Comprehensive Guide to Early Pregnancy Signs and Stages
This comprehensive guide covers early pregnancy signs, symptoms, stages, and prevention methods. It offers valuable insights for women to recognize early indicators, understand pregnancy progression across three trimesters, and explore contraceptive options for family planning. Whether preparing for pregnancy or avoiding unplanned conception, this detailed article provides essential information to help women navigate the early stages of pregnancy confidently and healthily.

Identifying Early Symptoms and Understanding the Stages of Pregnancy
Discovering pregnancy is a significant milestone in a woman’s life, often accompanied by a range of physical and emotional changes. Recognizing the early signs of pregnancy can help women prepare for this new chapter with confidence and clarity. From subtle hormonal shifts to more noticeable bodily changes, understanding these symptoms ensures timely medical consultation and proper prenatal care. Pregnancy typically spans approximately 40 weeks, which can seem daunting at first. However, familiarizing oneself with the common signs and the progression through different stages provides valuable insights into what to expect during each trimester.
Major Indicators of Pregnancy in the Early Stages
While symptoms can vary considerably among women, certain signs are commonly recognized as early pregnancy indicators. Identifying these signals early can prompt timely pregnancy testing and healthcare engagement, leading to healthier outcomes for both mother and baby.
Missed Menstrual Period: This is often the first and most noticeable sign of pregnancy. A woman with regular cycles might notice a delay in her period, which prompts further investigation. However, irregular cycles caused by stress, hormonal imbalance, or health issues can sometimes mask or mimic pregnancy symptoms.
Breast Changes and Tenderness: Hormonal fluctuations immediately affect breast tissue, making them tender, swollen, or more sensitive shortly after conception. These changes prepare the breasts for breastfeeding but can also be uncomfortable.
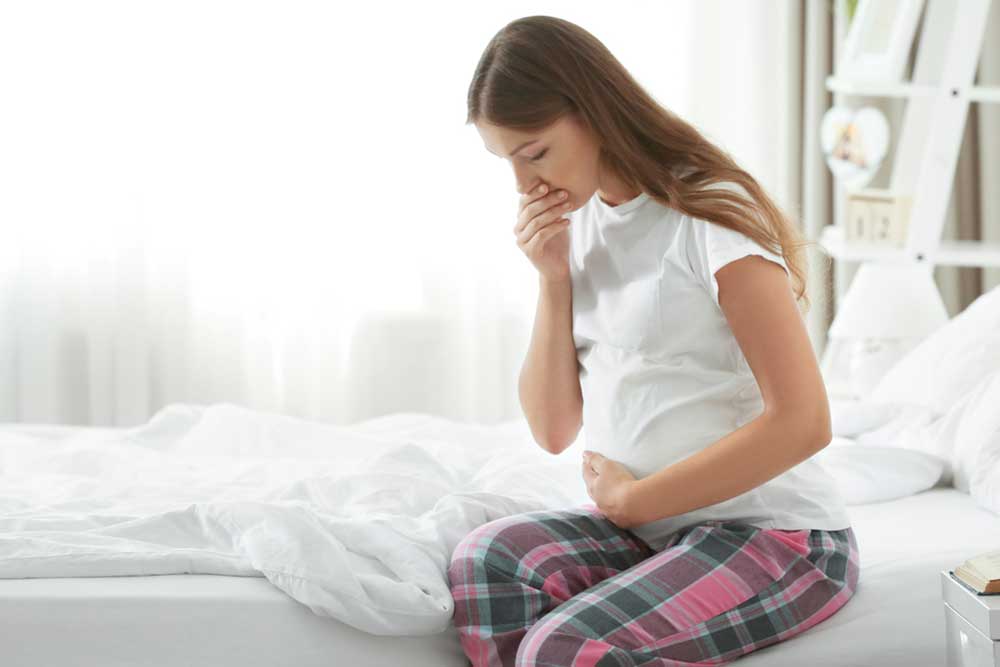
Nausea and Morning Sickness: Commonly referred to as morning sickness, this symptom can start as early as the first month after conception. While it is often experienced in the morning, nausea can strike at any hour and varies widely among individuals. Some women may also experience vomiting and heightened sensitivity to smells or certain foods.
Increased Urination: Elevated blood volume and hormonal changes cause the kidneys to work more efficiently, resulting in more frequent urination, often starting a few weeks into pregnancy.
Fatigue and Sleepiness: Rising levels of progesterone, a hormone essential for maintaining pregnancy, induce feelings of tiredness and the need for more rest during early gestation.
Additional early symptoms might include bloating, mood swings, cramping, constipation, and food aversions. Many women notice changes in their digestion, leading to discomfort or nausea when exposed to certain foods or smells. Emotional shifts such as irritability or heightened sensitivity are also common during this period, reflecting hormonal swings.
Understanding Pregnancy Trimesters
Pregnancy is divided into three main stages known as trimesters, each characterized by distinct developmental milestones:
First Trimester (Weeks 1–12): During this phase, the fertilized egg implants in the uterine lining, and rapid development of vital organs, muscles, and nerves takes place. The embryo is very small but undergoes significant growth in preparation for the next stage.
Second Trimester (Weeks 13–28): The fetus's bones begin to harden, and fingerprint patterns form. The fetus can reach about 12 inches in length, and many women start to feel the first fetal movements during this period. Organ systems continue to mature, and the body begins to develop more distinctly.
Third Trimester (Weeks 29–40): This final stage is marked by rapid growth, organ maturation, and increased weight. The fetus prepares for birth, and the mother might experience physical discomforts related to size and fetal movement patterns.
_Understandably, each trimester presents unique physical, emotional, and physiological changes that require appropriate care, proper nutrition, and regular medical monitoring to ensure a healthy pregnancy journey.Preventative Measures to Avoid Unplanned Pregnancy
Women seeking to prevent pregnancy have numerous contraceptive options available, each suited to different preferences and health considerations. Common methods include barrier methods like condoms and cervical caps, hormonal options such as oral contraceptive pills, patches, or injections, and intrauterine devices (IUDs). Consulting a healthcare professional helps determine the most suitable choice based on individual health, lifestyle, and family planning goals.
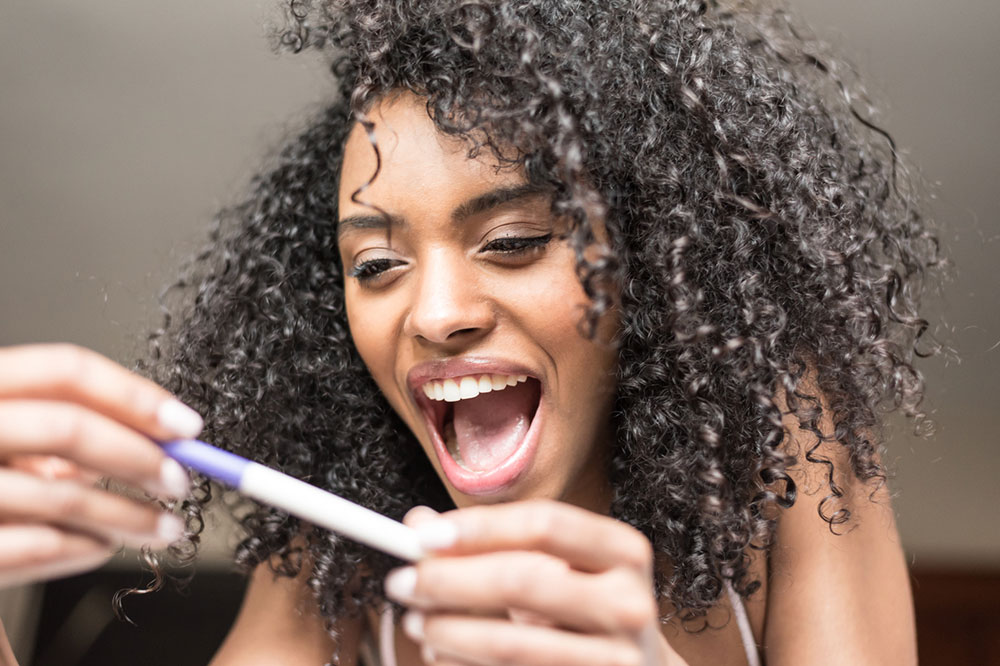
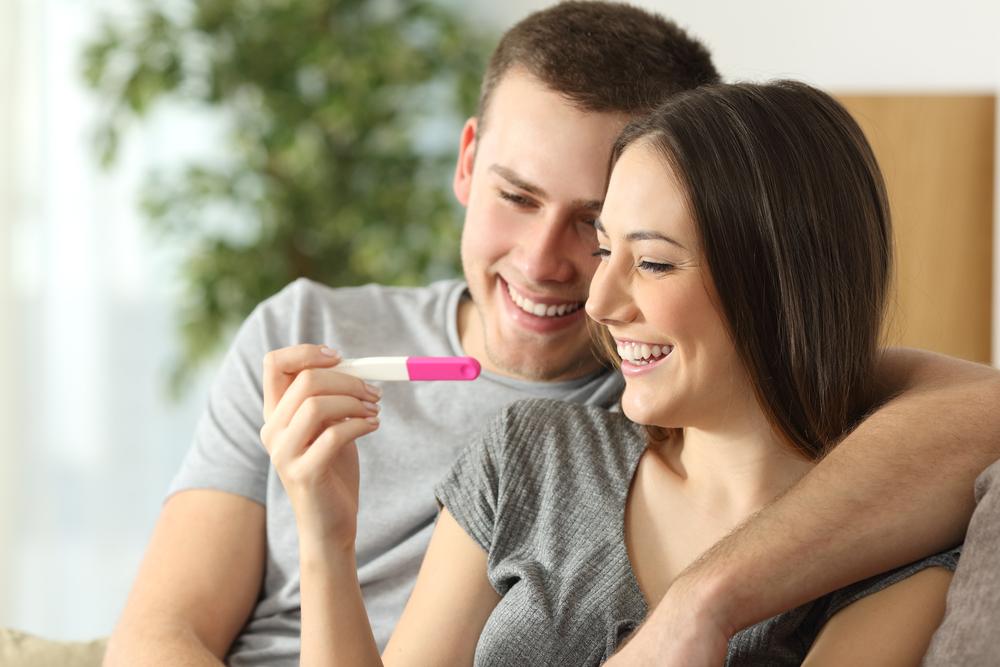
For women who suspect they might be pregnant, home pregnancy tests offer a reliable first step. These tests are accurate in detecting pregnancy hormones (hCG) in urine in up to 99% of cases when used correctly. Nevertheless, confirming pregnancy through a healthcare provider via urine or blood analysis ensures accuracy and allows for critical early prenatal assessments. Early medical intervention is vital for optimizing health outcomes for both mother and developing fetus.