Comprehensive Guide to Causes and Effective Management of Left Breast Discomfort in Women
This comprehensive guide explores the various causes of left breast discomfort in women, emphasizing the importance of differentiating benign from serious issues such as cardiac problems and breast cancer. It offers practical advice on symptoms to watch for, when to seek immediate medical attention, and effective management strategies to ensure early diagnosis and treatment, promoting overall women’s health and well-being.

Comprehensive Understanding of Causes and Management Strategies for Left Breast Discomfort in Women
Experiencing discomfort or pain in the left breast can be a source of significant concern for women, prompting questions about its underlying causes and appropriate management. While some instances of breast discomfort are benign and easily manageable, others may signal serious health issues such as cardiac problems or breast cancer. Therefore, understanding the nuances of this condition is crucial for prompt and effective treatment. This comprehensive guide explores the possible causes of left breast discomfort in women, how to differentiate between benign and serious issues, and recommended steps for management and timely medical intervention.
Understanding the Significance of Location and Symptoms
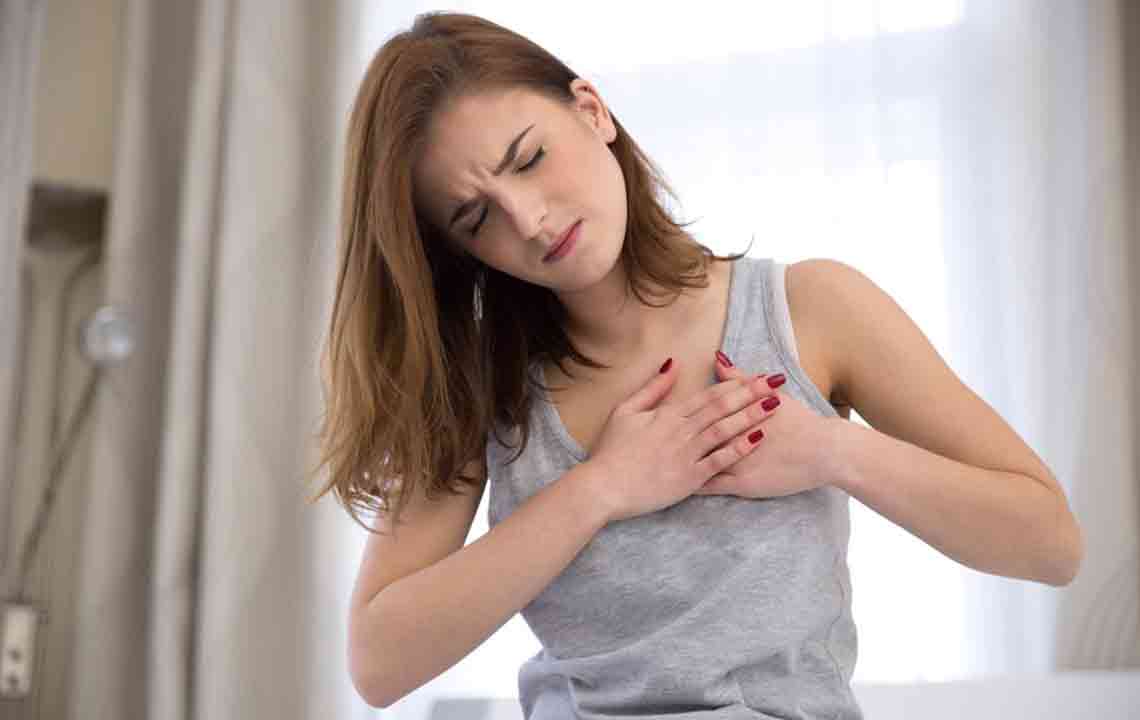
Breast discomfort can vary significantly based on its location, intensity, and associated symptoms. When discomfort occurs on the left side, it’s especially important to discern whether it could be linked to heart health concerns. Key symptoms that suggest cardiac issues include a sensation of pressure or squeezing in the chest, pain radiating down the arm, jaw, or neck, along with shortness of breath, nausea, excessive sweating, feelings of anxiety or panic, and light-headedness. If such symptoms are present, immediate medical attention is necessary, as these could indicate a heart attack or other serious cardiovascular conditions.
In contrast, if the pain is localized within the breast tissue, beneath the breast, or around the chest wall, and no associated heart symptoms are observed, the root cause may lie in benign conditions. Recognizing the nature of pain—is it sharp, dull, constant, or intermittent?—can provide clues about its origin. For instance, sharp, localized pain might stem from muscle strain or nerve issues, whereas dull, persistent discomfort could be linked to hormonal fluctuations or tissue inflammation.
Common Causes of Left Breast Discomfort
Various factors contribute to breast discomfort, and some are benign, while others require immediate medical attention. Here are some common causes:
Benign Breast Conditions: Conditions like fibrocystic breast changes, where tissue develops lumps or cysts mistaken for tumors, are common. These changes often fluctuate with the menstrual cycle and cause cyclical pain. Breast infections (mastitis) can also cause localized pain and redness.
Hormonal Fluctuations: Sudden shifts in hormones during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause can lead to swelling and tenderness in the breast tissue.
Previous Surgeries or Trauma: Scars, tissue damage, or injury to the chest or breast area might result in chronic discomfort.
Gastrointestinal Issues: Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or esophageal spasms may produce chest pain that mimics breast discomfort.
Musculoskeletal Problems: Muscle strains, costochondritis (inflammation of the cartilage connecting the ribs to the breastbone), or nerve compression can cause chest and breast pain.
Pneumonia or Respiratory Infections: These can cause chest pain radiating to the breast, often accompanied by cough and fever.
Serious Conditions: Breast cancer, particularly if a new lump is detected, persists, or is associated with other symptoms like nipple changes or skin alterations, must be excluded or diagnosed early for effective treatment.
Assessing and Differentiating Causes
To determine the cause of left breast discomfort, consider the timing, nature of pain, and associated symptoms:
Is the pain cyclical, worsening before menstruation, or more constant?
Are there any visible changes like skin dimpling, nipple discharge, or lumps?
Does the pain radiate to other regions, or is it localized?
Are you experiencing systemic symptoms such as fever, weight loss, or night sweats?
Keeping track of these details can aid healthcare providers in diagnosis and tailoring appropriate testing, which may include physical examination, imaging such as mammography or ultrasound, blood tests, or biopsy if necessary.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
While many causes of breast discomfort are benign, some require urgent care. Consult a healthcare professional promptly if you experience:
Severe chest pain or pressure, especially if radiating to the arm, neck, or jaw
Shortness of breath, dizziness, or loss of consciousness
Persistent or worsening pain in the breast, especially if associated with lumps or skin changes
Unexplained nipple discharge, especially if bloody
Fever accompanied by redness or swelling in the breast area
Management and Preventive Measures
The management of left breast discomfort depends on its underlying cause. Here are some general strategies:
Regular Monitoring: Routine breast self-exams and awareness of changes help in early detection of abnormalities.
Medical Evaluation: Seek professional assessment for persistent or suspicious symptoms. Diagnostic imaging and tests help confirm diagnoses.
Medication and Lifestyle: Hormonal treatments for menstrual-related discomfort, pain relievers, and antibiotics for infections may be prescribed.
Addressing Underlying Conditions: Managing reflux, muscle strains, or other systemic issues reduces associated chest discomfort.
Preventive Care: Maintain a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and avoid smoking to improve overall breast and cardiac health.
Early Detection and Its Importance
Early detection of serious conditions such as breast cancer significantly improves prognosis. Regular screenings like mammograms, especially for women over 40, are vital. Any new, persistent, or unusual breast symptoms should prompt a consultation with a healthcare provider. Timely diagnosis and intervention can prevent complications and facilitate effective treatment.
Conclusion
Left breast discomfort in women encompasses a broad spectrum of causes, ranging from benign hormonal changes and musculoskeletal issues to potentially life-threatening conditions like cardiac problems and breast cancer. Recognizing symptoms, differentiating between benign and serious issues, and seeking prompt medical care are essential steps toward effective management. Understanding your body and maintaining regular health checkups can help detect issues early and ensure peace of mind. Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment plans tailored to your specific health circumstances.