The Ultimate Guide to Effective Diabetes Management and Prevention
This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies for managing and preventing diabetes, emphasizing the importance of lifestyle changes, medication, and regular health monitoring. It provides insights into symptoms, dietary advice, exercise routines, and emerging treatments to help individuals lead healthier lives and reduce risks associated with diabetes. Staying informed and proactive is key to optimal management and improved well-being.
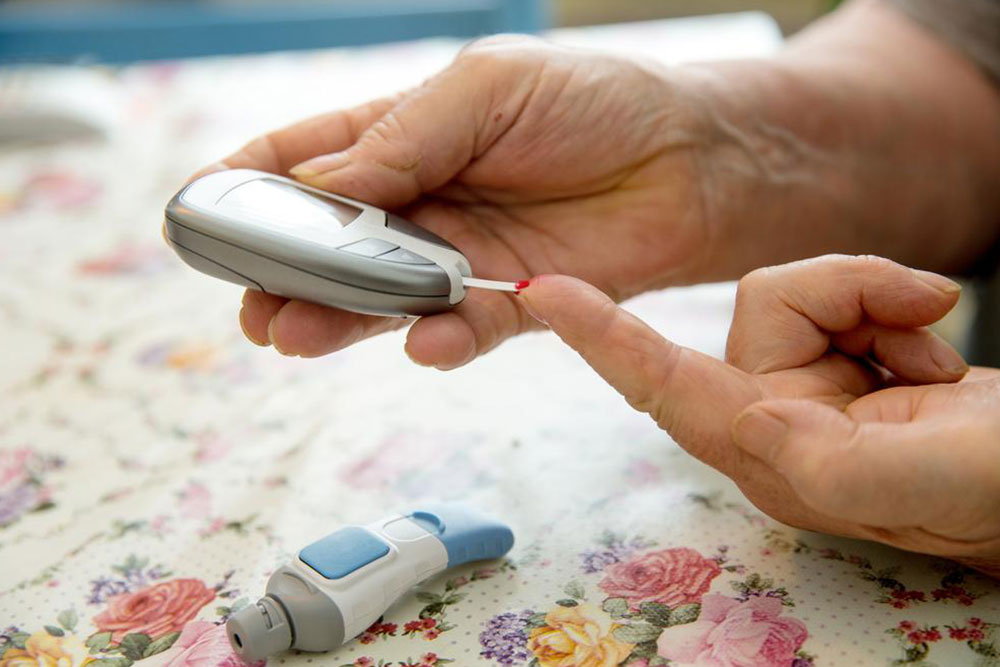
Comprehensive Approach to Managing and Preventing Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, widely known as diabetes, is a chronic metabolic disorder that affects millions worldwide. It is characterized by high blood sugar levels resulting from the body's inability to produce enough insulin or respond effectively to insulin's actions. Diabetes is a complex disease with a broad spectrum of symptoms and potential complications, making early detection and proper management vital for maintaining overall health and preventing serious health issues.
Over the past few decades, the prevalence of diabetes has increased dramatically. According to the World Health Organization, more than 380 million people worldwide received treatment for diabetes in 2013, and the numbers have only grown since then, reflecting a global health challenge that requires increased awareness, preventive strategies, and comprehensive management plans.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Diabetes
Many individuals with diabetes may not exhibit obvious symptoms in the early stages, which can lead to delayed diagnosis. Once symptoms become apparent, they often include:
Frequent urination (Polyuria): Elevated blood sugar levels cause the kidneys to work harder to filter out excess glucose. Since glucose isn't fully reabsorbed, water follows glucose into the urine, leading to increased urination.
Persistent Thirst (Polydipsia): Dehydration resulting from frequent urination triggers an intense need to drink fluids.
Unusual Hunger (Polyphagia): Insufficient insulin prevents glucose from entering cells for energy, prompting the body's craving for more nutrients.
Weight Fluctuations: Either unexplained weight loss or gain can occur, depending on the type and progression of diabetes.
Blurred Vision: High blood sugar levels can cause fluid to seep into the lenses of the eyes, affecting vision.
Fatigue and Weakness: Lack of glucose entering cells deprives the body of essential energy, leading to tiredness.
Irritability and Mood Changes: Blood sugar swings can affect mood and cognitive functions.
Identifying these symptoms early and seeking medical attention are critical steps towards effective management and reducing the risk of complications such as nerve damage, cardiovascular disease, and kidney failure.
Effective Strategies for Managing Diabetes
Although there is currently no cure for Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes, a combination of lifestyle changes, medication adherence, and preventive care can help individuals keep their blood glucose levels under control and lead healthier lives. A proactive approach can also prevent or delay the onset of associated complications.
1. Dietary Modifications
Nutrition plays a central role in managing diabetes. Adopting a balanced, nutritious diet can stabilize blood sugar levels, promote weight management, and improve overall health. Recommendations include:
Incorporating complex carbohydrates like whole grains and vegetables that have a low glycemic index to prevent spikes in blood sugar.
Reducing intake of processed foods, sugary snacks, and sweetened beverages that can cause rapid increases in blood glucose.
Monitoring portion sizes to avoid overeating and maintain a healthy weight.
Including healthy fats such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil to support cardiovascular health.
Eating regular, evenly spaced meals to sustain steady blood sugar levels throughout the day.
2. Regular Exercise
Physical activity is essential in managing diabetes. It helps improve insulin sensitivity, promotes weight loss, and enhances cardiovascular health. Suitable activities include walking, swimming, cycling, or low-impact aerobics. Experts recommend at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week, combined with strength training exercises twice weekly. Always consult your healthcare provider before initiating a new exercise regime, especially if you have existing health conditions.
3. Medication and Insulin Therapy
For many individuals, medications are necessary to control blood sugar levels. These may include oral hypoglycemic agents, insulin injections, or other injectable drugs. Correct dosage, timing, and adherence are critical to achieving optimal control. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels helps adjust treatment plans and prevent hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia.
4. Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Frequent blood glucose testing provides valuable insights into how diet, activity, and medication affect blood sugar. Home testing kits are widely available, and continuous glucose monitoring devices are increasingly used for real-time data tracking, allowing for more precise management.
5. Managing Stress and Mental Health
Stress can significantly impact blood sugar levels. Incorporating stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness can help stabilize blood glucose. Mental health support is equally important, and seeking professional counseling or joining support groups may benefit individuals dealing with the emotional challenges of diabetes.
6. Regular Medical Checkups and Preventive Care
Ongoing medical supervision is essential to monitor for and prevent complications. Routine screenings for blood pressure, cholesterol, kidney function, and eye health are vital components of comprehensive diabetes care. Your healthcare provider can tailor a management plan that adapts to your evolving needs.
Innovative Treatments and Future Outlook
Advancements in diabetes research are continually emerging. New medications, insulin delivery systems, and technological innovations aim to improve quality of life and reduce disease burden. For example, artificial pancreas systems, gene therapy, and personalized medicine hold promise for more effective management in the future.
In conclusion, managing diabetes requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses lifestyle modifications, medical treatment, regular monitoring, and emotional well-being. Empowering oneself with knowledge and working closely with healthcare professionals can significantly improve outcomes and offer a better quality of life despite the chronic nature of the disease.