Comprehensive Guide to Managing Excessive Tear Production: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatments
Excessive tearing, or epiphora, affects many individuals and can stem from various causes like allergies, infections, or structural issues. This comprehensive guide explores symptoms, triggers, and effective treatment options, including home remedies and medical procedures. Understanding the underlying causes is crucial for proper management and relieves discomfort and social embarrassment. The article emphasizes early diagnosis, the importance of consulting healthcare professionals, and lifestyle adjustments to maintain healthy, tear-balanced eyes.
Understanding Excessive Tear Production: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Strategies
Excessive tearing, medically known as epiphora, is a common condition that affects people of all ages. Unlike tears that are a response to emotional stimuli, persistent tearing without emotional triggers can be uncomfortable, socially awkward, and sometimes indicative of underlying health issues. Many individuals find themselves constantly wiping their eyes or experiencing irritation, which can interfere with daily activities. This detailed guide aims to shed light on the primary causes of excessive tear production, the typical symptoms one might observe, and the various treatment options available to manage and alleviate this condition effectively.
What Causes Watery Eyes?
The primary function of tears is to keep the eyes moist and clear away debris, dust, or other foreign particles. Tears are produced by tiny glands located above the outer corners of the eyes, known as lacrimal glands, which continuously release fluid to ensure the eyes remain comfortable and healthy.
Alongside maintaining eye moisture, tears play a role in the immune defense system, fighting off potential infections through their antibacterial and antiviral properties.
Excessive tear production or improper drainage of tears leads to persistent watery eyes, causing discomfort and blurred vision.
Why Do Eyes Produce Too Many Tears?
The tear glands produce a mixture of water, salt, and oils that are essential for maintaining the health of the ocular surface.
Any imbalance in these components—such as insufficient oil or salt—can lead to dry eye syndrome, which paradoxically causes the eyes to produce more tears as a compensatory response.
This overproduction of tears often results from dryness or irritation, prompting the tear ducts to overact and release excess fluid.
This condition, commonly referred to as ‘dry eye syndrome,’ illustrates how the body's attempt to compensate for dryness can lead to over-tearing.
Common Triggers for Excessive Tear Production
Environmental allergens like dust, pollen, pet dander, or aerosols are major contributors, especially in vulnerable individuals with existing allergies.
Extended use of digital devices without adequate breaks causes eye strain and fatigue, which can increase tearing.
Medical conditions affecting the eye structure or tear drainage system, such as blocked tear ducts, eyelash ingrowth, conjunctivitis, styes, or corneal abrasions, can provoke excessive tearing.
Respiratory illnesses like colds, sinusitis, or seasonal allergies often influence tear production due to inflammation and irritation.
Systemic health issues such as thyroid imbalance or hay fever can also impact tear regulation.
Side effects from medical treatments, including chemotherapy, or post-surgical reactions involving the eyes or nasal passages, may lead to tear overproduction.
Bright lights or glare from sunlight or artificial lighting can trigger sudden tearing in sensitive individuals.
Recognizing When to Seek Medical Advice
Most cases caused by allergies or environmental irritants tend to resolve once triggers are removed or minimized.
However, persistent redness, swelling, or changes in vision warrant professional assessment.
If you experience sensations of a foreign body in your eye, tenderness, or increasing discomfort, consult an eye care specialist promptly.
Immediate medical attention should be sought if symptoms include pus-like discharge, bleeding, or severe headaches accompanied by tearing.
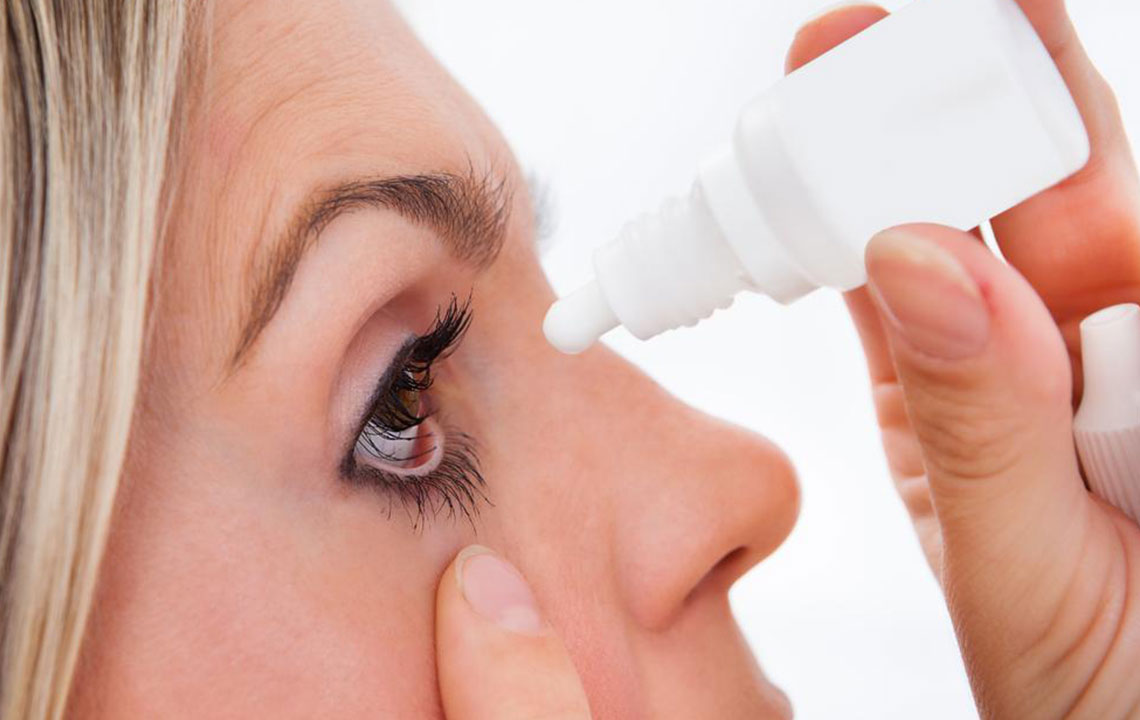
Effective Treatment Options for Excessive Tears
First and foremost, identifying and addressing the underlying cause is crucial for effective management.
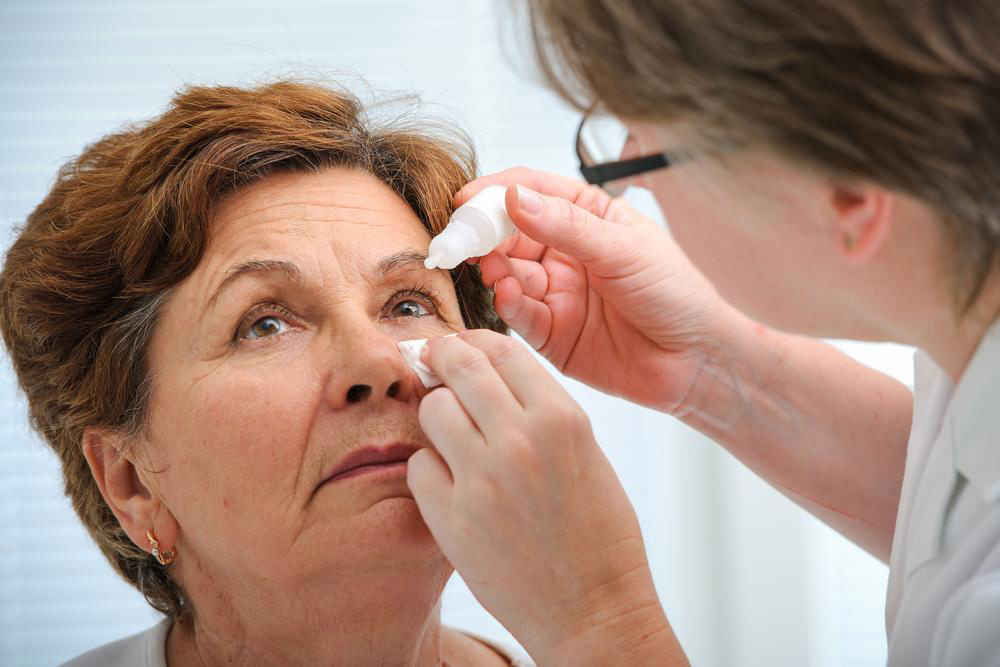
For conjunctivitis, allergy-induced tearing, or colds, doctors recommend specific medications such as antihistamine eye drops, lubricants, or anti-inflammatory drugs.
Severe cases involving structural issues like drooping eyelids (ectropion) may require surgical intervention to correct the eyelid position and improve tear drainage.
Blocked tear ducts, a common cause of watery eyes, can often be treated successfully through procedures like dacryocystorhinostomy, which creates new pathways for tear drainage.
In some cases, minor corrective surgeries or procedures aim to unblock or widen the tear ducts to restore normal tear flow.
Managing Excessive Tearing in Infants and Young Children
Many newborns experience watery eyes as a natural part of their development, often resolving within a few months without intervention.
Parents can gently clean the eyes with sterile water and a soft cloth to remove crusts or discharge, ensuring proper hygiene.
If symptoms persist beyond a few months, or if there is pus, swelling, or redness, consulting a pediatrician is essential.
Avoid applying unprescribed eye drops or medications to infants’ eyes, as these can cause further irritation or complications.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Adjustments for Managing Excessive Tears
Reducing digital screen time and taking regular breaks can significantly decrease eye strain and subsequent tearing.
Applying a warm, damp cloth over closed eyelids can soothe irritation, promote tear drainage, and help balance tear production.
Maintaining good eyelid hygiene and avoiding exposure to cigarette smoke or other irritants can also improve eye comfort.
Staying hydrated and ensuring a balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids can support overall eye health.
In summary, excessive tearing is a multifaceted condition influenced by many factors ranging from environmental allergies to structural anomalies within the eye's tear system. Proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plans—ranging from simple home remedies to advanced surgical procedures—are essential for effectively addressing this issue and restoring eye comfort and visual clarity.