Comprehensive Guide to Ingrown Hairs: Causes, Prevention, and Effective Treatments
This comprehensive guide explores the causes, prevention, and effective treatments for ingrown hairs. Learn how factors like hair type, skin care routines, and proper removal techniques influence ingrown hairs, and discover practical methods to prevent and treat them. From home remedies like warm compresses to professional medical advice, this article helps you achieve healthy, irritation-free skin by understanding and managing this common dermatological issue.

Comprehensive Guide to Ingrown Hairs: Causes, Prevention, and Effective Treatments
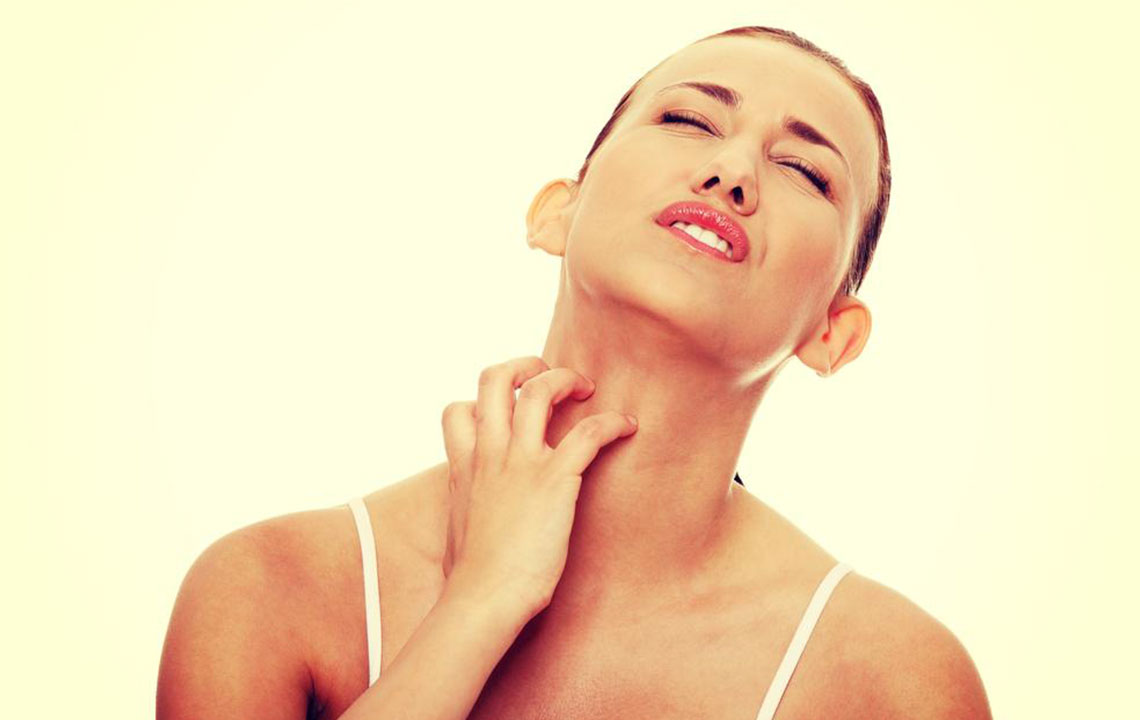
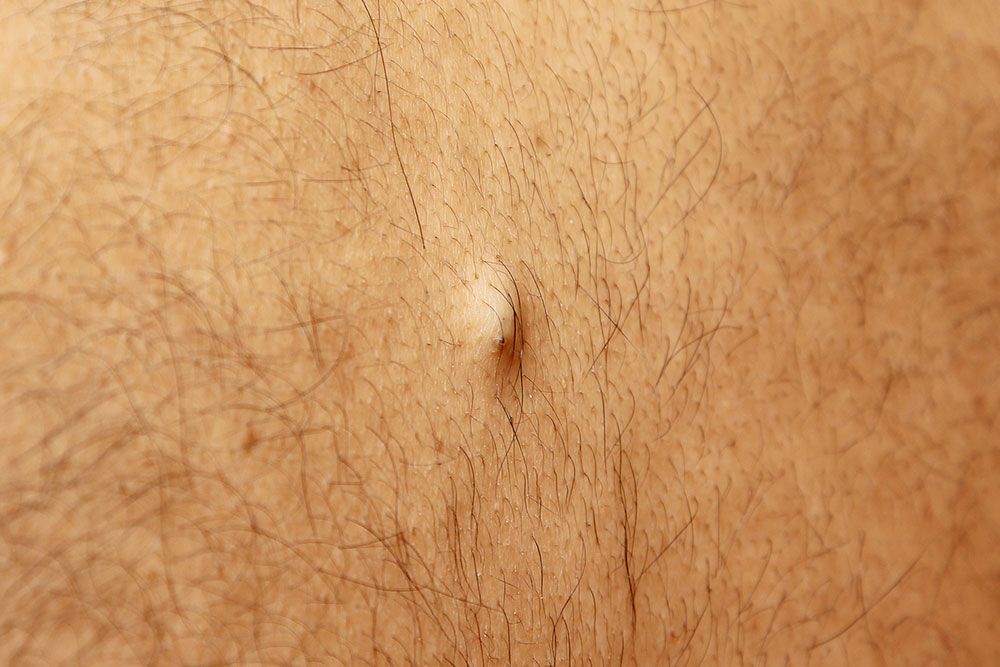
Ingrown hairs are a common dermatological concern that can affect individuals of all ages and skin types. They occur when hair strands from the body grow back into the skin instead of outward, leading to clusters of skin irritation often characterized by red, itchy bumps. While not life-threatening, ingrown hairs can cause significant discomfort, irritation, and sometimes lead to infections or scars if not properly managed. These skin issues are frequently encountered on the legs, armpits, and bikini areas in women, while men often experience them on the face and neck. Individuals with thick, curly, or coarse hair are especially prone to developing ingrown hairs, particularly when engaging in hair removal practices such as shaving, waxing, or tweezing.
Understanding the underlying causes and employing effective prevention and treatment strategies can significantly reduce the occurrence and severity of ingrown hairs. This comprehensive guide explores the causes, symptoms, prevention methods, and treatment options for ingrown hairs, ensuring you can maintain healthy, irritation-free skin.
What Are Ingrown Hairs?
Ingrown hairs happen when hair that has been shaved, waxed, or plucked begins to grow back into the skin instead of emerging outward. This abnormal hair growth pattern often results from hair follicles becoming blocked or scar tissue forming around hair follicles, trapping the hair beneath the skin’s surface. When this occurs, the body responds with an inflammatory reaction, leading to redness, swelling, pain, and sometimes pus formation. These symptoms can resemble acne, which often complicates diagnosis and treatment.
Causes of Ingrown Hairs
Recognizing the causes of ingrown hairs is crucial for effective prevention and management. Several factors contribute to their development:
Hair Type: Coarse, curly, or thick hair has a higher tendency to curl back into the skin, especially after shaving or waxing.
Hair Removal Techniques: Shaving with dull blades or shaving against the grain can cause hair to grow irregularly and penetrate the skin. Waxing and plucking can traumatize hair follicles, increasing the likelihood of ingrowth.
Skin Condition and Care: Dry, dehydrated skin reduces natural exfoliation, leading to the buildup of dead skin cells that can trap hair shafts. Excess oil production and clogged pores also contribute to follicle blockage.
Dead Skin Buildup: Accumulated dead skin cells can create a barrier over hair follicles, forcing hair to grow sideways or under the skin’s surface.
Skin Irritation: Skin irritation from aggressive hair removal methods or harsh skin products aggravates follicle inflammation, exacerbating ingrowth issues.
How to Prevent Ingrown Hairs
Prevention is paramount in maintaining healthy skin and avoiding the discomfort associated with ingrown hairs. Incorporate these strategies into your skincare regimen:
Proper Hair Removal Technique: Use sharp, single-blade razors and shave in the direction of hair growth. Avoid pressing hard or shaving against the grain, which can damage the skin and encourage hair curling.
Hydrate Your Skin: Adequate hydration helps maintain skin elasticity and promotes natural exfoliation. Drink plenty of water daily and apply moisturizing products suitable for your skin type.
Regular Exfoliation: Gentle exfoliation with scrubs or chemical exfoliants like salicylic acid or glycolic acid removes dead skin cells, reducing follicle blockage.
Avoid Tight Clothing: Wearing tight-fitting clothing, especially in areas prone to ingrown hairs, can cause friction and irritation, worsening ingrown issues.
Consider Alternative Hair Removal Methods: Laser hair removal or depilatory creams can offer longer-term solutions with reduced risk of ingrowth compared to traditional shaving or waxing.
Moisturize and Soothe: Apply soothing lotions and creams post-hair removal to reduce irritation and support skin healing.
Effective Treatments for Ingrown Hairs
If you already have ingrown hairs, several treatment techniques can alleviate symptoms and promote healing. It’s essential to approach treatment with care to avoid further irritation or scarring.
Warm Compresses
Applying warm compresses to the affected area helps soothe inflammation and encourages the embedded hair to surface. To do this, soak a clean cloth in warm water, wring out excess moisture, and gently press against the skin for 10-15 minutes. Repeating this process several times a day can soften the skin and facilitate hair removal. Gentle massage with a soft brush or cloth can also help loosen the ingrown hair from beneath the skin surface.
Leave It Alone
Resist the temptation to squeeze or pick at inflamed bumps, as this can increase the risk of infection and scarring. Instead, allow the area to heal naturally or with proper care.
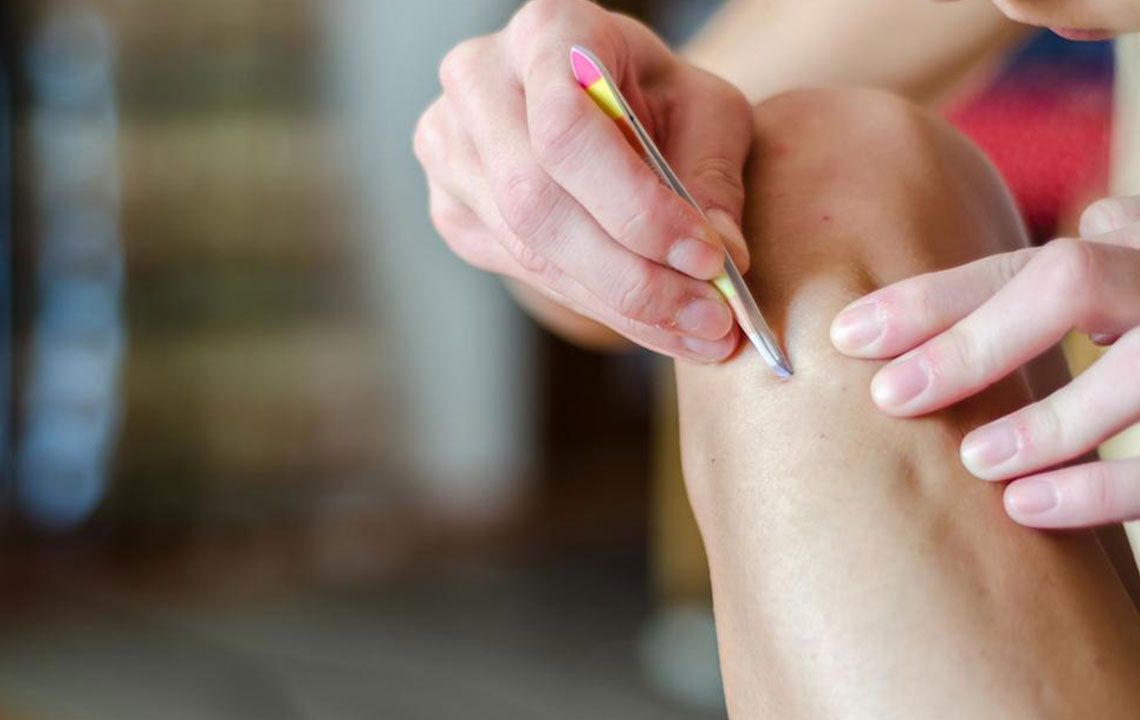
Careful Extraction
If the hair has broken through the skin or is visible, sterilized tweezers can be used to gently tease out the hair. Be sure to disinfect tools thoroughly before use. Do not insert tweezers deep into the skin or attempt to extract deeply embedded hairs, as this can cause injury and scarring. Consulting a dermatologist is advisable if the ingrown hair persists or becomes painful.
Topical Treatments
Applying medications can reduce inflammation and promote healing:
Steroid Creams: Over-the-counter or prescription steroid creams can reduce redness and swelling.
Topical Retinoids: These accelerate skin cell turnover, helping to free trapped hairs. Use them cautiously and under medical supervision, especially during pregnancy.
Antibiotic Creams or Washes: For cases with signs of infection, antibiotics may be prescribed by a healthcare professional.
When to See a Doctor
Persistent or painful ingrown hairs that do not improve with home treatment should be evaluated by a healthcare provider. In some cases, professional removal or prescription medication may be necessary to prevent complications such as infections or scarring.
Long-Term Prevention Strategies
To reduce the likelihood of future ingrown hairs, consider these long-term strategies:
Switch to less irritating hair removal methods such as laser or electrolysis treatments.
Use gentle, non-irritating shaving products and tools.
Maintain a consistent skincare routine that includes regular exfoliation and hydration.
Avoid aggressive plucking or squeezing skin bumps.
Final Thoughts
Managing and preventing ingrown hairs requires a combination of proper grooming habits, skin care routines, and, when necessary, professional medical intervention. By understanding the causes and adopting preventive measures, you can enjoy smoother, healthier skin free from irritation and discomfort. Persistent issues should not be ignored; consulting with skincare specialists or dermatologists ensures effective and safe treatment options tailored to your skin type and condition.