Comprehensive Guide to Choosing the Ideal Digital Hearing Aid for Your Needs
Discover the comprehensive guide to selecting the perfect digital hearing aid tailored to your hearing needs. Learn about different styles, their advantages, disadvantages, and the factors influencing cost. Find the right device for improved hearing and quality of life with expert insights on fit, features, and professional assessment.
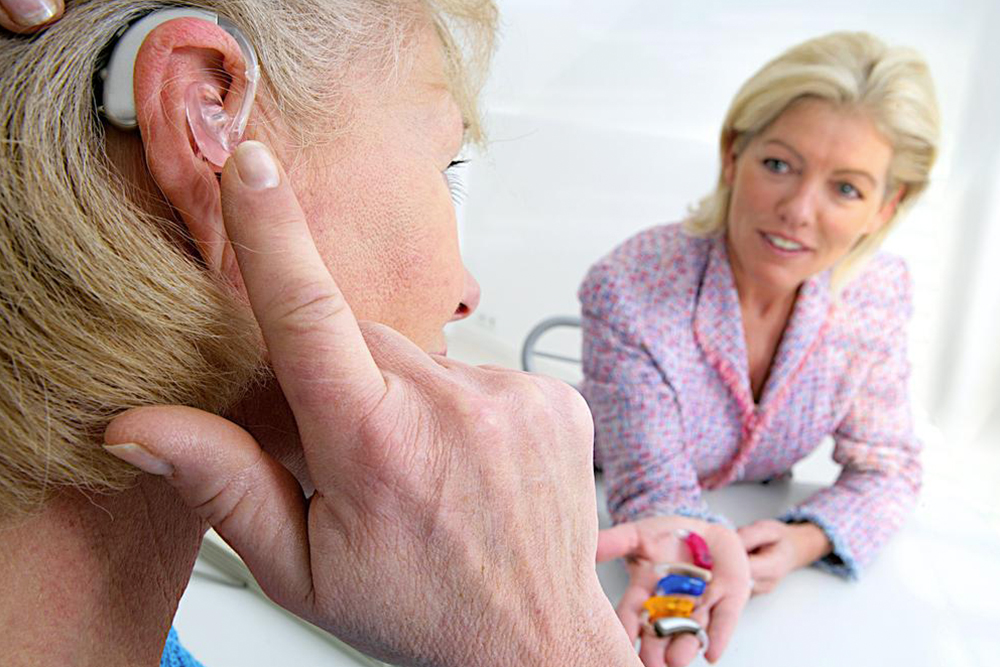

Comprehensive Guide to Selecting the Optimal Digital Hearing Aid
If you find yourself frequently asking "what!" or struggling to hear conversations clearly throughout your day, it might be time to explore the benefits of a digital hearing aid. Hearing difficulties can significantly impact your quality of life, communication, and overall well-being. While hearing aids do not cure deafness or profound hearing loss, they serve as powerful tools in amplifying sound, making auditory input clearer and more accessible. Modern digital hearing devices incorporate advanced technology that can be tailored to your specific hearing loss, environment, and lifestyle needs.
Understanding how digital hearing aids work is fundamental before making a purchase. These devices typically contain a microchip equipped with an amplifier designed to convert incoming sounds into digital signals. These signals are then processed—adjusted for amplification based on the user’s degree of hearing loss and the surrounding environment—and finally transformed back into audible sound waves delivered directly into your ear. This sophisticated process enhances speech clarity, reduces background noise, and improves overall hearing performance.
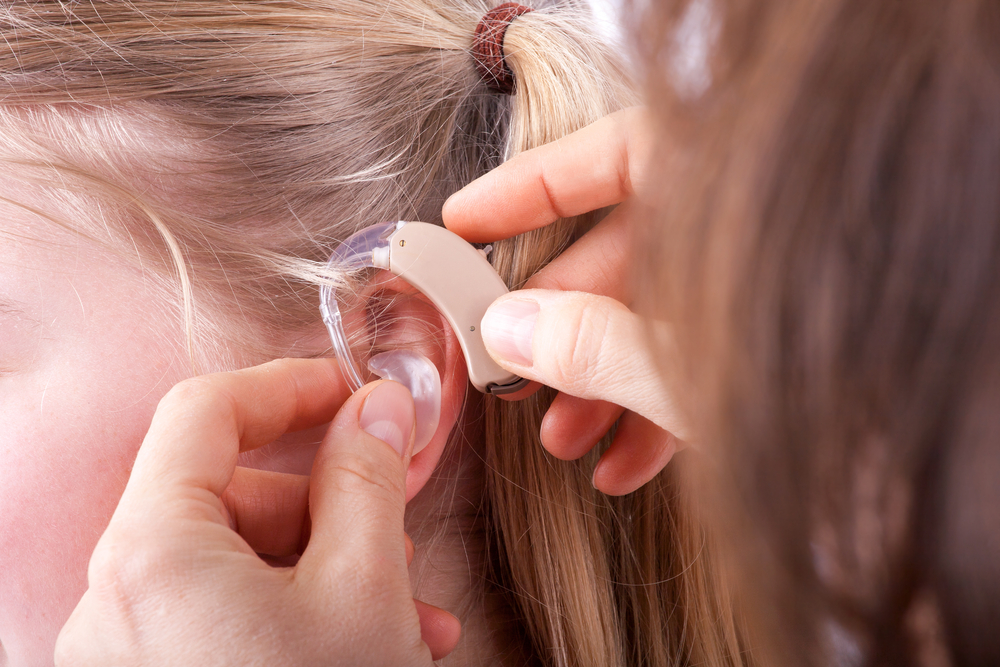
When selecting a digital hearing aid, customization is key. Fit, comfort, usability, and features tailored to your lifestyle ensure the device integrates seamlessly into your daily routine. There are various styles of digital hearing aids, each suited to different degrees of hearing loss, ear anatomy, and personal preferences. Let's explore the six primary categories of digital hearing aids to help you determine the best fit for your needs.
In-the-ear (ITE) Hearing Aids: Designed to sit comfortably inside your ear, ITE hearing aids are nearly invisible to others. They are particularly suitable for individuals with mild to moderate hearing impairment, offering a discreet solution without sacrificing functionality.
Advantages of ITE Hearing Aids:
Discreet design that blends with your ear
Reduces interference from background noise due to proximity to the eardrum
Disadvantages:
Susceptible to earwax buildup, which can affect performance
Limited space for advanced controls like volume adjustment or multiple programs
Small batteries with shorter lifespan, requiring frequent replacements
In-the-canal (ITC) Hearing Aids: Slightly larger than ITE models, ITC hearing aids are molded to fit within the ear canal, offering a balance between discreteness and ease of handling. These are ideal for those with mild to moderate hearing loss who prefer a less conspicuous device.
Pros of ITC Devices:
More manageable size for handling and operation
Easy to insert and remove with a comfortable fit
Cons:
Potential for earwax interference similar to ITE devices
Buttons and controls may be somewhat harder to operate due to smaller size
Full-shell or Half-shell In-the-ear Aids: These styles cover most or part of the outer ear, offering a larger casing for easier handling and accommodation of bigger batteries, which extend usage time.
Advantages:
Better handling and easier maintenance due to larger size
Utilize larger batteries providing longer operational periods
Disadvantages:
More visible than smaller models
Potential to pick up more ambient noise, influencing sound quality
Risk of earwax accumulation affecting device function
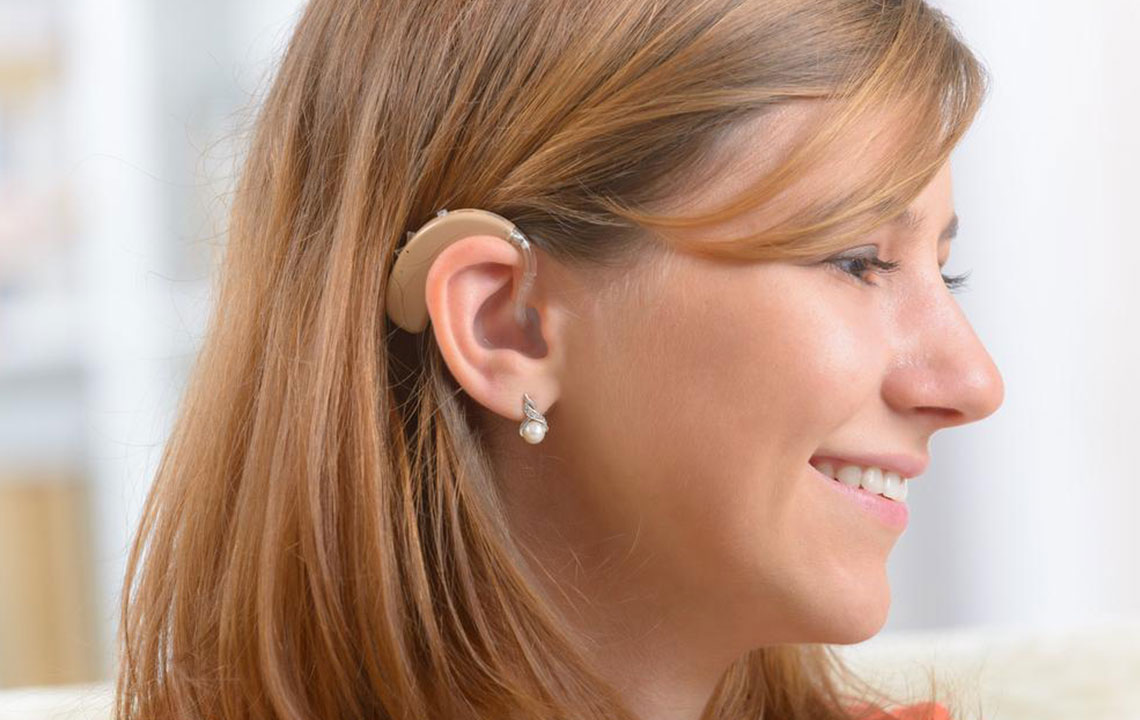
Behind-the-ear (BTE) Hearing Aids: Featuring a component that rests behind the ear connected via a tube or wire to an earmold or receiver inside the ear canal. BTE models are versatile and suitable for a wide range of hearing loss levels.
Pros of BTE Devices:
High amplification capacity suitable for severe hearing loss
Ease of handling, adjustments, and repairs
Cons:
More visible presence, which may affect aesthetic preferences
Can pick up background noise depending on the environment
Receiver-in-canal (RIC) Hearing Aids: Similar to traditional BTE aids, RIC devices utilize a thin wire rather than a full-sized tube, making them less conspicuous and more comfortable for users seeking a discreet profile.
Pricing for digital hearing aids generally begins around $1,500. The final cost varies based on several factors, including features like noise reduction, rechargeable batteries, wireless connectivity, additional accessories, professional fitting services, warranty options, and durability. It is highly recommended to try different devices under professional guidance before making a purchase. This hands-on approach ensures you choose a device that fits well, sounds natural, and meets your specific hearing needs.