such as amyloid polyneuropathy, inherited conditions impacting nerve tissues
Chemotherapy and exposure to heavy metals, both neurotoxic agents
Vascular inflammation (vasculitis), which impairs blood flow to nerves
Sarcoidosis and Guillain-Barre syndrome, autoimmune conditions affecting nerve tissues
Recognizing Symptoms of Foot Neuropathy
Symptoms can vary widely depending on the severity and location of nerve damage. The most common initial symptom is a burning sensation in the feet, often accompanied by numbness, tingling, or a pins-and-needles feeling. Patients frequently report a reduction in their ability to sense temperature changes or pain, increasing the risk of unnoticed injuries. Over time, skin, hair, and nail changes may occur, alongside coordination difficulties and muscle weakness. Recognizing these symptoms early is vital for prompt diagnosis and management.
Diagnostic Tools for Foot Neuropathy
In diabetic patients, foot burning often indicates neuropathy, and physicians may initiate treatment based on clinical judgment. However, in non-diabetic cases, comprehensive diagnostic procedures are employed to confirm the diagnosis and identify underlying causes:
Electromyography (EMG) assesses muscle response and nerve signal conduction
Nerve conduction studies (NCS) measure the speed and strength of nerve signals
Skin biopsies may be used in rare cases to evaluate nerve fiber density
Blood tests, urine analysis, and cerebrospinal fluid examination help identify systemic conditions and deficiencies
Effective Management and Treatment Approaches
While a definitive cure for neuropathy remains elusive, significant strides have been made in controlling symptoms and preventing disease progression. The core principles of management involve addressing the underlying cause, reducing nerve irritation, and alleviating patient discomfort. A multi-faceted approach includes medication, lifestyle changes, nutritional support, and home remedies.
Control blood sugar levels meticulously in diabetic patients to minimize nerve damage
Use medications like amitriptyline, duloxetine, and pregabalin, which are effective in pain relief
Supplement deficiencies with vitamin B12, B6, and folate, as needed
Adopt a nutrient-rich diet emphasizing proteins from dairy, eggs, lean meats, fish, and green vegetables
Engage in gentle massage, warm foot soaks, and wear comfortable footwear to enhance circulation
Limit or avoid neurotoxic substances like excessive alcohol and certain medications
Address underlying autoimmune or thyroid conditions to support nerve health
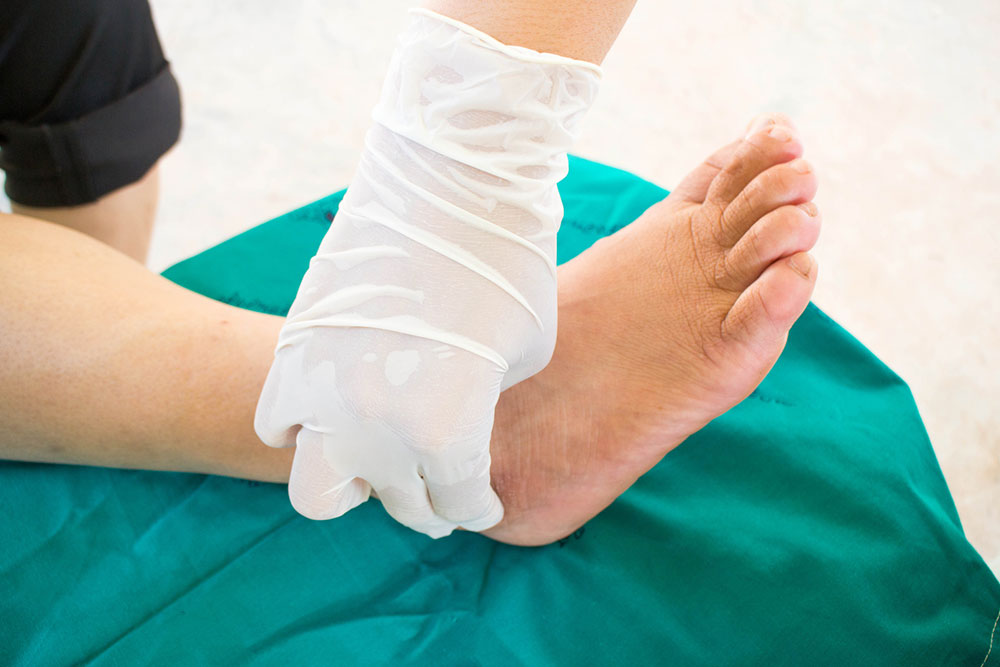
Implement regular foot care routines to prevent injuries and infections
Additional Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Alongside medical treatments, lifestyle modifications can significantly improve nerve health and reduce symptoms:
Maintain an active lifestyle with low-impact exercise such as walking, swimming, or cycling to promote blood flow and nerve regeneration
Avoid prolonged exposure to cold or heat that may exacerbate symptoms
Practice good foot hygiene, including daily inspection and moisturization
Wear supportive and well-fitting shoes to prevent injuries and skin breakdown
Manage stress through relaxation techniques, as stress can worsen neuropathy symptoms
In conclusion, managing foot neuropathy effectively relies on a combination of medical intervention, lifestyle modifications, and home care. Regular consultation with healthcare professionals and diligent foot care can significantly improve quality of life and prevent severe complications. Advancements in treatments continue to emerge, offering hope for better prognosis for those affected by this challenging condition.