Comprehensive Guide to Supporting a Family Member Through Illness: Practical Tips and Emotional Care
Supporting a family member during illness requires emotional resilience, effective communication, and self-care. This comprehensive guide offers practical tips for caregivers, highlighting their crucial role in patient wellbeing while emphasizing the importance of maintaining their mental and physical health. From managing responsibilities to seeking professional help, learn how to navigate the challenges of caregiving and foster a supportive environment that encourages recovery and personal growth for both patients and caregivers.

Supporting a Family Member Through Illness: A Complete Guide
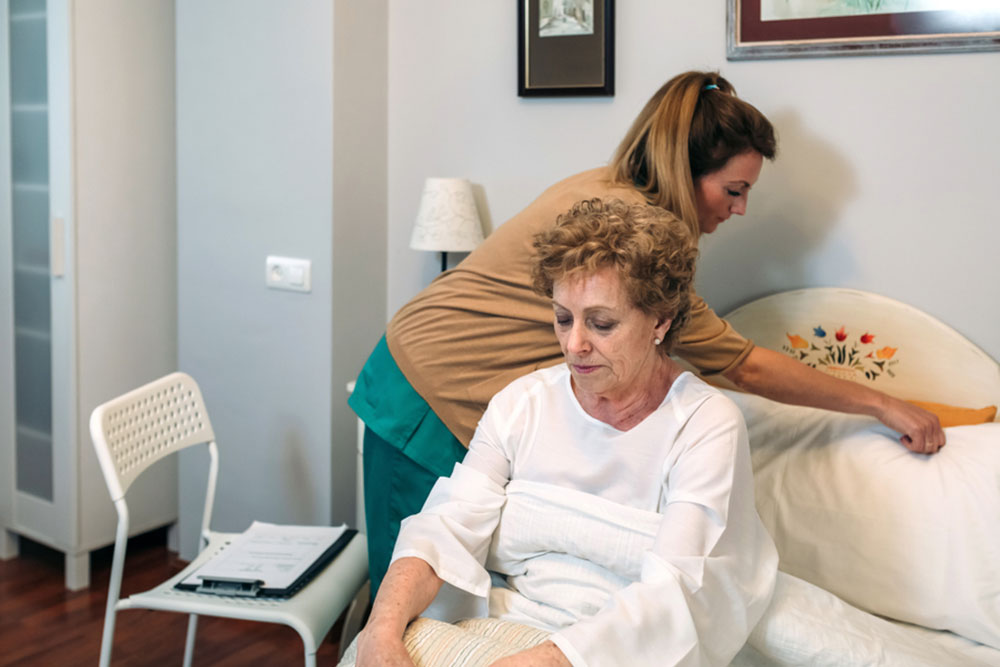
In today’s healthcare landscape, an increasing number of patients with chronic illnesses, including cancer, are opting for or needing to receive treatment at home. Advances in medical technology and a shift toward outpatient care have significantly reduced hospital stays, making home-based care more common and accessible. This trend emphasizes the vital role of family members and loved ones who step into caregiver roles, providing essential physical, emotional, and logistical support to patients during their recovery or ongoing treatment cycles.
As survival rates improve for many diseases, particularly cancer, the demand for at-home care is likely to rise. This shift not only impacts patients but also transforms the caregiving responsibilities of family members, who often find themselves navigating complex medical routines, emotional challenges, and logistical hurdles to ensure their loved ones receive proper care and attention.
The Vital Role of Family Caregivers
Cancer treatments and other illnesses often bring a rollercoaster of emotions and uncertainty. Caregivers must stay resilient and adaptable to support their loved ones through unpredictable periods.
The dynamics within families can be affected as caregiving responsibilities might shift relationships and roles, sometimes leading to emotional strain or conflicts.
Providing continuous care can lead to feelings of being overwhelmed, especially when caregivers juggle multiple responsibilities without adequate support.
Financial burdens associated with ongoing treatment—such as medication costs, therapy sessions, and transportation—can add considerable stress, particularly if the patient or caregiver is unable to work regularly.
The caregiving role often demands a significant investment of time, which can limit social interactions, hobbies, and personal pursuits.
Personal relaxation or self-care may be sacrificed, increasing vulnerability to emotional exhaustion and burnout.
Constant vigilance and availability—day and night—are often necessary, which can lead to physical fatigue and emotional strain.
Feelings of guilt or inadequacy may surface if caregivers perceive their efforts as insufficient or worry about neglecting other family members or responsibilities.
The Integral Role of Caregivers in Healthcare Teams
Family caregivers often work closely with healthcare professionals to coordinate care and ensure treatment adherence.
Managing medication schedules and monitoring side effects become part of their routine responsibilities.
Effective communication with medical teams keeps everyone informed about the patient’s progress and concerns.
Organizing appointments, tests, and treatment milestones ensures continuous and effective care delivery.
Caregivers also serve as advocates during medical consultations, helping to understand complex medical information and making informed decisions.
Self-care Strategies for Caregivers
Prioritizing physical health through proper nutrition, exercise, and regular medical checkups is essential.
Mental well-being should not be neglected; engaging in relaxing activities or mindfulness practices can help reduce stress.
Sharing responsibilities with other family members or trusted friends can distribute the workload more evenly.
Setting aside at least 15 to 30 minutes daily for personal relaxation or hobbies can mitigate exhaustion.
Managing personal affairs—such as finances, transportation, and household chores—helps reduce daily stress.
Attempting new activities, seeking emotional support from peer groups, or counseling can enhance resilience and emotional health.
Recognizing When to Seek Professional Support
Caregivers experiencing persistent stress, depression, anxiety, or burnout should seek mental health support promptly.
Symptoms of severe emotional distress—such as feelings of hopelessness, anger, or thoughts of self-harm—necessitate urgent intervention.
If dependency on alcohol, drugs, or other substances as coping mechanisms occurs, it’s critical to seek professional help.
Relationship conflicts or communication breakdowns within the family should also be addressed with the help of therapists or counselors.
Prioritizing self-care is vital; caregivers must remember their health and well-being are essential to effectively support their loved ones.
The Benefits of Compassionate Caregiving
Effective caregiving significantly improves the patient’s quality of life by providing comfort, companionship, and practical support.
Engaging in caregiving fosters a deep sense of purpose and personal fulfillment, offering emotional rewards that can uplift caregivers’ spirits.
Caregiving often strengthens family bonds, creating opportunities for shared experiences, mutual understanding, and emotional growth.
Creating a nurturing and respectful environment promotes compassion, patience, and empathy—all vital in healing and recovery processes.
Remember, balancing the act of caring for loved ones with self-care is essential for sustained support and personal health. Nurturing oneself enables caregivers to provide more effective and compassionate care, ultimately benefiting everyone involved.