Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
This comprehensive guide details the key signs and symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), including abdominal pain, altered bowel habits, diarrhea, constipation, nausea, and bloating. Recognizing these indicators early helps in prompt diagnosis and effective management, which is vital since IBS currently has no cure. The article emphasizes the importance of consulting healthcare professionals for ongoing symptoms and offers insights into symptom variations, diagnosis processes, and treatment options to help patients better understand and cope with this common gastrointestinal disorder.

Understanding the Key Indicators and Symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
In the realm of gastrointestinal health, Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) remains one of the most common yet complex disorders that challenge both patients and healthcare providers. Despite significant advances in medical research, a definitive cure for IBS has yet to be discovered, making early recognition and symptom management essential for improving patients' quality of life. The condition’s symptoms can vary greatly from person to person, often mimicking other digestive issues, which underscores the importance of understanding its hallmark signs to facilitate prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Recognizing the Symptoms of IBS
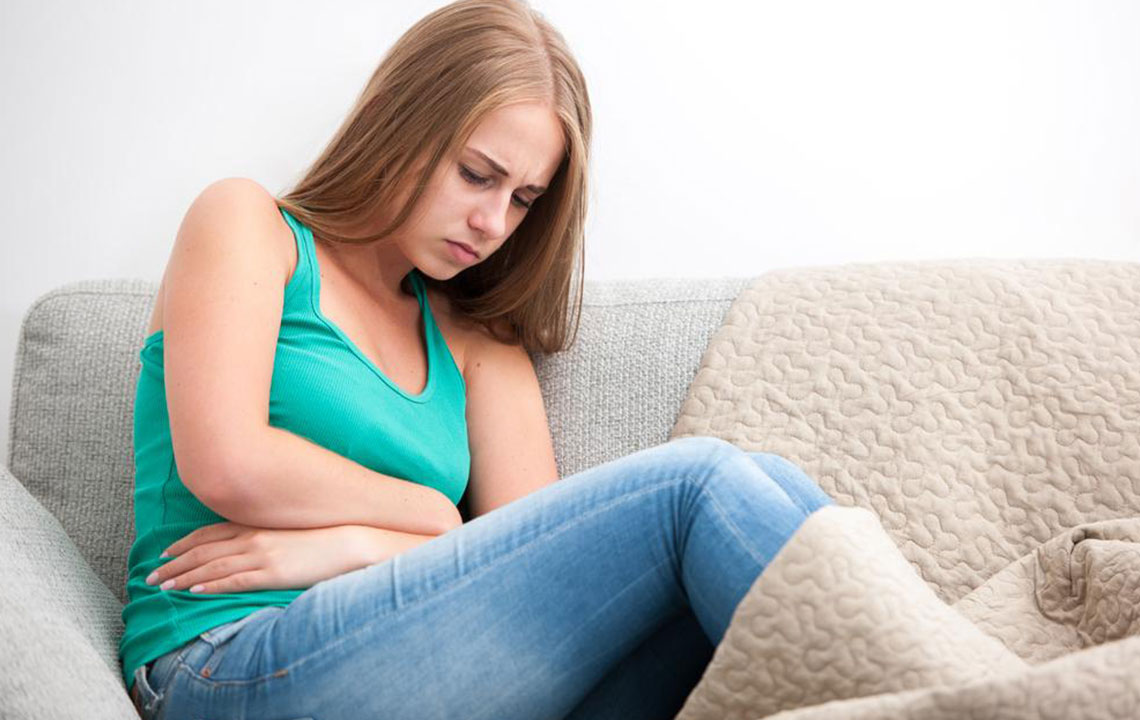
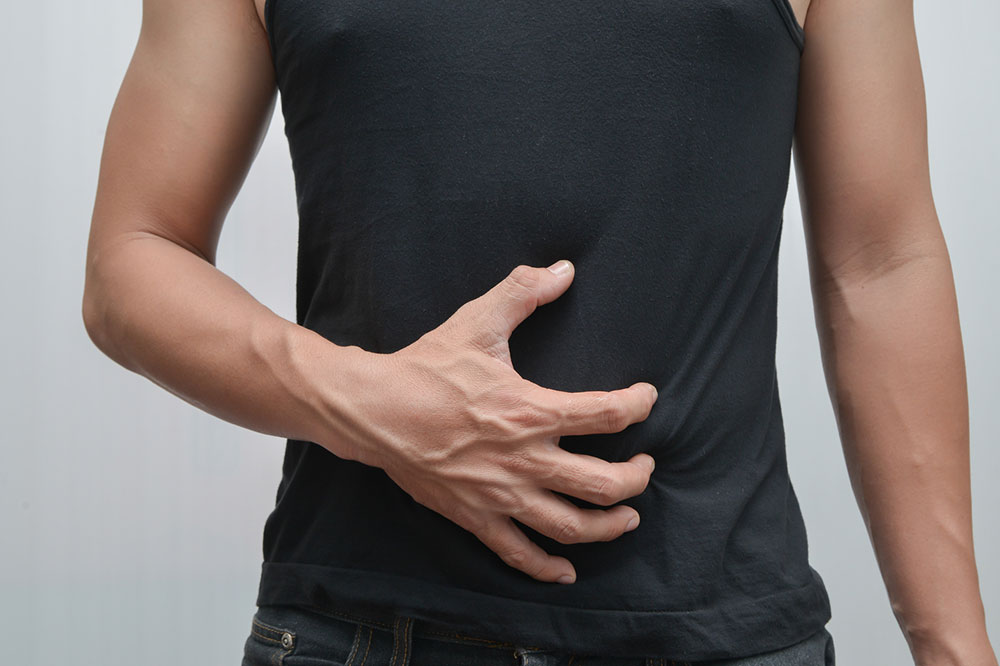
Abdominal Pain and Cramping: One of the most frequent complaints among individuals with IBS is persistent abdominal discomfort, which can manifest as cramping, stabbing sensations, or a dull ache. These symptoms often fluctuate and may occur before or after bowel movements. The pain is typically localized in the lower abdomen and can be relieved temporarily after passing stool or gas, but it tends to recur frequently.
Alterations in Bowel Habits: IBS is characterized by abnormal bowel movements, including episodes of diarrhea and constipation. Some individuals experience predominantly diarrhea (IBS-D), marked by frequent, loose stools, often accompanied by urgency and a feeling of incomplete evacuation. Others may suffer from constipation (IBS-C), with difficulty passing stools, straining, and a sensation of blockage. A subset of patients alternates between both, experiencing alternating episodes of diarrhea and constipation, known as mixed IBS (IBS-M).
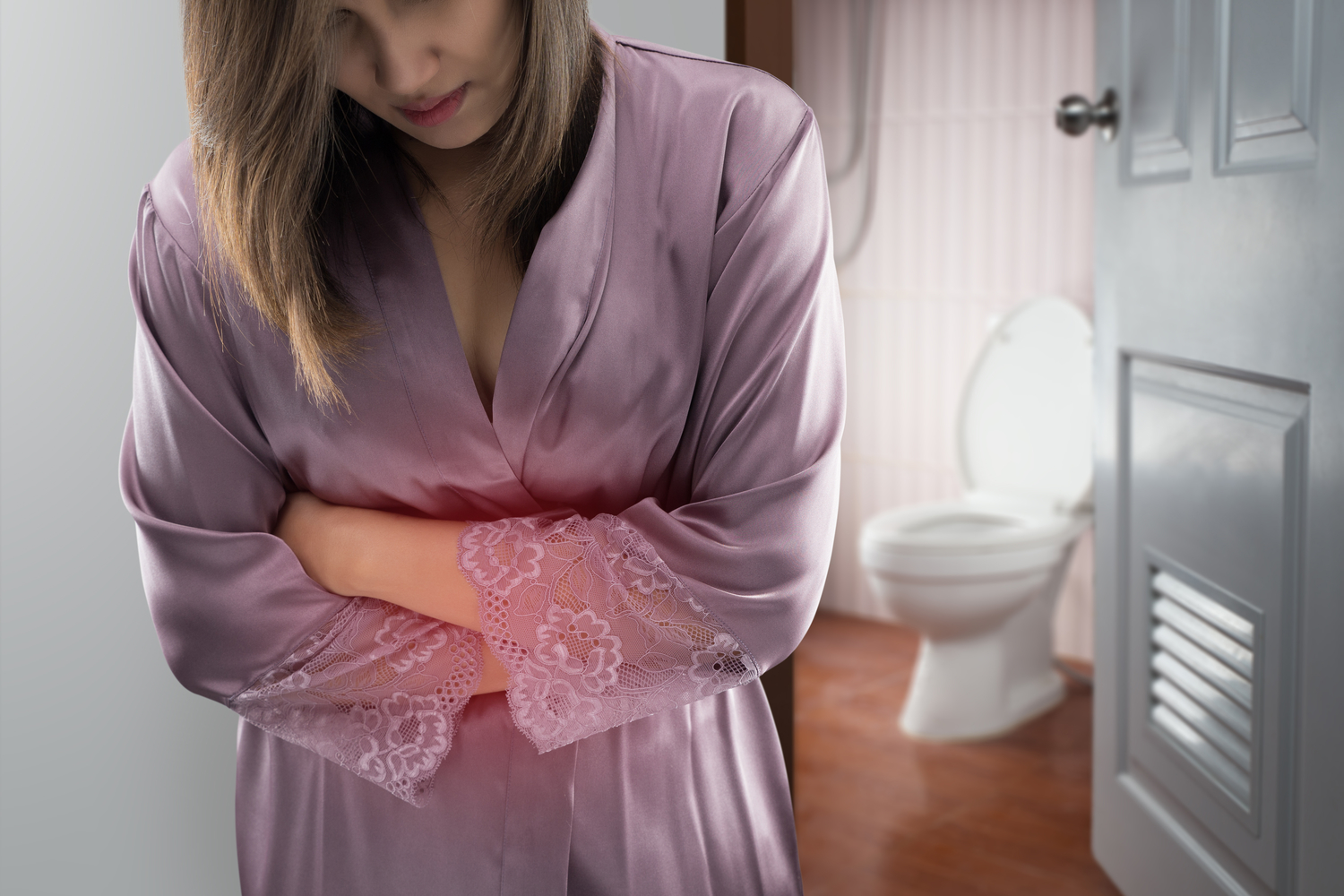
Diarrhea and Urgency: An increase in the frequency of loose or watery stools over a period of three months or more is a common symptom. These episodes are often sudden and accompanied by a compelling need to use the bathroom, sometimes without warning, significantly affecting daily routines and causing distress.
Constipation and Straining: Difficult or painful bowel movements, feelings of incomplete evacuation, and infrequent stools are hallmark signs of IBS-C. This symptom complex may also include straining during bowel movements and the passage of hard, dry stools.
Nausea and Gastrointestinal Discomfort: Many IBS sufferers report episodes of nausea, especially after eating. This, combined with generalized abdominal discomfort or bloating, can be quite distressing and may lead to reduced appetite or nutritional concerns.
Bloating and Visible Swelling: Persistent abdominal bloating, regardless of meal size, is a hallmark sign of IBS. Patients often feel full, tight, or swollen in the abdominal area, which can be uncomfortable and may cause psychological stress or embarrassment.
If these symptoms persist longer than a few weeks, or if they significantly interfere with daily life, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial. Proper diagnosis typically involves medical history, physical examination, and sometimes laboratory or imaging tests to rule out other conditions. Early detection can lead to effective management strategies, including diet modifications, medications, and lifestyle adjustments that can significantly improve patient comfort and quality of life.