Comprehensive Strategies for Managing and Treating Enlarged Prostate (Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia)
This comprehensive guide explores various management and treatment options for enlarged prostate (BPH), including medications, minimally invasive procedures, surgical options, and lifestyle changes. Tailored strategies help improve urinary symptoms, prevent complications, and enhance quality of life for aging men. Knowledge of each approach allows patients and healthcare providers to make informed decisions for effective treatment and better health outcomes.

Comprehensive Strategies for Managing and Treating Enlarged Prostate (Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia)
As men grow older, many experience benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), commonly referred to as an enlarged prostate. This condition involves an increase in prostate size, which can exert pressure on the urethra and disrupt normal urinary functions. If not addressed promptly, BPH can lead to significant health complications, including urinary retention, recurrent urinary tract infections, bladder stones, and even kidney damage due to obstructed urine flow. Understanding effective management and treatment options is essential to improve quality of life and prevent adverse health outcomes.
Understanding Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
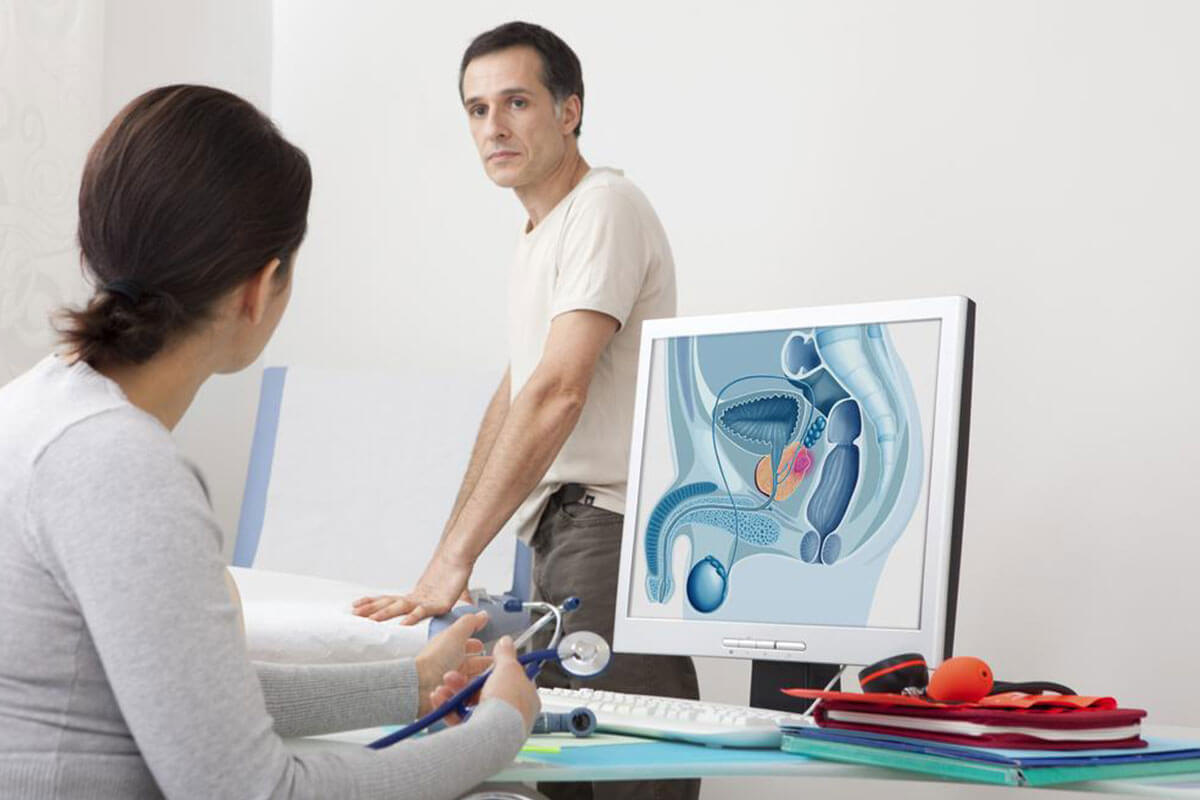
Benign prostatic hyperplasia is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland that typically occurs as part of the aging process. The prostate, a small walnut-sized gland located below the bladder, surrounds the urethra—the duct through which urine exits the body. As the prostate enlarges, it can constrict the urethral passage, making urination difficult or incomplete. Symptoms often include frequent urination, nocturia (waking at night to urinate), weak urine stream, hesitancy, and a feeling of incomplete bladder emptying. The severity of symptoms varies among individuals and depends on prostate size, patient age, and overall health.
Personalized Treatment Approaches Based on Patient Factors
Managing BPH requires a tailored approach, considering factors like age, prostate size, symptom severity, presence of complications, and overall health status. Healthcare providers often perform comprehensive evaluations including medical history, physical exams, urinary flow tests, prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels, and imaging studies such as ultrasound. Treatment options range from conservative management to more invasive surgical procedures, each suited to specific patient needs.
Medications for BPH Relief
Medications constitute the first line of defense for many patients with moderate symptoms. Two primary classes are commonly prescribed: alpha-adrenergic blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors.
Alpha-blockers: Drugs such as tamsulosin, alfuzosin, and silodosin relax muscles in the prostate and bladder neck, facilitating easier urine flow. These medications often work within days to weeks, providing rapid symptom relief.
5-alpha reductase inhibitors: Medications like dutasteride and finasteride reduce prostate volume over time by inhibiting the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which stimulates prostate growth. While their effects may take several months to manifest, they can significantly decrease prostate size and improve urinary symptoms in the long term. Combining α-blockers with 5-alpha reductase inhibitors often results in more effective symptom management.
Patients should be aware of potential side effects, including sexual dysfunction, decreased libido, and, in rare cases, mood changes. Regular follow-up with healthcare providers is essential to monitor treatment efficacy and manage adverse effects.
Minimally Invasive and Surgical Treatments
For individuals who do not achieve sufficient relief with medications or cannot tolerate side effects, minimally invasive procedures and surgical options are available.
Transurethral Microwave Thermotherapy (TUMT): This procedure uses microwave energy delivered through a specially designed catheter to heat and destroy excess prostate tissue, leading to symptom relief. It offers the advantage of being less invasive with a quicker recovery timeframe.
Steam Therapy (Rezum): Utilizing heated water vapor injected directly into the prostate, steam therapy targets and destroys obstructive tissue with minimal damage to surrounding areas. Many patients experience improvements within a few weeks.
Laser Surgeries: These include photoselective vaporization (PVP) and Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate (HoLEP). Laser treatments vaporize or remove excess tissue, providing significant symptom relief with reduced bleeding risks compared to traditional surgery.
Open Prostatectomy: In cases of very large prostates or complicated cases, open surgery may be necessary. This involves removing the obstructive tissue via small abdominal incisions under general anesthesia. Despite being more invasive, it remains an effective treatment for severe cases.
Additional Procedures: These include transurethral needle ablation (TUNA), which uses radiofrequency energy to ablate tissue, and transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), often regarded as the gold standard for surgical intervention in BPH. TURP involves removing enlarged prostate tissue through a scope inserted via the urethra.
Non-Surgical and Lifestyle Management
For mild symptoms, lifestyle modifications and non-pharmacological strategies can provide symptom relief. These include pelvic floor exercises, weight management, and avoiding bladder irritants such as caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods. Patients should also refrain from holding urine for prolonged periods and avoid unnecessary medications that may worsen symptoms, such as decongestants.
Implementing bladder training and fluid management strategies can further improve urinary symptoms. Additionally, regular medical check-ups help track disease progression and determine the best course of action.
In conclusion, managing an enlarged prostate involves a combination of medical therapy, minimally invasive procedures, surgical interventions, and lifestyle modifications. Early diagnosis and personalized treatment plans are key to reducing symptoms, preventing complications, and enhancing overall well-being. Patients are encouraged to seek professional medical advice to determine the most appropriate treatment for their specific condition, ensuring a better quality of life and long-term health.