Comprehensive Guide to Multiple Myeloma: Causes, Risk Factors, Prevention, and Management
Discover an in-depth overview of multiple myeloma, including its causes, risk factors, symptoms, prevention tactics, and the latest treatment progress. Learn how early detection and healthy lifestyle choices can enhance management and outcomes for patients. This comprehensive guide offers valuable insights into understanding and combating this complex blood cancer.

Comprehensive Guide to Multiple Myeloma: Causes, Risk Factors, Prevention, and Management
Multiple myeloma is a complex form of blood cancer that originates from abnormal plasma cells within the bone marrow. These plasma cells, which normally play a critical role in the immune system by producing antibodies to combat infections, become malignant in this disease, leading to their uncontrolled proliferation. As they multiply, these cancerous cells form tumors that can damage bones, suppress normal blood cell production, and impair immune function. Understanding this disease requires an exploration of its underlying causes, risk factors, early detection methods, and strategies for prevention and management.
At present, the precise cause of multiple myeloma remains elusive. However, extensive research suggests that genetic mutations and chromosomal abnormalities in plasma cells might set the stage for malignant transformation. Certain genetic markers and inherited predispositions could also influence susceptibility. While environmental exposures are under investigation, factors such as radiation, exposure to specific chemicals, and lifestyle choices are believed to contribute to the risk profile.
Multiple myeloma predominantly affects older adults, with the median age at diagnosis around the mid-60s. It has been observed more frequently in men than women and shows higher prevalence among certain ethnic groups, particularly African Americans. These variations highlight the importance of considering geographical and genetic factors in understanding disease risk.
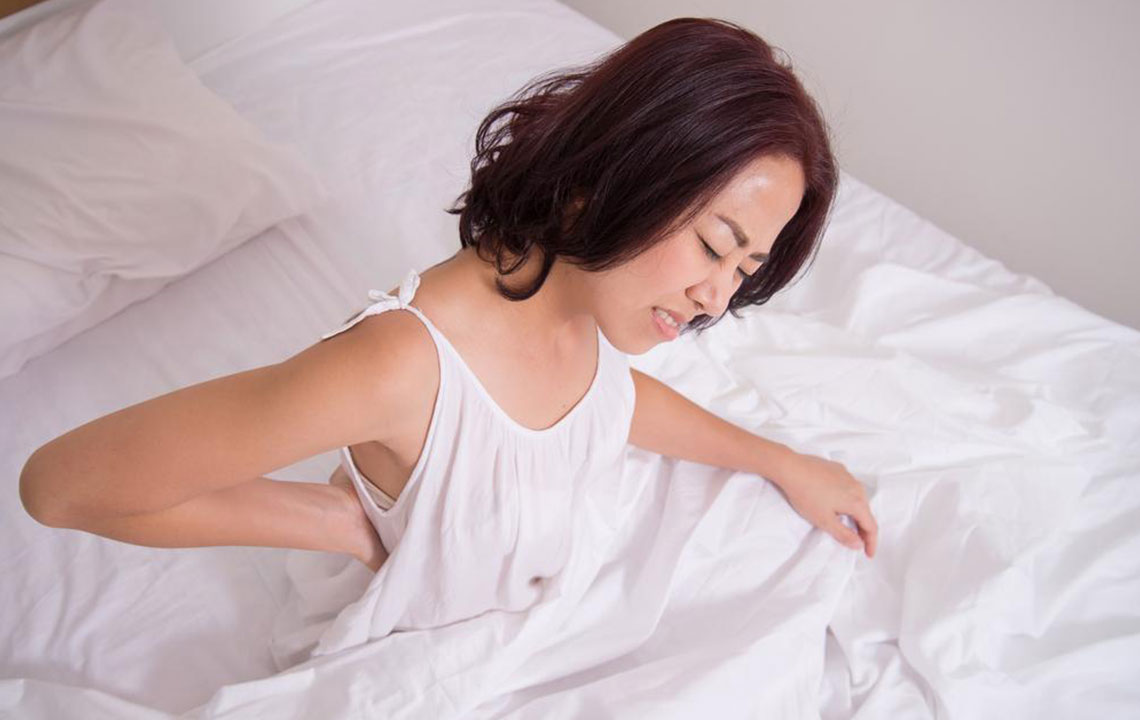
Symptoms of multiple myeloma often develop gradually, making early detection challenging. Common signs include persistent bone pain, especially in the back or ribs, fatigue, weakness, anemia, susceptibility to infections, and unexplained weight loss. Elevated calcium levels, kidney dysfunction, and fractures may also indicate disease progression and require prompt medical evaluation.
Risk Factors for Multiple Myeloma
Age: The risk increases significantly with age, particularly after 60 years.
Family History: A history of multiple myeloma or other plasma cell disorders in family members elevates risk.
Race and Ethnicity: African Americans have a higher incidence, possibly linked to genetic factors.
Obesity: Excess body weight is associated with increased risk due to inflammatory processes and hormonal influences.
Radiation and Chemical Exposure: Exposure to high levels of radiation and certain chemicals may contribute to disease development.
Other Medical Conditions: Conditions like monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) can be precursors to multiple myeloma.
Prevention Strategies and Lifestyle Tips
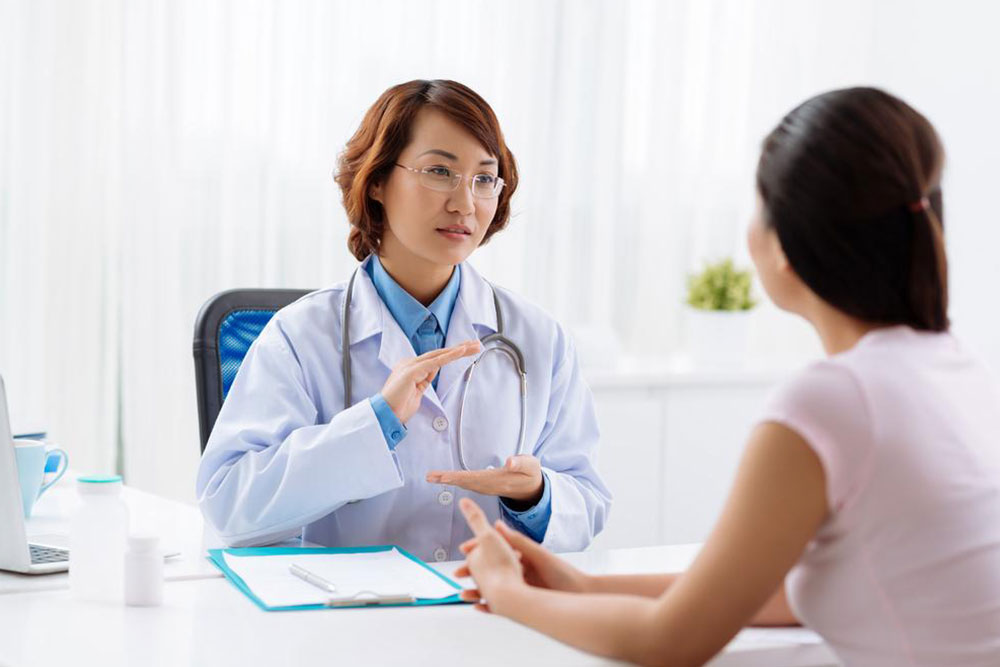
While specific prevention methods are limited due to the complex nature of the disease, adopting healthy lifestyle habits can help reduce overall risk. Regular health screenings and blood tests can assist in early detection, especially in high-risk populations.
Maintaining a nutritious, balanced diet rich in vegetables, fruits, and lean proteins supports immune health and reduces chronic inflammation. It is advisable to limit processed foods, sugar intake, excessive alcohol consumption, and smoking, as these factors can negatively impact overall health and immune function.
Engaging in regular physical activity, managing weight effectively, and avoiding unnecessary exposure to radiation or hazardous chemicals are proactive steps toward lowering risk. For individuals with a family history or other risk factors, consulting healthcare professionals for personalized screening plans can be highly beneficial.
Advances in Treatment and Management
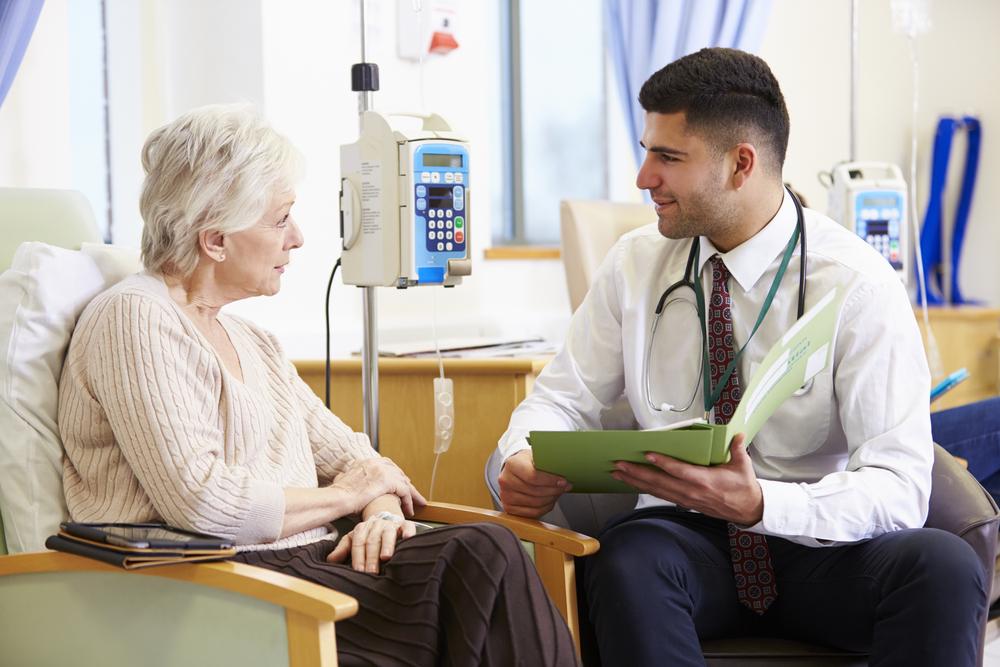
Over the past decades, significant progress has been made in the treatment of multiple myeloma. Innovative therapies such as targeted drugs, immunotherapy, and stem cell transplants have improved survival rates and quality of life. Early diagnosis combined with personalized treatment plans can effectively manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
Patients are encouraged to work closely with their healthcare team to monitor disease status, manage side effects, and explore clinical trials. Supportive care measures, including pain management and bone health support, are essential components of comprehensive care for multiple myeloma patients.
Conclusion
Although multiple myeloma remains a challenging disease, increased awareness, early detection, and lifestyle modifications can significantly impact outcomes. Regular medical check-ups, understanding risk factors, and adopting health-promoting behaviors are key to prevention and effective management. Advances in medical research continue to provide hope for better therapies and improved survival for those affected by this blood cancer.