Understanding Excessive Tear Production in the Eyes: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Remedies
Excessive tearing can be caused by allergies, irritants, or environmental factors. Recognizing key symptoms like redness, itching, swelling, and discharge is vital for timely treatment. Remedies include wearing sunglasses, rinsing eyes, using artificial tears, avoiding contact lenses, and preventing eye rubbing. Proper eye care and consultation with an ophthalmologist are essential for alleviating symptoms and maintaining eye health. Understanding these causes and solutions helps improve comfort and vision quality for affected individuals.

Understanding Excessive Tear Production in the Eyes: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Remedies
The human eye is a remarkably sensitive organ that constantly adapts to environmental stimuli. While tears serve a vital role in lubricating, cleaning, and protecting the eyes, an overproduction of tears—known as excessive tearing or epiphora—can cause discomfort and disrupt daily life. Recognizing the underlying causes and exploring the most effective remedies are essential steps toward alleviating this ocular issue.
The phenomenon of excessive tear production is often triggered by a combination of environmental factors, internal health issues, and sensitivities. Among the leading causes are allergic reactions, irritants, and external environmental influences. Allergies are a common culprit, eliciting immune responses that lead to inflamed, watery eyes. Exposure to dust, pollen from grasses and weeds, indoor allergens such as pet dander, mites in bedding, and certain cosmetics can all trigger these allergic responses. Additionally, contact lenses and artificial tears containing preservatives may exacerbate eye irritation, further stimulating tear production.
When the eyes detect these allergens or irritants, the immune system reacts by releasing chemicals like histamine. This response causes inflammation, swelling of the eyelids, itching, and increased tear formation as the body's attempt to flush out the irritants. While tears are generally beneficial—helping to remove debris and pathogens—overproduction can result in blurred vision, discomfort, and an increased risk of eye infections if not managed properly.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Excessive Tear Production
Allergic and irritant-related tearing often manifests with a variety of observable symptoms. These symptoms may appear rapidly after exposure to a trigger or develop gradually over several days. Recognizing these signs early can help seek timely treatment and prevent further complications. Common symptoms include:
Redness and a burning sensation in the eyes
Persistent itching around the eyelids and conjunctiva
Swelling and puffiness around the eyelids
Excessive watery discharge from the eyes
Persistent discomfort and pain in and around the eyes
Increased sensitivity to light (photophobia)
Difficulty focusing or blurred vision
Effective Treatments and Preventive Measures
Addressing excessive tear production caused by allergies and environmental factors requires a combination of lifestyle adjustments and medical interventions. While over-the-counter remedies can provide relief, it is crucial to seek professional ophthalmological advice to tailor treatments to individual needs. Some effective remedies include:
Wearing protective eyewear: Sunglasses with UV protection prevent exposure to harmful sunlight, pollen, dust, and other airborne allergens, reducing the likelihood of eye irritation and teariness.
Regular eye rinsing: Gentle cleansing with sterile water or saline solutions helps remove surface allergens and debris, providing immediate relief and reducing inflammation.
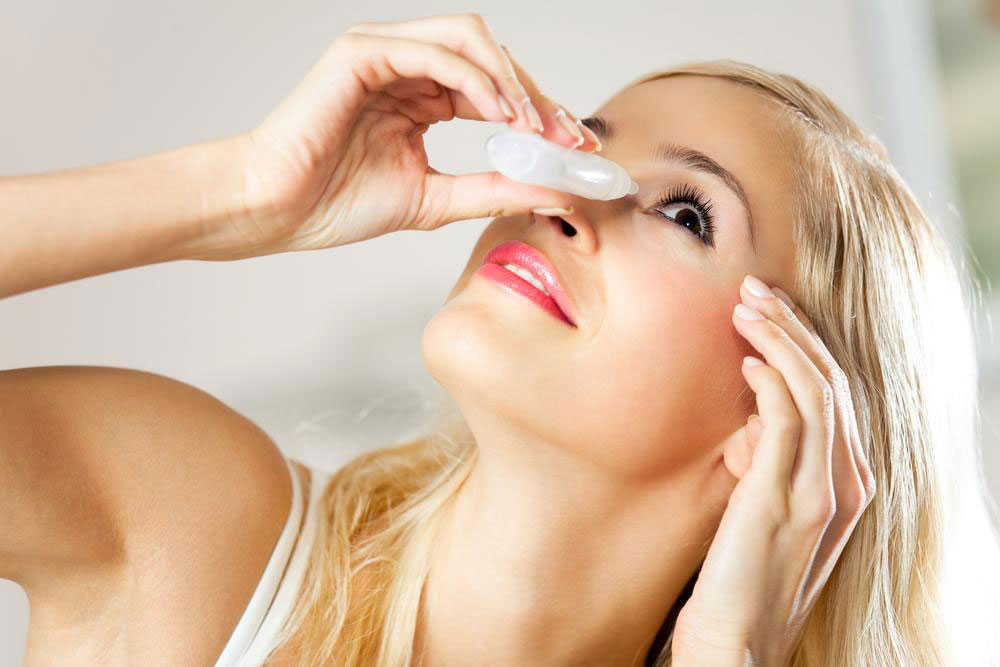
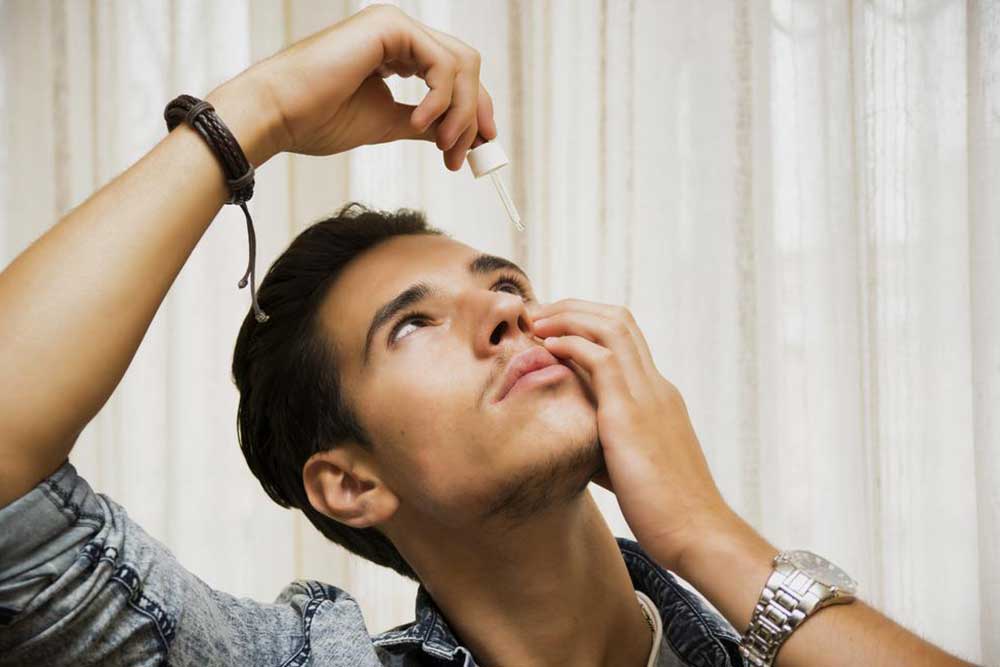
Use of artificial tears: Lubricating eye drops help soothe dryness, wash away allergens, and stabilize tear production. Always consult with an eye care professional before choosing specific brands or formulations.
Removing contact lenses: If you wear contact lenses and experience allergy symptoms, temporarily discontinuing their use can help reduce irritation. Switching to glasses during allergy seasons is advisable.
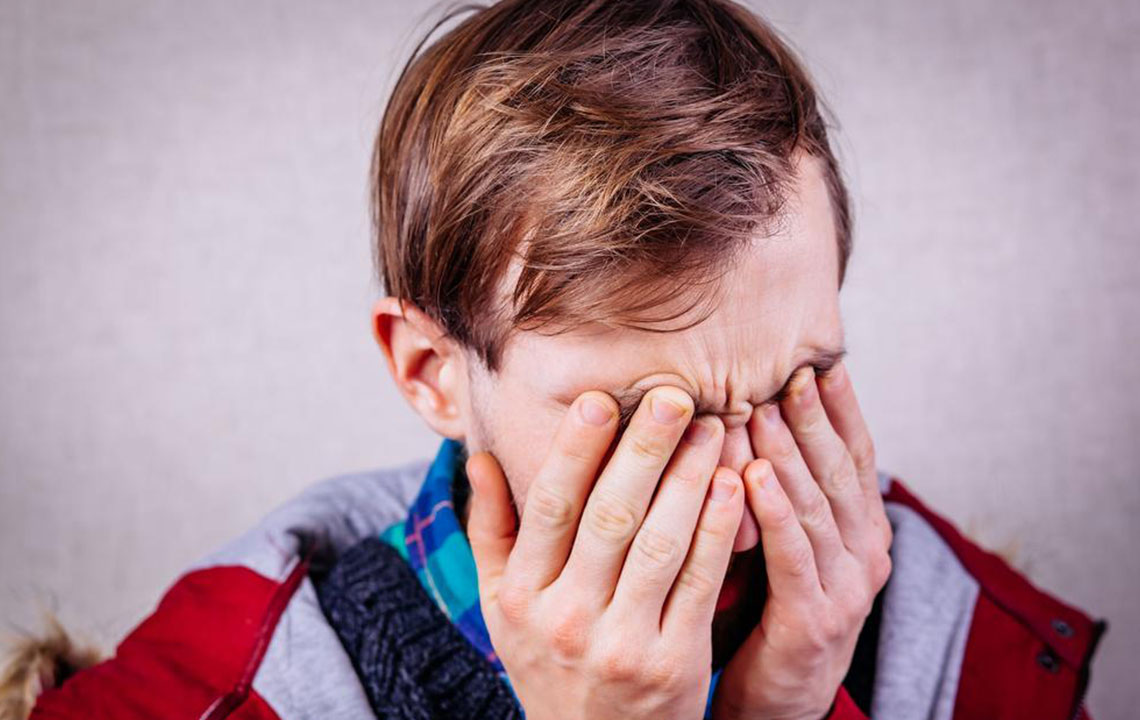
Avoiding eye rubbing: Rubbing eyes can worsen inflammation, scratch the cornea, and promote secondary infections. Instead, apply cold compresses or use prescribed antihistamine eye drops to manage itching.
Keeping the eyes protected from environmental allergens and irritants, maintaining good eye hygiene, and seeking prompt medical advice can significantly reduce the discomfort associated with excessive tearing. With proper management, individuals can restore clear vision and enjoy daily activities without ocular distress.