Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Managing Mouth Sores
Explore comprehensive insights into the causes of mouth sores, from medication effects to stress and infections. Learn how to identify, treat, and prevent ulcers effectively with practical advice and when to seek medical help for persistent or severe symptoms. Maintain optimal oral health and address underlying issues for quicker healing and better overall well-being.
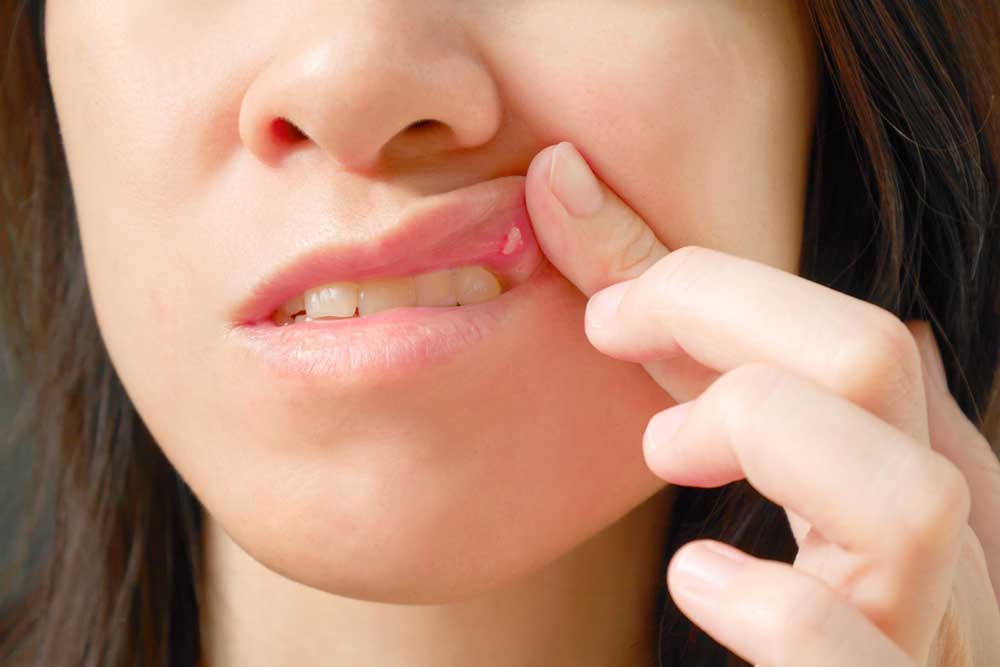
Recognizing Causes of Mouth Ulcers and Exploring Effective Treatments
Experiencing mouth sores suddenly is a common concern that many people face at some point in their lives. These lesions, often painful and uncomfortable, can be caused by various internal and external factors. While they may seem minor, mouth ulcers can sometimes indicate underlying health issues that need attention. Early identification of the root causes is essential to prevent potential complications and promote quicker healing. One of the most frequent contributors to mouth sores is poor digestive health, which can lead to inflammation within the oral cavity. In fact, various internal health concerns, such as nutritional deficiencies, immune system disorders, and chronic illnesses, can manifest as mouth ulcers. Therefore, understanding these causes and addressing them promptly is vital for maintaining overall health and well-being.
Mouth sores, also known as oral ulcers or canker sores, can appear anywhere inside the mouth, including the tongue, cheeks, gums, and the roof of the mouth. They may vary in size, appearance, and duration. Recognizing the underlying causes not only helps in effective treatment but also assists in preventing recurrence. Below, we delve into the primary causes of mouth sores and outline practical measures for managing them effectively.
Medication Side Effects
Many prescription drugs can lead to the development of mouth sores as an adverse reaction. This is often observed with medications such as antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), or certain chemotherapeutic agents. Usually, these ulcers resolve once the medication regimen is adjusted or discontinued under medical supervision. If you suspect your medication is causing mouth ulcers, consult your healthcare provider for alternative treatments or adjustments to your current prescriptions.
Oral Candidiasis (Thrush) and Poor Oral Hygiene
Fungal infections like oral thrush, characterized by a white or cream-colored coating on the tongue and inside of the cheeks, are common in individuals with compromised immune systems or poor oral hygiene. This condition often causes soreness and discomfort. Maintaining good oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups, can prevent thrush. Treatment typically involves antifungal medications prescribed by a dentist or doctor.
Stress and Physical Trauma
Emotional stress and psychological factors can weaken the immune response, making the mouth more susceptible to ulcers. Additionally, physical injuries from biting your cheeks, lip trauma, or irritation from dental appliances can cause painful sores. Such trauma-induced ulcers often heal spontaneously within one to three weeks. However, persistent or recurrent sores should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to rule out other underlying conditions.
Significance of Sore Location and Additional Symptoms
Paying close attention to the location of mouth sores can provide valuable clues about their underlying causes. For example, ulcers that appear on the sides of the tongue may be linked to stress or minor trauma, whereas sores on the roof of the mouth could indicate irritation from hot foods or beverages. Moreover, accompanying symptoms such as fever, fatigue, swollen lymph nodes, or difficulty swallowing may suggest systemic issues like infections or immune disorders. Recognizing these signs enables timely medical intervention and tailored treatment strategies.Effective management of mouth sores involves a combination of lifestyle changes, proper hygiene, and medical treatments when necessary. Avoiding spicy or acidic foods, reducing stress, maintaining good oral health, and staying hydrated can promote faster healing. In cases where ulcers persist longer than two weeks, recur frequently, or are particularly painful, consulting a healthcare provider is essential for further evaluation. Doctors may perform blood tests, biopsies, or imaging to diagnose potential underlying conditions like nutritional deficiencies, autoimmune diseases, or other systemic illnesses.
In summary, understanding the underlying causes of mouth ulcers is crucial for effective treatment and prevention. Whether caused by medications, infections, stress, or physical injury, addressing these factors promptly can lead to quicker recovery and improved oral health. Maintaining good dental hygiene, managing stress levels, and seeking medical advice for persistent symptoms are key steps in keeping your mouth healthy and free from discomfort.





