Comprehensive Guide to Ovarian Cyst Detection and Diagnosis
This comprehensive guide explores the various methods used for ovarian cyst detection, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis. It covers pelvic exams, ultrasound imaging, laparoscopy, and blood tests like CA-125, helping women and healthcare professionals understand the process of identifying ovarian cysts accurately. Early detection is key in managing ovarian health effectively, preventing complications, and ensuring suitable treatment options. Whether symptoms are present or not, understanding these diagnostic techniques empowers women to seek timely medical advice and care.

Understanding Ovarian Cyst Detection Techniques
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on or inside the ovaries, and recognizing their presence early is vital for effective management and treatment. Proper diagnosis begins with a thorough clinical evaluation, including a pelvic examination, which can sometimes detect enlarged or irregularly shaped ovaries. Additionally, understanding symptoms such as pelvic pain, bloating, or changes in menstrual patterns helps healthcare providers decide the next steps for diagnosis.
Once a suspicion of an ovarian cyst arises, doctors utilize a set of specialized tests to accurately identify its type, size, and potential risk factors. These tests are crucial not only for confirming the presence of a cyst but also for ruling out malignancy and planning appropriate treatment options. Early detection and precise diagnosis can significantly improve patient outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
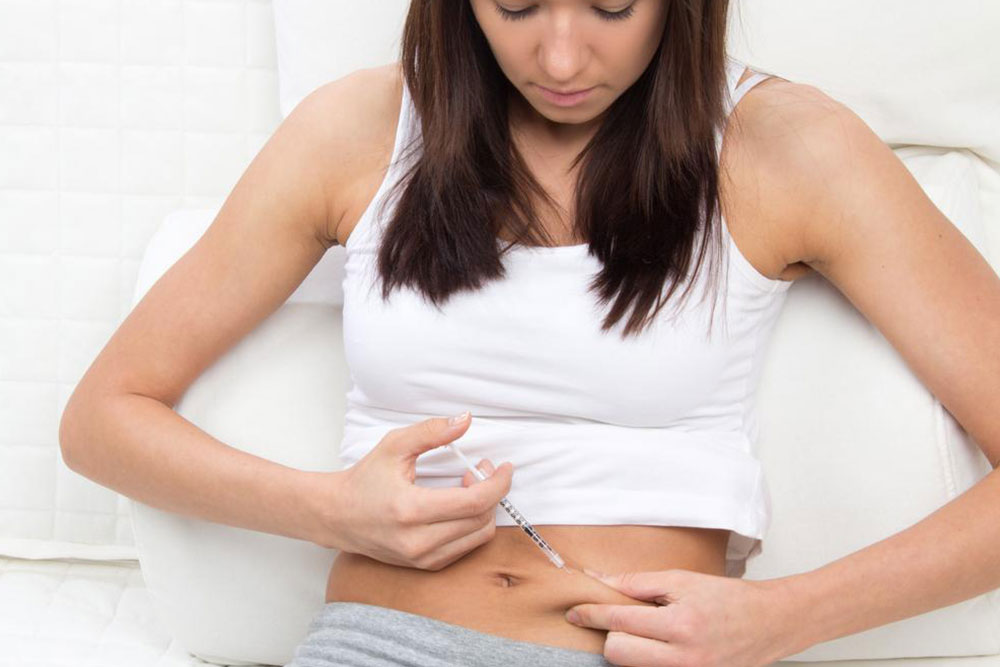
Pregnancy Testing: Despite being primarily used to confirm pregnancy, simple pregnancy tests can also help identify certain ovarian cysts, particularly corpus luteum cysts, which form after ovulation. Even in the absence of symptoms, a positive pregnancy test can hint at hormonal activities that might be linked with ovarian cyst formation.
Pelvic Ultrasound: As the cornerstone of ovarian cyst diagnosis, pelvic ultrasound provides detailed images of the ovaries and surrounding reproductive organs. This imaging modality helps determine the size, number, and nature (fluid-filled, solid, or complex) of cysts. Ultrasound can be transabdominal or transvaginal, with transvaginal ultrasound offering higher resolution and better visualization of smaller cysts.
Laparoscopy: For cases where non-invasive methods are inconclusive or when surgical intervention is needed, laparoscopy offers a minimally invasive approach. During this procedure, a thin, flexible tube with a camera (laparoscope) is inserted into the abdomen through small incisions. This allows direct visualization of the ovaries and surrounding tissues, enabling both diagnosis and treatment options like cyst removal or biopsy.
Blood Tests (including CA-125): Blood tests, especially measuring levels of the CA-125 protein, aid in evaluating the risk of ovarian cancer. Elevated CA-125 levels are common in malignant ovarian tumors but can also be seen in benign conditions like endometriosis or even large benign cysts. Therefore, this test is particularly useful for women with complex or persistent cysts, or when there are other suspicious signs.
In addition to these primary methods, additional diagnostic tools such as MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) or CT scans may be employed for complex cases. These imaging techniques help differentiate between benign and potentially malignant cysts with higher precision, offering comprehensive insights necessary for tailored treatment plans.
Overall, timely and accurate diagnosis of ovarian cysts involves a combination of clinical assessment and advanced imaging and laboratory tests. Understanding these methods ensures women receive prompt and appropriate care, reducing the risk of complications and enhancing the overall prognosis.