Comprehensive Dietary Approaches to Lower Triglyceride Levels for Better Heart Health
Discover comprehensive dietary strategies to effectively lower triglyceride levels, reduce heart disease risk, and enhance overall health. Learn about nutrient guidelines, foods to avoid, and healthy eating tips supported by experts to maintain optimal triglyceride levels and promote cardiovascular well-being.

Comprehensive Dietary Approaches to Lower Triglyceride Levels for Better Heart Health
Triglycerides are a type of fat found in the human bloodstream, serving as a vital energy source when stored in fat cells. However, when triglyceride levels become elevated, they significantly increase the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks and strokes. Understanding how to manage and lower these levels through dietary strategies is essential for maintaining optimal heart health and preventing chronic health issues.
During digestion, the body converts excess calories from food into triglycerides, which are then transported and stored in fat tissues. While this process is necessary for energy reserves, an imbalance caused by excess caloric intake, poor lifestyle choices, or underlying health conditions can lead to abnormal high triglyceride levels. Such elevations, known as hypertriglyceridemia, are linked to atherosclerosis, which narrows and hardens arteries, eventually increasing the risk of heart-related events.
Several factors contribute to high triglyceride levels, including obesity, excessive alcohol consumption, kidney problems, unmanaged diabetes, and diets rich in refined or high-calorie foods. Addressing these factors through targeted dietary modifications and lifestyle changes can effectively lower triglycerides and improve overall cardiovascular health.
High triglyceride levels are prevalent among many populations worldwide, making awareness and proactive management critical. Understanding your triglyceride numbers is a key step in preventing cardiovascular complications.
Understanding Triglyceride Numbers and Their Implications
Normal triglyceride levels are classified as less than 150 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). When levels rise above this threshold, the risk of cardiovascular problems increases. It is important to monitor these numbers regularly and work with your healthcare provider to develop an appropriate management plan.
Here are the key ranges for triglyceride levels:
Desirable: less than 150 mg/dL
Borderline high: 150-199 mg/dL
High: over 200 mg/dL
Very high: over 500 mg/dL
Effective Dietary Tips to Manage and Reduce Triglyceride Levels
For individuals dealing with conditions like diabetes, thyroid issues, or obesity, dietary management is often the first line of defense. A structured approach guided by healthcare professionals can significantly impact triglyceride levels and overall health.
Incorporating healthy dietary habits is crucial for controlling triglycerides. These practical nutritional tips can help maintain optimal levels, reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, and promote better health outcomes:
Limit Sugar Intake
Excess added sugars, including those found in candies, desserts, fruit juices, and sugary sodas, are major contributors to elevated triglycerides. The American Heart Association recommends keeping added sugar intake within 6 teaspoons for women and 9 teaspoons for men daily to prevent detrimental effects.
Embrace a Low-Carbohydrate Diet
Carbohydrates, especially processed ones like white bread, pastries, and white rice, convert into triglycerides during digestion. A low-carb diet reduces this conversion process, aiding in fat reduction and triglyceride management.
Prioritize High-Fiber Foods
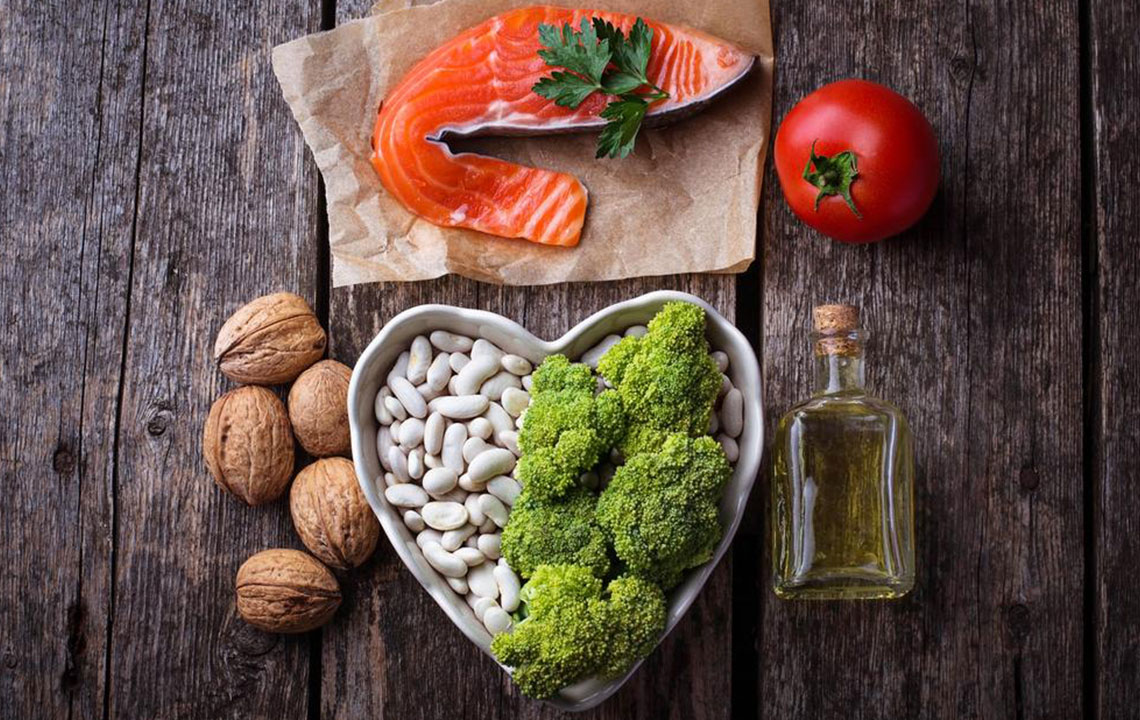
Dietary fiber—found abundantly in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts—helps slow the absorption of sugar and fats in the intestines, leading to a decrease in blood triglyceride levels.
Avoid Trans Fats
Trans fats, frequently present in processed foods, baked goods, and fried items made with hydrogenated oils, are harmful to heart health. Eliminating these fats can lower both bad cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
Consume Omega-3 Rich Fatty Fish Twice Weekly
Fish such as salmon, sardines, mackerel, and anchovies are high in omega-3 fatty acids, which have been shown to support heart health and effectively reduce triglyceride concentrations.
Choose Unsaturated Fats
Incorporate healthy fats from sources like nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil. These fats are beneficial for heart health and help lower triglyceride levels compared to saturated and trans fats.
Limit Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol intake adds extra calories and sugar into the diet. Excess alcohol can significantly raise triglycerides; therefore, moderation is essential. Moderate drinking may offer some health benefits, but overconsumption increases cardiovascular risk.
Include Nuts Regularly in Your Diet
Almonds, walnuts, pistachios, and other nuts provide essential omega-3s, fiber, and healthy fats that aid in triglyceride reduction. They also promote satiety and help in weight management.
Implementing these dietary strategies, combined with regular physical activity and mindful eating habits, can lead to substantial improvements in triglyceride levels. Lifestyle modifications like maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, stress management, and engaging in routine exercise are also vital in this holistic approach to cardiovascular health.