Comprehensive Guide to Skin Infections: Types, Symptoms, and Effective Treatments
This comprehensive guide explores the various types of skin infections, including bacterial, fungal, and viral causes. It details symptoms, external and internal infections, and effective treatment options like medications and natural remedies. The article aims to educate readers on accurate diagnosis and holistic treatment approaches to ensure rapid recovery and skin health maintenance.

Comprehensive Guide to Skin Infections: Types, Symptoms, and Effective Treatments
An In-Depth Look at Skin Infections: Causes, Classifications, and Remedies
Skin infections are among the most common health issues affecting individuals worldwide. They are caused by various microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, and viruses that invade the skin tissue, leading to a wide range of symptoms including itching, rashes, sores, blisters, and inflammation. Understanding the different types of skin infections is essential for timely and effective treatment, minimizing complications, and preventing spread.
Most skin infections are bacterial, but fungal and viral infections are also prevalent and can sometimes coexist, complicating diagnosis and treatment. Proper identification of the infection type, along with appropriate medical intervention, can significantly improve recovery outcomes.
Categories and Causes of Skin Infections
Skin infections are generally classified into three main categories based on their causative microorganisms: bacterial, fungal, and viral. Each category has distinct characteristics, symptoms, and treatment protocols. A clear understanding of these categories helps in choosing the correct treatment strategy.
Bacterial Skin Infections
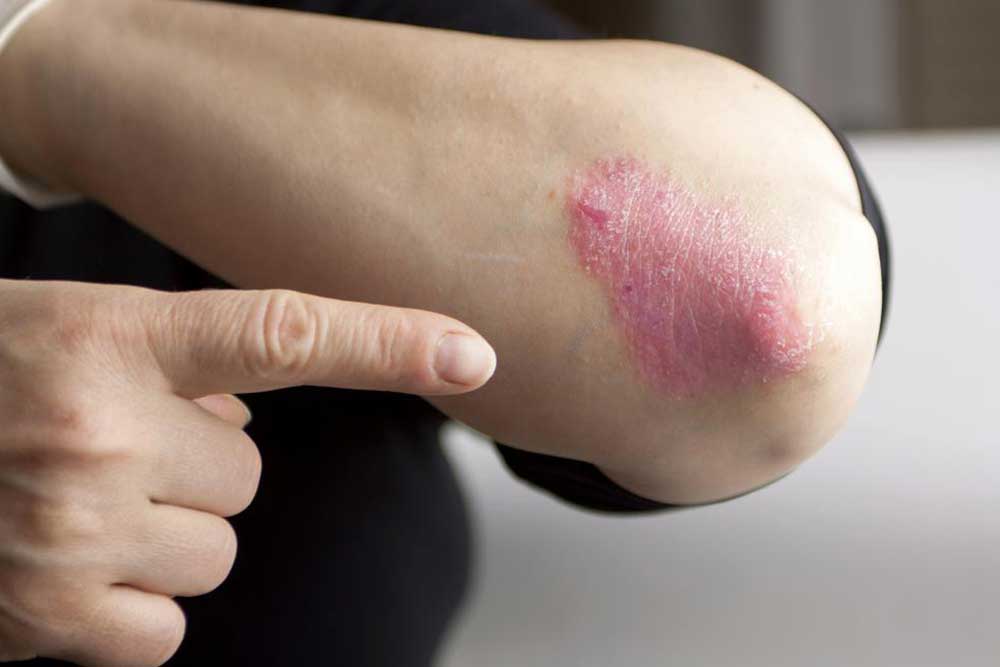
The skin hosts numerous beneficial bacteria that form a protective barrier. However, when harmful bacteria invade or overgrow due to injury, immune suppression, or other factors, they cause infections. These include common conditions such as impetigo, cellulitis, abscesses, carbuncles, and more severe infections like leprosy and staph infections.
Impetigo
A highly contagious bacterial skin infection characterized by honey-colored crusted sores, common among children.
Cellulitis
An acute bacterial infection of the skin and subcutaneous tissues, resulting in redness, swelling, warmth, and pain, often requiring antibiotics.
Staph Infections
Caused by Staphylococcus bacteria, leading to boils, abscesses, and other skin infections, especially in skin wounds.
Fungal Skin Conditions
Fungal infections occur when fungi invade the skin or nails. They are common worldwide, especially in humid and moist environments.
Athlete’s Foot
A contagious fungal infection affecting the feet, causing scaling, itching, and cracking skin in between toes.
Nail Fungus
Fungal invasion of the nails, leading to thickening, discoloration, and crumbling of the nails, primarily on toes.
Ringworm
A highly contagious fungal infection presenting as circular, ring-shaped rash with clear centers.
Candidiasis
An overgrowth of Candida fungi, leading to red, itchy patches, especially in warm, moist areas like armpits and groin.
Viral Skin Conditions
Viral infections tend to be persistent because viruses can hide within human cells, making eradication challenging.
Chickenpox & Measles
Childhood diseases featuring characteristic rashes, usually once-infection conditions.
Shingles
Reactivation of the chickenpox virus causing painful, blistering rashes that can recur multiple times.
Warts & Cold Sores
Caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) and herpes simplex virus, respectively, both contagious through skin contact.
External and Internal Skin Infections
Skin infections can be classified based on whether they involve superficial or deeper tissues.
External Infections
These involve the outer layers of the skin and are typically visible and easier to diagnose. Common external infections include:
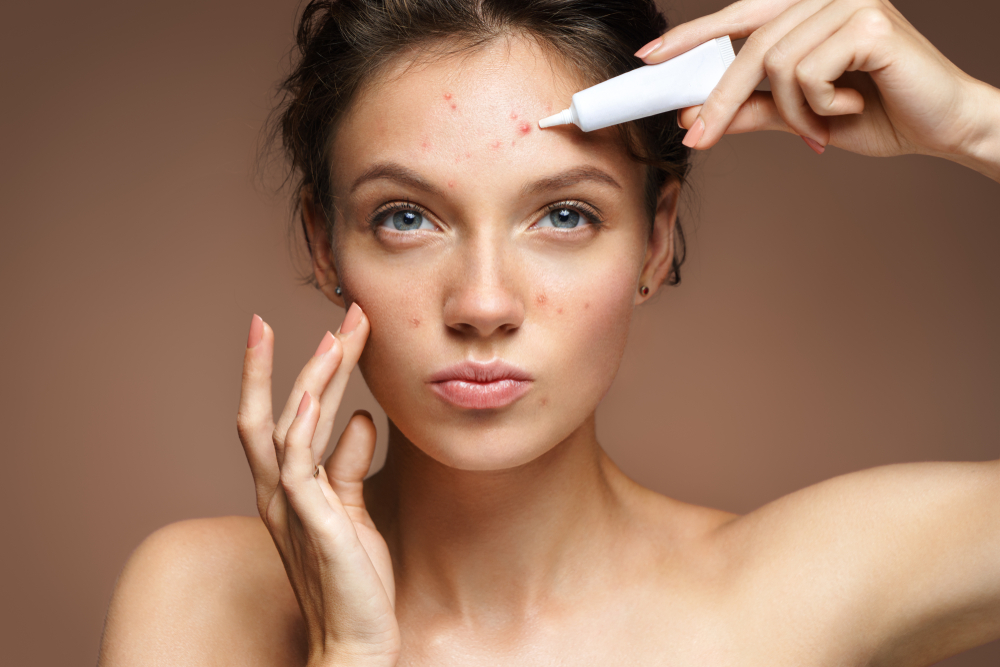
Acne
Hormonal fluctuations or excess oil production lead to blocked pores, resulting in pimples, cysts, and pustules, typically on the face, chest, and back.
Warts
Caused by HPV, often appearing on hands, feet, and other exposed areas. Highly contagious.
Ringworm
A fungal infection presenting as ring-shaped lesions that are itchy and scaly.
Athlete’s Foot
Common in athletes or those exposed to moist environments, affecting feet with cracking and scaling.
Fungal Nail Infection
Leading to thickened, discolored, and brittle nails, mostly affecting toenails.
Candidiasis
A yeast infection causing red, itchy patches in skin folds like the groin and armpits.
Internal Infections
These involve deeper tissues and can lead to serious complications if untreated:
Carbuncle
A cluster of boils infected by bacteria, often in hair follicles, requiring medical intervention.
Cellulitis
A deep bacterial infection causing painful, red, swollen skin, sometimes spreading rapidly, requiring antibiotics.
Effective Treatment Strategies for Skin Infections
The choice of treatment depends on the infection type, severity, and location. Common options include:
Medications such as antiseptic agents, antifungal creams, corticosteroids, antibiotics, antivirals, and vaccines.
Antibiotics and antivirals are prescribed for bacterial and viral infections, respectively, with some resistant strains like MRSA necessitating specialized drugs administered in healthcare settings.
In addition to conventional medicine, natural remedies have been used traditionally to manage skin infections, though medical consultation is advisable before use.
Natural Remedies and Alternative Treatments for Skin Infections
Neem leaf paste possesses natural antiseptic properties effective against bacteria and fungi.
Tea tree oil has potent antimicrobial effects and can be applied topically.
Apple cider vinegar and fermented dairy products like yogurt help combat fungal overgrowths.
Aloe vera gel promotes skin healing, reduces inflammation, and soothes affected areas.
Turmeric contains curcumin, which has anti-inflammatory and antiseptic benefits.
Echinacea, thyme, and calendula extracts support immune response and aid recovery.
Tomatoes are rich in lycopene, known for reducing inflammation and oxidative stress.
Garlic paste, with its natural allicin compound, offers antibacterial and antifungal effects.
Coconut oil exhibits broad-spectrum antimicrobial properties beneficial in managing skin infections.
Understanding the diversity of skin infections and the available treatment options—including natural therapies—plays a crucial role in achieving quick recovery and maintaining healthy skin.