Comprehensive Dietary Approaches to Effectively Manage Gout Symptoms and Improve Joint Health
Discover comprehensive dietary strategies to effectively manage gout symptoms. Learn about foods to avoid, dietary tips, and lifestyle changes that can reduce flare-ups, improve joint health, and enhance overall well-being. Combined with medical advice, these strategies empower patients to lead healthier, pain-free lives.

Comprehensive Dietary Approaches to Effectively Manage Gout Symptoms and Improve Joint Health
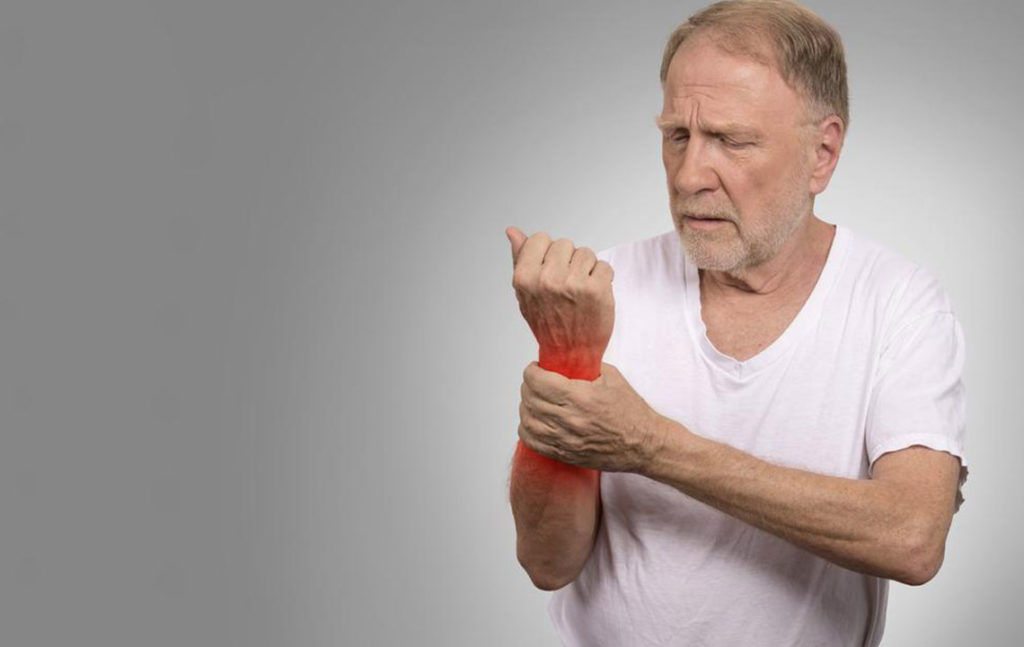
Gout is a complex form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by sudden and severe pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness in the joints. It is primarily caused by elevated levels of uric acid in the bloodstream, which crystallizes and deposits around the joints. These uric acid crystals provoke intense inflammatory responses that can severely impair daily activities and diminish quality of life. Proper management of gout, particularly through targeted dietary modifications, plays a pivotal role in reducing the frequency and severity of flare-ups. A well-structured diet can help maintain healthy uric acid levels, reduce joint inflammation, and promote overall well-being.
Understanding the pathophysiology of gout is essential for developing effective dietary strategies. Uric acid is a waste product formed when the body breaks down purines—substances found naturally in many foods. When uric acid production exceeds the body's ability to eliminate it via the kidneys, levels rise and increase the risk of crystal formation. Therefore, controlling purine intake through diet is a cornerstone of gout management. Alongside medication, lifestyle modifications, particularly dietary habits, can significantly impact the course of the disease.
Key Dietary Guidelines for Managing Gout
Achieving optimal health status and minimizing gout flare-ups involves a multifaceted approach centered on diet. Here are some essential guidelines:
Maintain a Healthy Body Weight: Excess body weight is strongly associated with increased serum uric acid levels and heightened risk of gout attacks. Obesity puts additional stress on joints and can trigger inflammatory responses leading to pain. Gradual weight loss—approximately one to two pounds per week—by reducing calorie intake and adopting a balanced diet can dramatically decrease gout symptoms. Incorporating regular physical activity alongside dietary adjustments enhances weight management efforts and improves joint function.
Limit High-Purine Foods: Certain foods are naturally rich in purines and can substantially raise uric acid levels. These include red meats such as beef, lamb, and pork, as well as organ meats like liver and kidneys. Shellfish, including shrimp, lobster, and mussels, are also high in purines and should be consumed sparingly. Processed meats and certain types of fish, such as anchovies, sardines, and mackerel, are best avoided or eaten in moderation. Replacing these with lower-purine options can greatly influence gout management.
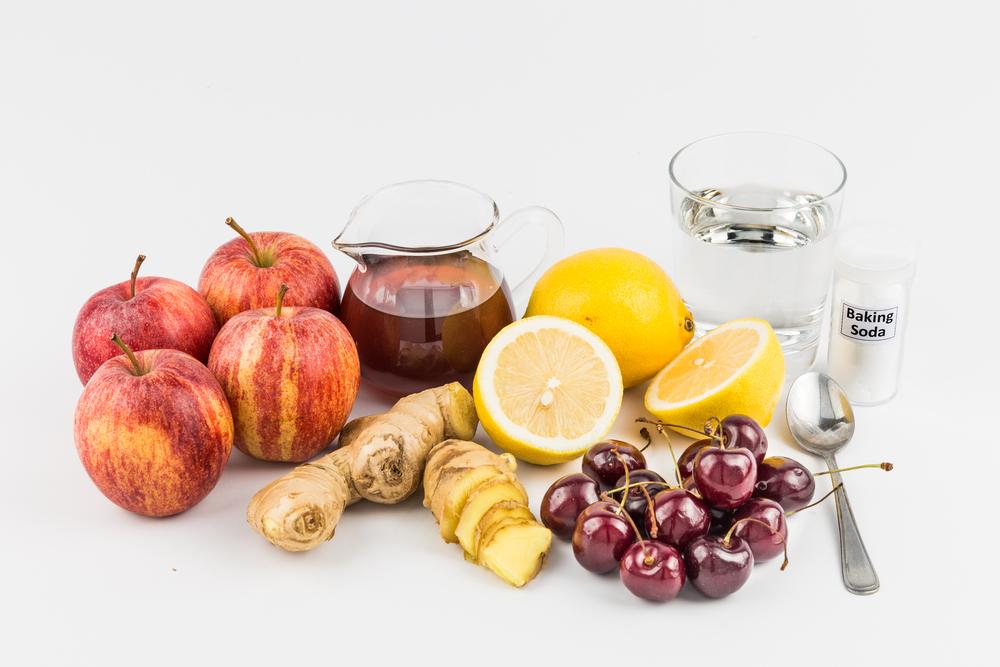
Reduce Intake of Processed Sugars and Fructose: Foods and beverages containing high-fructose corn syrup (HFCS)—such as soft drinks, candies, and sweetened cereals—are linked to increased uric acid production. Limiting these sugary items helps control uric acid levels and reduces inflammatory responses. Instead, opt for natural sweeteners and fresh fruits in moderation, focusing on fruits like cherries, which have been linked to decreased gout attacks.
Avoid Alcohol Consumption, Especially Beer and Spirits: Alcohol interferes with uric acid elimination and promotes its accumulation in the body. Beer is particularly problematic due to its high purine content, whereas spirits can also elevate uric acid levels. Limiting or abstaining from alcohol is strongly recommended for gout sufferers. Non-alcoholic beverages like herbal teas, infused water, or natural fruit juices can offer enjoyable alternatives that support hydration and health.
Choose Low-Purine Proteins and Replace with Plant-Based Options: Lean proteins such as poultry (chicken and turkey) and fish like salmon (in moderation) are preferable over red meats. Additionally, plant-based protein sources like lentils, beans, and tofu can be incorporated to diversify protein intake while managing purine levels. Milk alternatives like almond milk, coconut milk, and other plant-based options are excellent substitutes for soy milk, especially for individuals sensitive to soy’s purine content.
Stay Well-Hydrated: Proper hydration assists in flushing out uric acid from the body. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day can prevent uric acid crystals from forming and depositing around joints. Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water daily, and increase intake during flare-ups or hot weather.
Include Anti-Inflammatory and Nutrient-Rich Foods: Incorporating foods with anti-inflammatory properties can help reduce joint inflammation and pain. These include cherries, berries, green leafy vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids found in flaxseeds and walnuts. Consuming a diet rich in antioxidants and phytochemicals can support overall joint health and complement medical treatments.
Additional Lifestyle Considerations
Beyond diet, other lifestyle modifications can significantly influence gout management:
Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, and cycling can help control weight and improve joint flexibility. Exercise also promotes better circulation and waste elimination, including excess uric acid.
Avoid Trauma and Stress to Joints: Protecting joints from injuries and overuse can minimize inflammation and pain episodes. Proper footwear and ergonomic practices contribute to joint health.
Medication and Medical Supervision: Adherence to prescribed treatments, including urate-lowering therapies, and regular medical check-ups are crucial. Dietary changes should complement medical management for optimal results.
In conclusion, managing gout effectively requires a comprehensive approach that combines dietary modifications, weight management, hydration, and lifestyle changes. By understanding the role of purines, avoiding trigger foods, and adopting anti-inflammatory eating habits, individuals can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of gout attacks. Coupled with medical guidance, these strategies empower sufferers to maintain joint health, improve their quality of life, and prevent long-term joint damage. Staying informed and proactive is the key to successful gout management and achieving a healthier, pain-free life.