Effective Strategies for Managing Acid Reflux through Diet and Lifestyle Changes
This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies for managing acid reflux through dietary and lifestyle modifications. It covers common symptoms, useful habits, foods to include or avoid, and additional factors that influence the condition. Implementing these practical tips can significantly reduce reflux symptoms, improve quality of life, and prevent progression to GERD. Whether through small lifestyle changes or dietary adjustments, individuals can take proactive steps toward better digestive health with this detailed, actionable information.

Effective Strategies for Managing Acid Reflux through Diet and Lifestyle Changes
Comprehensive Approaches to Alleviate Acid Reflux Symptoms with Dietary Modifications and Lifestyle Adjustments
Acid reflux, a common digestive disorder, occurs when stomach acids or bile flow back into the esophagus, causing irritation and discomfort. When this condition happens more than twice weekly, it may develop into gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), which requires more targeted intervention. Typical symptoms include a burning sensation in the chest, often called heartburn, especially after eating, and these symptoms tend to worsen when lying down or bending over.
Addressing acid reflux effectively involves a combination of lifestyle changes and dietary modifications. While over-the-counter and prescription medications can be prescribed by healthcare professionals to manage severe cases, many individuals find significant relief by adopting certain habits and dietary patterns. Some conditions, such as hiatal hernia—where a part of the stomach pushes above the diaphragm—can worsen reflux symptoms, making lifestyle management critical alongside medical treatment. This comprehensive guide explores practical solutions, dietary tips, and lifestyle strategies to help you control and reduce acid reflux symptoms naturally and safely.
Recognizable symptoms of acid reflux include:
Persistent burning chest pain that may radiate to the throat or jaw
Frequent burping and belching
Regurgitation of bitter-tasting acid or food
Bloating, nausea, and discomfort after meals
Difficulty swallowing or feeling like food is stuck in the throat
Dark stools or vomiting blood, which indicate complications
Persistent cough, sore throat, or laryngitis
Unintentional weight loss and wheezing
Can lifestyle and dietary modifications effectively manage acid reflux? The answer is yes. Making informed changes to daily habits and eating patterns can significantly reduce symptoms and improve quality of life. Here are key strategies:
Cease smoking, as tobacco increases acid production and impairs esophageal sphincter function
Eat smaller, more frequent meals instead of large portions to prevent overfilling the stomach
Avoid eating within two to three hours before bedtime to reduce nighttime reflux
Maintain an upright position after meals; avoid lying down immediately after eating
Wear loose-fitting clothing around the waist and abdomen to reduce pressure on the stomach
Elevate the head of your bed by 4-6 inches to prevent acid from traveling back into the esophagus during sleep
Lose weight if overweight or obese, through a combination of a balanced diet and regular exercise, since excess weight can increase abdominal pressure
Consult with healthcare professionals for personalized medication plans if symptoms persist or worsen
Foods that can help alleviate acid reflux symptoms include:
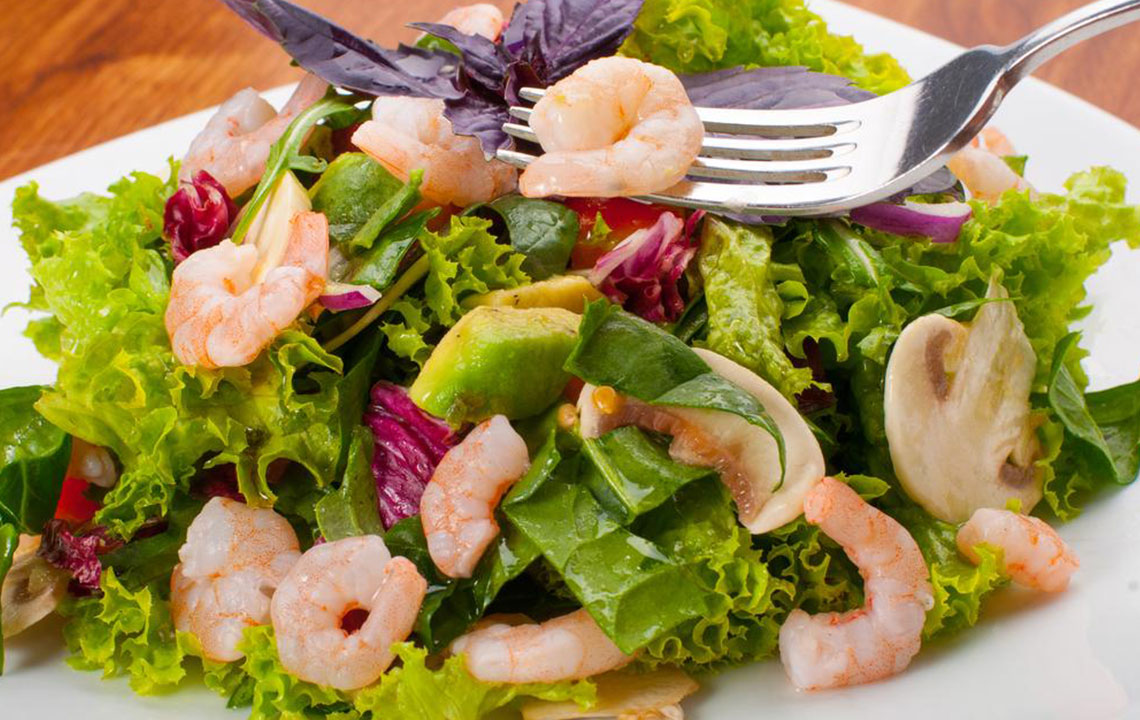
Vegetables that are low in fat and sugar, such as leafy greens, broccoli, and carrots
Ginger, which exhibits natural anti-inflammatory properties and helps soothe the stomach
Non-citrus fruits like bananas, apples, and pears, which are less likely to trigger reflux
Oatmeal and whole grains, which absorb stomach acid and provide steady energy
Healthy fats found in nuts, seeds, olive oil, and avocados
Lean meats such as chicken, turkey, and fish, prepared without excessive fats or spices
Egg whites instead of yolks, as they are lower in fats that can provoke reflux
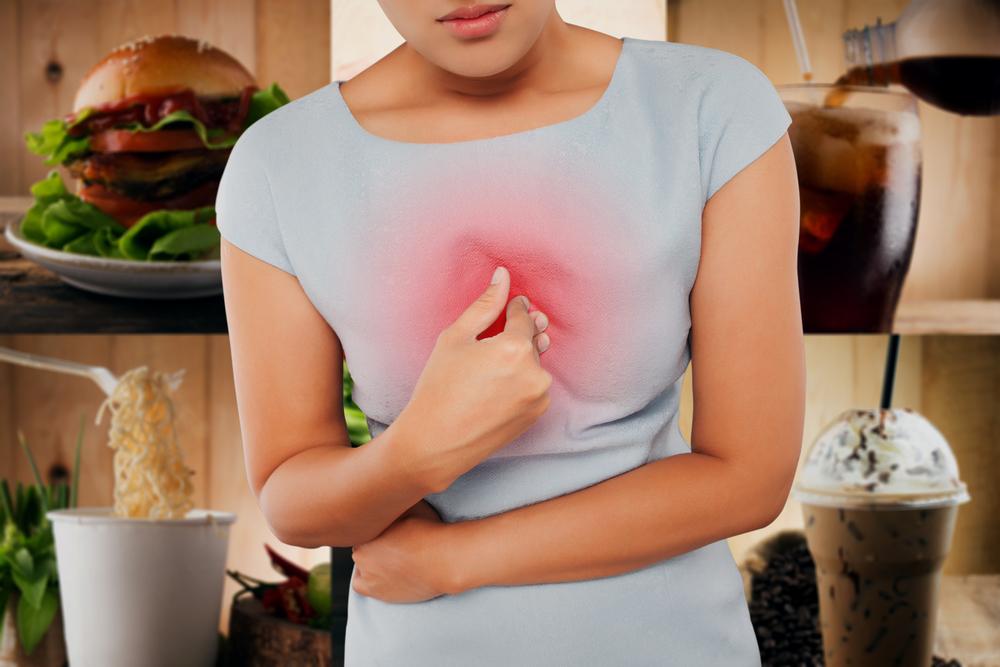
Foods and substances to avoid if you suffer from acid reflux include:
Fried foods and high-fat snacks like chips, cheese, ice cream, and fried potatoes
Pain relievers such as aspirin and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which can aggravate the esophageal lining
Spicy foods, including hot peppers and spicy sauces
Fruits and vegetables like citrus fruits, garlic, onions, pineapple, and tomatoes, which are common reflux triggers
Nitrates and processed meats such as sausages and bacon
Devitalizing drinks like alcohol, citrus juices, soda, caffeine, and tea
Chocolate and mint, both known to relax the lower esophageal sphincter
Processed and fast foods, which are often high in unhealthy fats, preservatives, and additives
Certain medications like alpha-blockers, which can influence reflux patterns
Additional factors that influence acid reflux include:
The body position after meals; remaining upright helps reduce reflux occurrences
The type and amount of food consumed; fatty and large meals tend to trigger symptoms more often
Managing acid reflux requires a holistic approach that combines dietary habits, lifestyle adjustments, and medical support when necessary. Consistency and awareness of individual triggers are vital in maintaining long-term relief and preventing complications.