Comprehensive Guide to Managing and Treating Trigger Finger Effectively
Trigger finger is a common hand condition characterized by inflammation of tendons, causing pain and restricted movement. Early diagnosis and a combination of conservative treatments, including medication, physical therapy, and injections, can effectively manage symptoms. Severe cases may require surgical intervention. Preventive measures like ergonomic adjustments and hand exercises are essential for long-term health. This comprehensive guide offers detailed insights into managing trigger finger to restore hand function and prevent recurrence, emphasizing timely medical consultation for optimal outcomes.
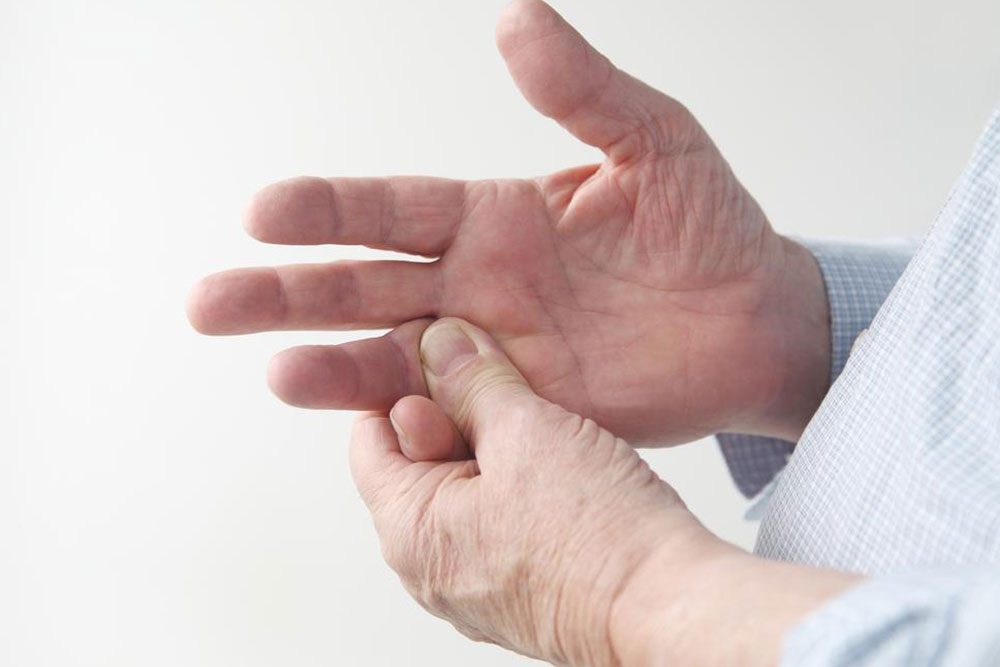
Comprehensive Strategies for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Trigger Finger
Trigger finger, medically known as stenosing tenosynovitis, is a common condition affecting the tendons in the fingers and thumbs, leading to pain, stiffness, and difficulty in movement. This condition arises when the tendons that facilitate finger movement become inflamed or swollen, causing a catching or locking sensation. The severity of trigger finger can vary from mild discomfort to significant impairment in hand function. Proper understanding of its causes, symptoms, and available treatment options is essential for effective management.
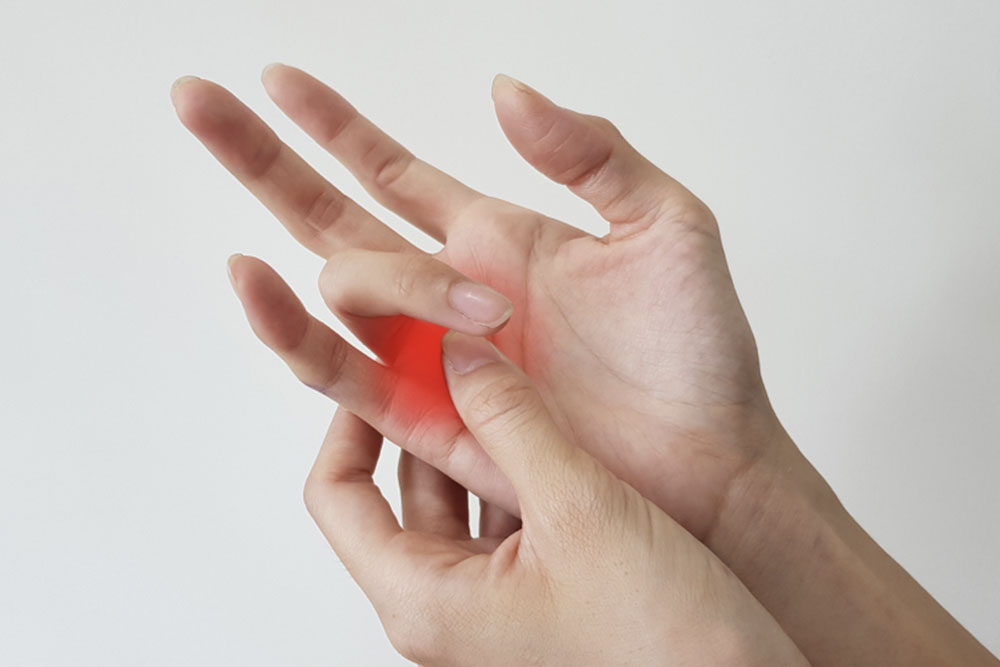
Persistent discomfort or pain at the base of the finger or thumb
Strengthening or catching sensations during finger movement
Audible popping or clicking sounds when moving the fingers or thumb
Limited range of motion, difficulty in straightening or bending fingers
Trigger finger often affects individuals who perform repetitive gripping or grasping motions, such as musicians, manual workers, or athletes. It is also more prevalent among people with underlying health conditions, like arthritis, diabetes, gout, or rheumatoid arthritis, which predispose them to tendon inflammation. Recognizing the early signs of trigger finger allows for timely intervention, preventing progression to more severe stages.
Diagnosis of Trigger Finger
Diagnosis typically involves a thorough physical examination, where a healthcare provider assesses the affected finger’s movement, swelling, and clicking sensations. Sometimes, imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI may be used to confirm inflammation or thickening of the tendons.
Effective Treatment Strategies for Trigger Finger
Managing trigger finger requires a combination of conservative measures, medical interventions, and in some cases, surgical procedures. Each treatment approach is tailored to the severity of the condition, patient health, and lifestyle considerations.
1. Conservative Treatments
Most cases of trigger finger respond well to conservative management, especially when diagnosed early. These strategies aim to reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and improve finger mobility.
**Rest and Immobilization:** Avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms and using splints or braces to immobilize the finger or thumb can decrease tendon irritation and facilitate healing.
**Ice and Heat Therapy:** Applying ice packs helps reduce swelling and inflammation, especially during acute phases. Heat therapy can relax muscles and improve blood flow during recovery periods.
**NSAIDs:** Over-the-counter non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen, naproxen, or aspirin can alleviate pain and decrease inflammation in tender tendons.
**Stretching and Strengthening Exercises:** Specific hand exercises prescribed by a physical therapist help increase flexibility, strengthen tendons, and prevent recurrence.
2. Medical Interventions
If conservative treatments do not produce sufficient relief, more targeted medical procedures may be necessary. These include:
**Corticosteroid Injections:** Administered directly into the tendon sheath, corticosteroid injections significantly reduce inflammation and swelling, often providing relief for several months or longer.
**Percutaneous Release:** A minimally invasive procedure where a healthcare provider uses a needle or small instrument to release the constricted tendon, providing quick symptom relief with minimal recovery time.
3. Surgical Options
When non-invasive treatments fail or if the condition is severe, surgical intervention might be the best course of action. The goal of surgery is to release the pulley constricting the tendons, allowing smooth movement. Types of surgical procedures include:
**Open Release Surgery:** The most common form, involving a small incision over the affected area to cut the pulley and free the tendons.
**Percutaneous Release:** Similar to the injection method but using a needle or small blade to release the pulley without a large incision.
Postoperative recovery generally involves brief immobilization followed by physical therapy to restore movement and strength. Most patients experience immediate relief after surgery and can return to normal activities within a few weeks.
Prevention and Long-Term Management
Preventing trigger finger involves reducing repetitive strain and maintaining hand health. Regular breaks during activities involving gripping, ergonomic modifications at workstations, and exercises to strengthen hand muscles can help prevent recurrence. Managing underlying health conditions like diabetes and arthritis is also crucial in minimizing risk factors.
Summary
Trigger finger is a prevalent condition that can significantly impair daily activities if left untreated. Early diagnosis and intervention through conservative treatments can lead to excellent outcomes, while persistent or severe cases may require surgical correction. Consulting with a healthcare provider specialized in hand and wrist conditions ensures personalized treatment planning for optimal recovery and long-term hand health.





