Comprehensive Guide to Causes and Effective Strategies for Relieving Abdominal Bloating
Abdominal bloating is a common issue caused by various factors, including digestive disorders, fluid retention, and food sensitivities. This comprehensive guide explores the main causes of bloating, practical home remedies, and when to seek medical help. By understanding these factors, individuals can implement effective lifestyle changes to alleviate discomfort and improve digestive health, ensuring a better quality of life. The article emphasizes the importance of medical consultation for persistent or severe symptoms to rule out serious underlying conditions.

An In-Depth Look at Causes and Practical Solutions for Managing Abdominal Bloating
Experiencing a swollen or distended stomach is a common concern for many people, often accompanied by discomfort, pain, or a feeling of fullness. This condition, medically termed as abdominal bloating, can stem from various minor to serious health issues. While some cases are harmless and can be treated with simple lifestyle changes at home, persistent or severe bloating warrants medical attention to diagnose underlying causes accurately. Understanding the root causes of bloating is the first step towards effective management and relief.
This detailed guide explores the primary causes of abdominal bloating, practical remedies, lifestyle adjustments, and when to seek professional medical help. Whether your bloating is occasional or chronic, gaining insights into its causes can help mitigate discomfort and improve your digestive health.
Understanding the Major Causes of Abdominal Bloating
Digestive Disorders and Conditions
Conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), ulcerative colitis, and celiac disease are well-known for causing abdominal distension. Studies have shown that a significant portion of IBS sufferers experience symptoms like bloating, causing both physical discomfort and disruption to daily life. These digestive conditions alter normal gut motility and contribute to excess gas formation, leading to a swollen belly.
Fluid Retention and Ascites
Fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity, often referred to as ascites, can cause noticeable puffiness and discomfort. This condition may signal underlying health issues, including liver disease, infections, or even certain types of cancers. Ascites requires medical evaluation and management to address its root cause effectively.
The Role of Hydration and Dehydration in Bloating
Interestingly, inadequate water intake can paradoxically contribute to bloating by slowing down the digestive process. Proper hydration is crucial for maintaining optimal digestion, preventing constipation, and reducing gas buildup.
Constipation and Its Impact
When stool accumulates in the intestines, it causes the abdomen to become hard, swollen, and often painful. Factors like low fiber consumption, dehydration, and sedentary lifestyle contribute significantly to constipation, which in turn exacerbates bloating.
Food Sensitivities, Allergies, and Bloating
Certain foods such as dairy products, gluten, and specific types of carbohydrates can trigger gas production and bloating in sensitive individuals. Lactose intolerance and food allergies are common culprits. An elimination diet or food diary can help identify problematic foods and reduce bloating episodes.
SIBO (Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth)
Overgrowth of bacteria in the small intestine causes fermentation of foods, producing excess gas and resulting in bloating, flatulence, and discomfort. SIBO can be triggered by antibiotics, inflammation, or motility disorders, requiring targeted treatment.
Infections and Inflammatory Conditions
Gastrointestinal infections or inflammation of the pelvic organs can lead to swelling, fluid accumulation, and bloating. These conditions tend to be associated with other symptoms such as diarrhea, fever, or pain, and necessitate prompt medical attention.
Intestinal Blockages and Their Consequences
Tumors, scar tissue, or hernias can obstruct the intestines, leading to severe bloating, pain, nausea, and constipation. Medical emergencies, intestinal obstructions require immediate intervention to prevent serious complications or life-threatening situations.
Hormonal Fluctuations and Bloating
Hormonal changes during menstruation or pregnancy often cause fluid retention and slowed digestion, resulting in temporary bloating. Women may notice this symptom recurring cyclically, but persistent bloating may involve underlying issues such as fibroids or hormonal imbalances that need medical assessment.
Potential Indicators of Serious Conditions like Cancer
Although rare, persistent and unexplained bloating should not be ignored, as it could indicate ovarian, colon, or other cancers. If bloating persists despite lifestyle changes and treatment, consulting a healthcare provider for early diagnosis is critical.
Effective Home Remedies and Lifestyle Adjustments
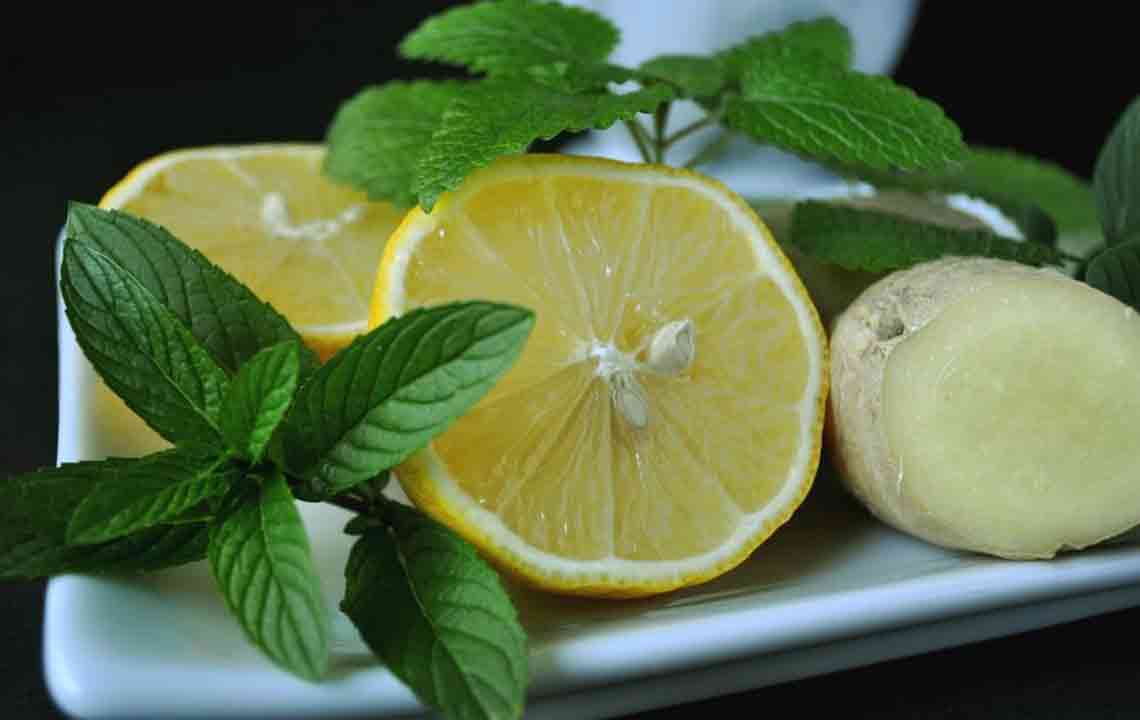
The good news is that many cases of abdominal bloating can be alleviated through simple at-home strategies and lifestyle modifications. Keeping a detailed food journal can help identify specific triggers. Incorporating digestive-friendly foods such as ginger, peppermint, and chamomile tea can promote digestion and reduce gas. Applying heat to the abdomen with a heating pad can relax muscles and ease discomfort. Staying well-hydrated with adequate water intake facilitates smooth digestion and prevents constipation.
Over-the-counter medications, including anti-gas remedies and mild laxatives, can be helpful in managing occasional bloating and constipation. However, if symptoms worsen or last longer than a few days, it is essential to seek medical advice for proper diagnosis and treatment.
In summary, while abdominal bloating can be uncomfortable and disruptive, understanding its causes and applying effective remedies can provide relief. Maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and monitoring symptoms are key steps to a healthier digestive system. Persistent or severe bloating should always be evaluated by a healthcare professional to rule out underlying health conditions and ensure proper treatment.