Comprehensive Guide to Accurate Body Temperature Measurement Techniques
This comprehensive guide explores various accurate methods for measuring body temperature, including rectal, oral, armpit, and ear techniques. It emphasizes safety, proper procedures, and best practices to ensure reliable readings, helping parents and caregivers monitor health effectively. Up-to-date insights on thermometer choices and measurement tips promote better health management and early illness detection for people of all ages.

Comprehensive Guide to Accurate Body Temperature Measurement Techniques
Monitoring body temperature plays a crucial role in assessing health status, especially in vulnerable groups such as infants and children. Fever, which indicates an immune response to infection, is a common symptom that requires careful monitoring to determine the severity and appropriate treatment. While fevers are often self-limiting, persistent or unusual fever patterns can signal underlying health issues that need medical evaluation. Accurate measurement of body temperature is essential for proper diagnosis and management, and there are multiple methods suitable for different age groups and situations.
In recent years, concerns about mercury thermometers have increased due to environmental and safety issues, prompting a shift towards safer, digital alternatives. Understanding the different techniques for measuring body temperature, along with their proper procedures and precautions, ensures reliable results and better health monitoring.
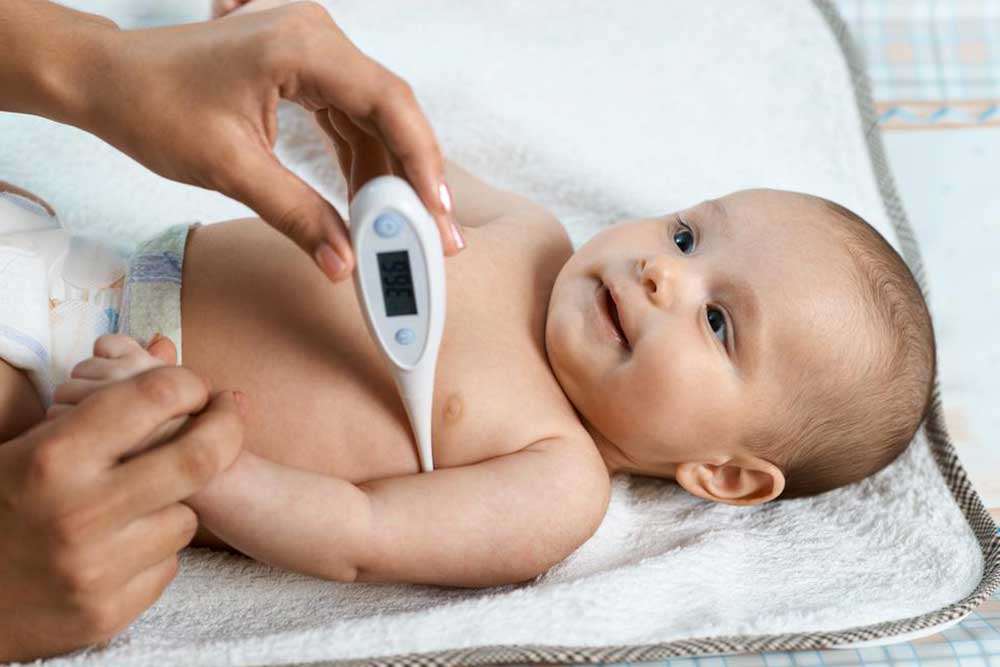
Rectal Temperature Measurement: Widely regarded as the most precise method, especially for infants and young children. This technique provides accurate readings critical for assessing infants' health. To perform, thoroughly clean the thermometer, apply a small amount of petroleum jelly to facilitate smooth insertion, gently insert approximately 2.5 centimeters into the anus, and hold it in place for about a minute or until the device beeps. Record the temperature reading, then clean the thermometer thoroughly and store it in a safe, sanitized place. Precautions include ensuring the child is calm and comfortable to prevent injury or discomfort.
Oral Temperature Measurement: Suitable for children aged five years and older who can hold a thermometer steadily under their tongue. Before starting, clean the thermometer and instruct the child to place it under the tongue, ensuring it stays in place without biting. Keep the thermometer there for about a minute or according to the device’s instructions, then note the reading. Oral measurement can be affected by recent eating, drinking, or physical activity, so it's advisable to wait at least 15 minutes after such activities for accurate readings. Proper hygiene and consistent technique are key for reliable results.
Armpit (Axillary) Temperature Measurement: Often used for quick assessments, especially in children, but tends to be less accurate compared to rectal or oral methods. Place the thermometer under the armpit, making sure it contacts the skin directly and the arm is snug against the body to prevent air pockets. Wait for the measurement to stabilize, typically about a minute. If a child shows signs of warmth but the armpit temperature remains normal, consider confirming with a rectal measurement for accuracy. This method is convenient and non-invasive but should be interpreted cautiously.
Ear (Tympanic) Temperature Measurement: This method involves inserting an infrared sensor into the ear canal to measure the temperature of the eardrum. Proper technique involves gentle insertion of the thermometer probe, ensuring a snug fit for accurate readings. Nonetheless, ear measurements can vary depending on the ear canal's shape, presence of wax, or improper positioning, making it less reliable for critical assessments. This method is quick and suitable for routine checks, especially in clinical settings.
For the most accurate and reliable results, digital thermometers are now preferred over traditional mercury or fever strip methods. Regularly calibrating thermometers and measuring at consistent times of the day can help monitor temperature fluctuations more effectively. It's also important to consider the context—fever patterns, associated symptoms, and recent activities—to interpret temperature readings accurately in relation to overall health status.