Comprehensive Guide to Dry Eye Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Strategies
Dry eye syndrome is a common condition caused by insufficient tear production or rapid evaporation, leading to discomfort and vision problems. This comprehensive guide explores its causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatments, including lifestyle adjustments, environmental changes, and medical procedures. Preventive tips and management strategies help maintain eye health, especially for older adults or those exposed to environmental stressors. Regular check-ups, proper eye hygiene, and dietary habits play a crucial role in alleviating symptoms and preventing progression, ensuring better eye comfort and wellness.

Comprehensive Guide to Dry Eye Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Strategies
Dry eye syndrome, also known as keratoconjunctivitis sicca, is a widespread eye condition affecting millions of individuals around the world. It is characterized by a deficiency in tear production or an increase in tear evaporation, leading to dryness, discomfort, and potential vision issues. Understanding the complex causes, recognizing the symptoms early, and knowing the available treatment options are essential steps towards maintaining healthy eyes and improving overall quality of life.
What Is Dry Eye Syndrome?
Dry eye syndrome occurs when the eyes do not produce enough tears or when the tears evaporate too rapidly, disrupting the natural tear film that coats and protects the eye surface. Tears play a crucial role in nourishing the cornea, flushing out irritants, preventing infections, and ensuring clear vision. When the tear film is compromised, symptoms such as persistent dryness, irritation, redness, and fluctuating vision can develop.
Understanding this condition thoroughly involves exploring its underlying causes, common risk factors, symptoms, diagnostic processes, and available management strategies. Whether you are experiencing early signs or aiming to prevent potential issues, knowledge is key to effective eye health maintenance.
Major Factors Contributing to Dry Eye Development
Several interconnected factors can contribute to the development of dry eye syndrome, including environmental influences, biological changes, and lifestyle habits. Identifying these factors helps in tailoring personalized treatment plans and preventive measures.
Age: Tear production naturally declines with age, especially after the age of 50, increasing susceptibility to dry eyes.
Hormonal Fluctuations: Hormonal changes associated with pregnancy, menopause, and the use of contraceptives can influence tear secretion levels.
Environmental Conditions: Exposure to wind, smoke, dry air, and air conditioning diminishes tear stability and accelerates evaporation.
Prolonged Screen Time: Extended periods of digital device usage reduce blinking frequency, leading to tear film instability and dryness.
Health Conditions: Chronic illnesses such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, and autoimmune diseases like Sjögren’s syndrome adversely impact tear production.
Contact Lens Usage: Long-term wear of contact lenses can interfere with tear film integrity and cause discomfort.
Medications: Certain drugs including antihistamines, antidepressants, blood pressure medications, and diuretics can diminish tear secretion.
Previous Eye Surgeries: Procedures like LASIK or cataract surgeries may temporarily or permanently alter tear dynamics.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Dry Eye Syndrome
Early recognition of symptoms is critical in preventing progression and enhancing treatment effectiveness. Common signs include:
Persistent Eye Irritation: Feeling of grittiness, sandy sensation, or foreign body presence.
Redness and Inflammation: Eyeballs may appear red and inflamed due to irritation.
Fluctuating or Blurry Vision: Vision problems often arise from irregular tear coverage on the eye surface.
Light Sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to light (photophobia) can occur.
Excessive Tearing: Reflex tearing may happen as a response to dryness, ironically worsening discomfort in some cases.
Contact Lens Discomfort: Increased irritation and discomfort when wearing lenses.
Diagnostic Techniques Employed by Eye Care Professionals
Proper diagnosis involves comprehensive eye examinations utilizing various tests, including:
Tear Film Break-Up Time (TBUT): Assesses the stability of the tear film and identifies rapid tear evaporation.
Schirmer’s Test: Measures baseline tear production via absorbent strips placed under the eyelids over a specified period.
Slit-Lamp Examination: Provides a detailed view of the ocular surface, eyelids, and tear film integrity.
Vital Dyes and Staining Tests: Uses fluorescein, lissamine green, or rose bengal dyes to reveal dry or damaged areas and evaluate tear distribution.
Effective Management Strategies for Dry Eye Relief
Addressing dry eye syndrome effectively requires a combination of lifestyle modifications, environmental adjustments, and medical interventions tailored to individual needs.
Environmental and Lifestyle Changes:
Use humidifiers in dry indoor environments to maintain adequate moisture levels.
Take regular breaks during screen work (e.g., following the 20-20-20 rule: every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds).
Wear protective glasses or sunglasses in windy, dusty, or dry conditions to shield the eyes from irritants.
Healthy Habits and Dietary Considerations:
Practice conscious blinking exercises to spread tears evenly across the eye surface.
Stay well-hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
Incorporate foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), walnuts, and flaxseeds, which support tear quality and reduce inflammation.
Eye Hygiene and Care Practices:
Apply warm compresses regularly to stimulate the oil-producing glands in eyelids, preventing tear film evaporation.
Gently clean eyelids and lashes to remove debris, oil buildup, and bacterial factors that can disrupt tear stability.
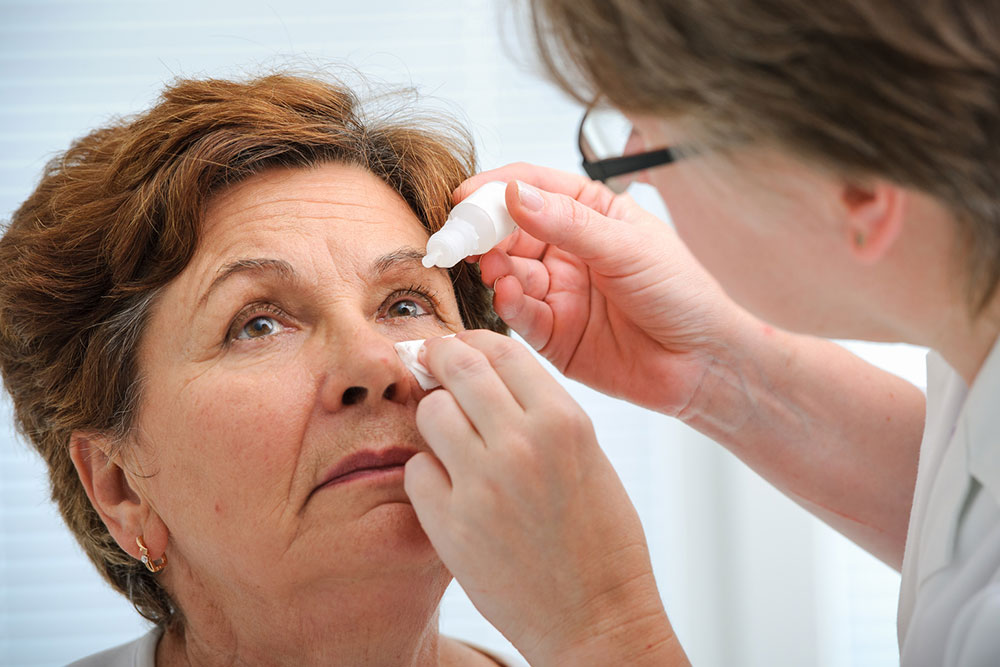
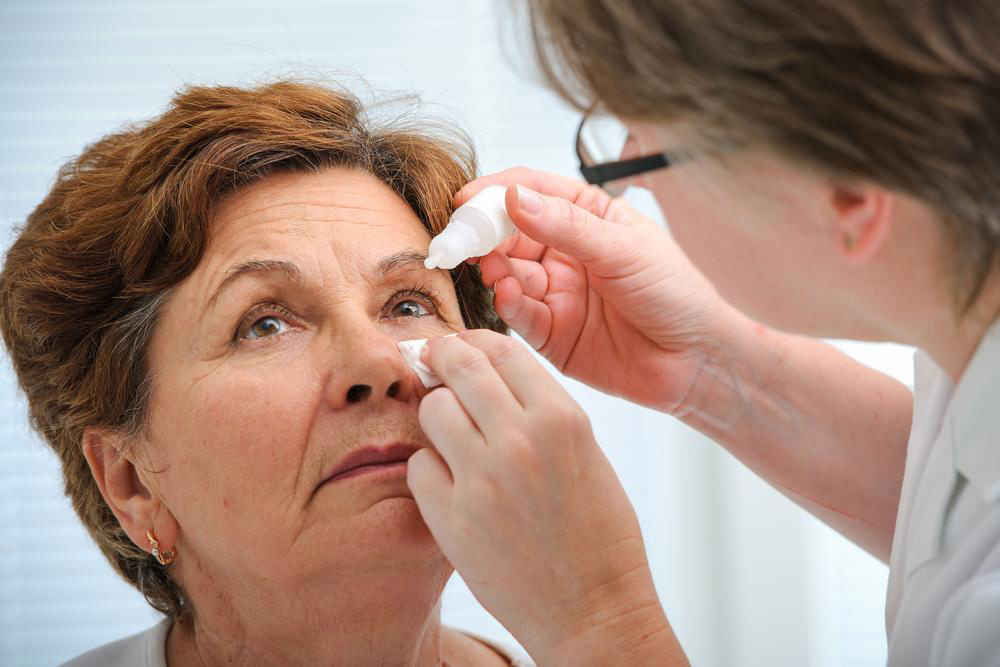
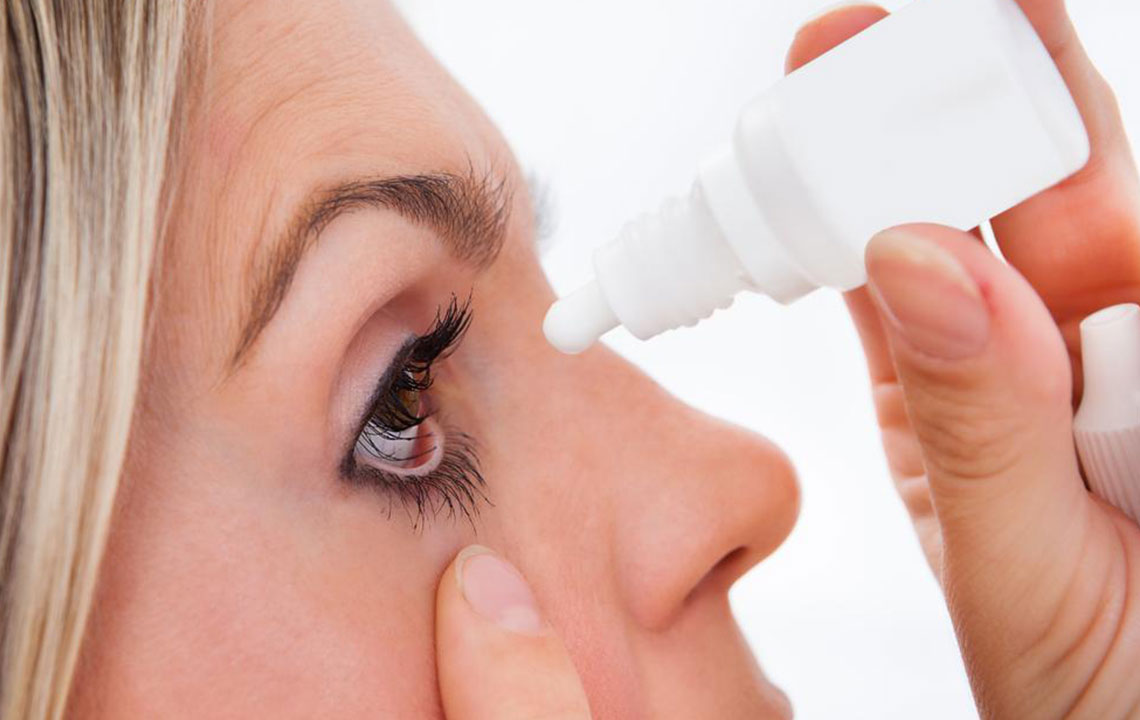
Lubricating Eye Drops and Artificial Tears:
Use preservative-free artificial tears or lubricant eye drops to supplement natural tears and relieve dryness.
Select products suited to your specific needs, such as gels or ointments for nighttime use.
Advanced Medical and Surgical Treatments:
Inserting punctal plugs to block tear drainage and retain tears on the ocular surface.
Thermal pulsation therapy to unblock meibomian glands, improve oil secretion, and stabilize the tear film.
Other interventions like autologous serum tears or prescription medications may be recommended for severe cases.
Preventative Measures to Reduce Risk
While it may not always be possible to prevent dry eye syndrome entirely, adopting certain habits can significantly lower your risk:
Avoid exposure to cigarette smoke, dry, windy conditions, and environmental pollutants.
Limit screen time, especially in poorly lit environments, and take frequent visual rest breaks.
Wear high-quality sunglasses or protective glasses outdoors to shield against wind and UV rays.
Follow a balanced diet rich in nutrients vital for eye health, including vitamins A, C, E, and omega-3 fatty acids.
Understanding the intricacies of dry eye syndrome and proactively implementing effective care routines can dramatically enhance comfort and preserve eye health over time. Regular eye examinations and prompt management of symptoms are fundamental to preventing complications and ensuring sustained eye wellness.
References
American Academy of Ophthalmology
National Eye Institute
Dry Eye Syndrome Resources