Comprehensive Guide to Arthritis: Causes, Symptoms, and Types
This comprehensive article provides an in-depth overview of arthritis, covering its causes, symptoms, and various types. It emphasizes early diagnosis and personalized management strategies to improve patient outcomes. Whether dealing with osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or gout, understanding these conditions helps in effective treatment and lifestyle adjustments. The guide aims to educate readers on the complexities of arthritis and the importance of timely medical intervention to maintain joint health and overall well-being.

Comprehensive Guide to Arthritis: Causes, Symptoms, and Types
Arthritis is a common yet complex health condition that primarily affects the joints, leading to inflammation, pain, and reduced mobility. It encompasses more than 200 different diseases, each with unique characteristics and impacts on the body. Understanding arthritis is crucial for early detection, proper management, and improved quality of life. This extensive guide explores the underlying causes, diverse symptoms, and various types of arthritis, offering valuable insights into managing this widespread ailment.
Arthritis is not a singular disease but a term covering a broad spectrum of joint disorders. These conditions can result from degenerative processes, immune system dysfunctions, infections, or metabolic irregularities. Recognizing the different categories of arthritis helps tailor treatment strategies to individual needs, ultimately aiming to reduce pain, improve joint function, and prevent long-term damage. This article delves into the causes, symptoms, and classifications of arthritis, providing comprehensive information to patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals alike.
Understanding the causes of arthritis involves exploring genetic factors, lifestyle influences, environmental exposures, and underlying health conditions. Family history plays a significant role, especially in degenerative diseases like osteoarthritis, where genetic predisposition influences cartilage health. Autoimmune conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus are triggered by immune dysregulation, causing joint inflammation and tissue damage. Metabolic disorders, notably gout, stem from irregularities in uric acid metabolism, leading to crystal deposits in joints. Additionally, trauma and infections can initiate or exacerbate certain forms of arthritis, often resulting in chronic discomfort and disability if left untreated.
Recognizing the symptoms early is vital for effective management. Common signs include persistent joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased range of motion. These symptoms often vary depending on the specific type of arthritis involved. For instance, osteoarthritis typically causes pain worsening with activity and stiffness after periods of inactivity, while rheumatoid arthritis often presents with symmetrical joint swelling and systemic symptoms such as fatigue and fever. Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly slow disease progression and enhance patient outcomes.
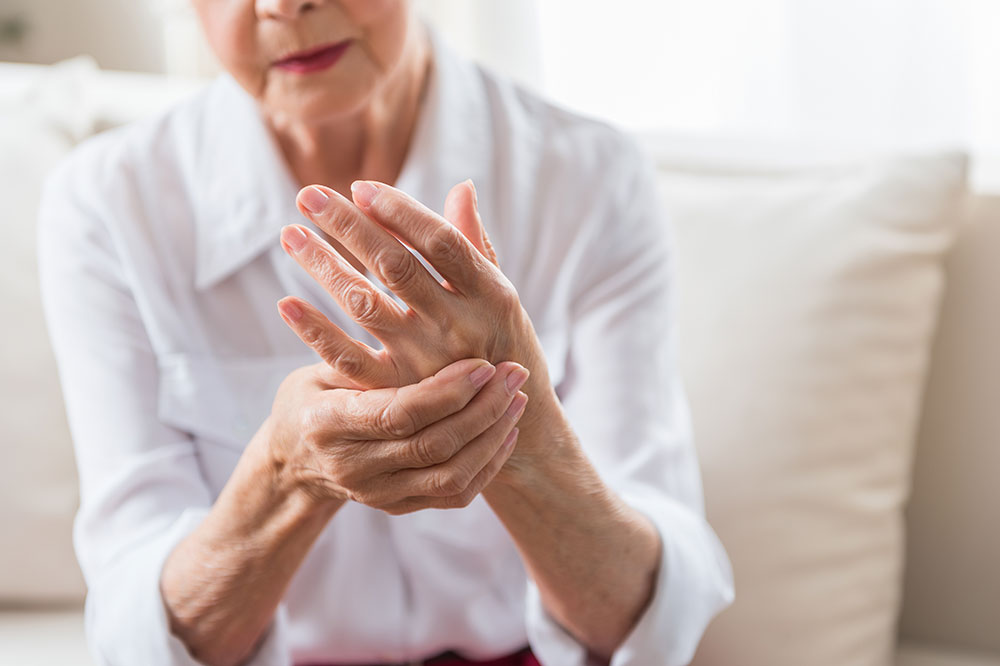
Joint pain and discomfort – This is the hallmark symptom, manifesting as aching, throbbing, or burning sensations in affected joints, including the knees, hips, shoulders, elbows, or wrists. The pain can be episodic or persistent, greatly impacting daily activities.
Joint stiffness – Usually pronounced after waking up or after prolonged inactivity, stiffness can last from a few minutes to several hours, restricting movement and function.
Swelling and inflammation – Inflamed joints often appear swollen, tender, warm, and sometimes red, indicative of underlying inflammation.
Reduced mobility and function – Difficulty moving or performing routine tasks signals joint deterioration and potential arthritis, affecting quality of life.
When these symptoms are evident, seeking medical advice is essential for diagnosis and tailored treatment. Recognizing the specific type of arthritis guides appropriate intervention strategies, which may include medication, physical therapy, lifestyle changes, and sometimes surgical options. Different forms of arthritis have unique features:
Osteoarthritis – Characterized by the degeneration of cartilage, leading to bone-on-bone contact. Pain worsens with activity and improves with rest, often accompanied by crepitus (grating sounds) during movement.
Rheumatoid arthritis – An autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks joint linings, causing persistent inflammation, pain, swelling, and potential joint deformities over time.
Psoriatic arthritis – A form associated with psoriasis, involving inflammation of joints and connective tissues, often causing persistent pain, swelling, and skin lesions.
Gout – Develops due to uric acid crystal deposits, mostly affecting the big toe but also other joints. It causes sudden, intense pain, redness, and swelling during flare-ups.
Fibromyalgia – A chronic condition characterized by widespread muscular pain, fatigue, sleep disturbances, and mood disorders, often co-occurring with other forms of arthritis.
Lupus – An autoimmune disease affecting multiple organs, with joint pain, skin rashes, fatigue, and systemic inflammation as common symptoms.
Effective management of arthritis requires a comprehensive approach, including medications such as NSAIDs, corticosteroids, DMARDs, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications like regular exercise and balanced diet. Early intervention is crucial to prevent joint damage and maintain mobility. Advances in medical research continue to improve treatment options, aiming for better symptom control and disease progression mitigation. Living with arthritis is manageable with proper medical care, supportive therapies, and proactive health strategies.