Comprehensive Natural Approaches to Regulate PSA Levels and Promote Prostate Health
This comprehensive article explores natural methods to effectively manage PSA levels and support prostate health. It covers essential dietary strategies, lifestyle tips, and the importance of regular screenings to prevent prostate issues such as benign hyperplasia and cancer. Learn how to incorporate prostate-friendly foods like tomatoes, broccoli, and green tea into your diet, while avoiding harmful habits. Empower yourself with knowledge to promote long-term male reproductive health through natural approaches and early detection measures for a healthier future.

Effective and Natural Strategies to Manage PSA Levels for Better Prostate Health
Understanding PSA Levels and How to Manage Them Naturally
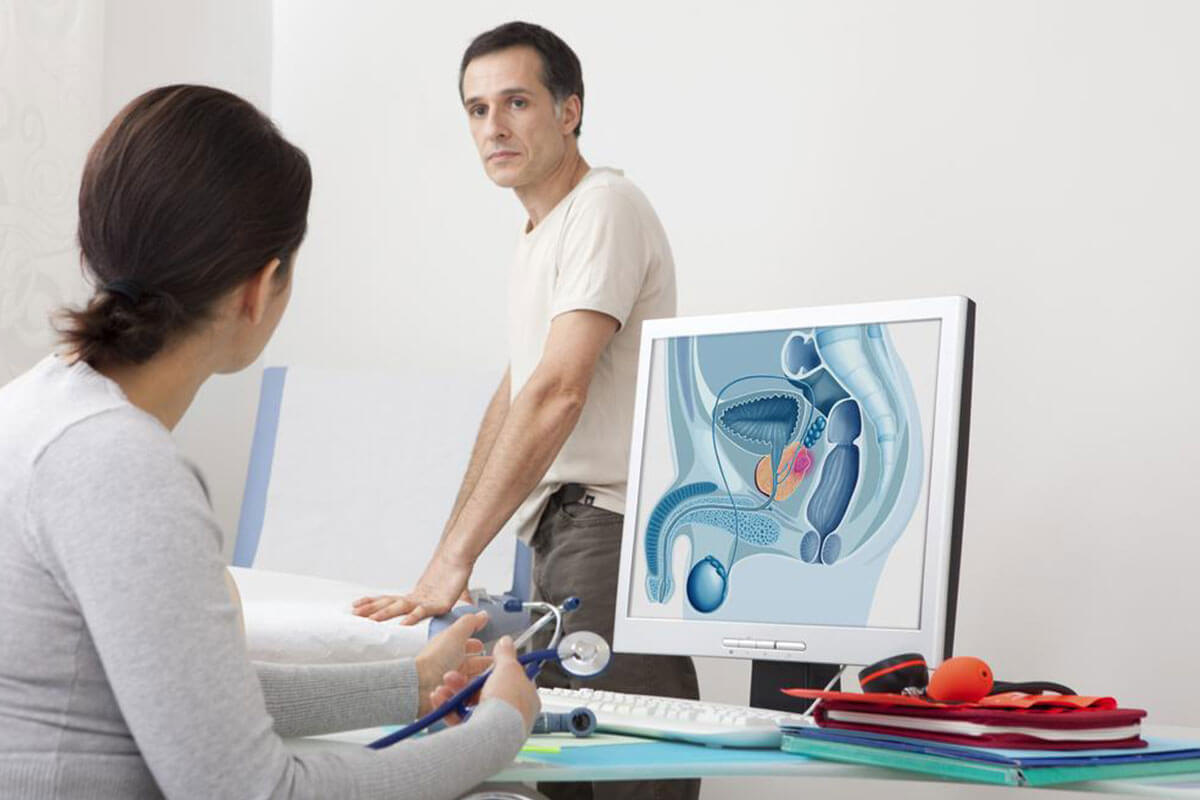
The prostate is a vital gland in the male reproductive system, situated just below the bladder and surrounding the urethra. Its primary role is to produce seminal fluid, which nourishes and protects sperm. As men age, the prostate naturally enlarges—a condition known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)—which may lead to urinary difficulties and other health concerns. Additionally, abnormal prostate growth and hardening can increase the risk of developing prostate cancer, one of the most prevalent types of cancer affecting men globally and a leading cause of male mortality.
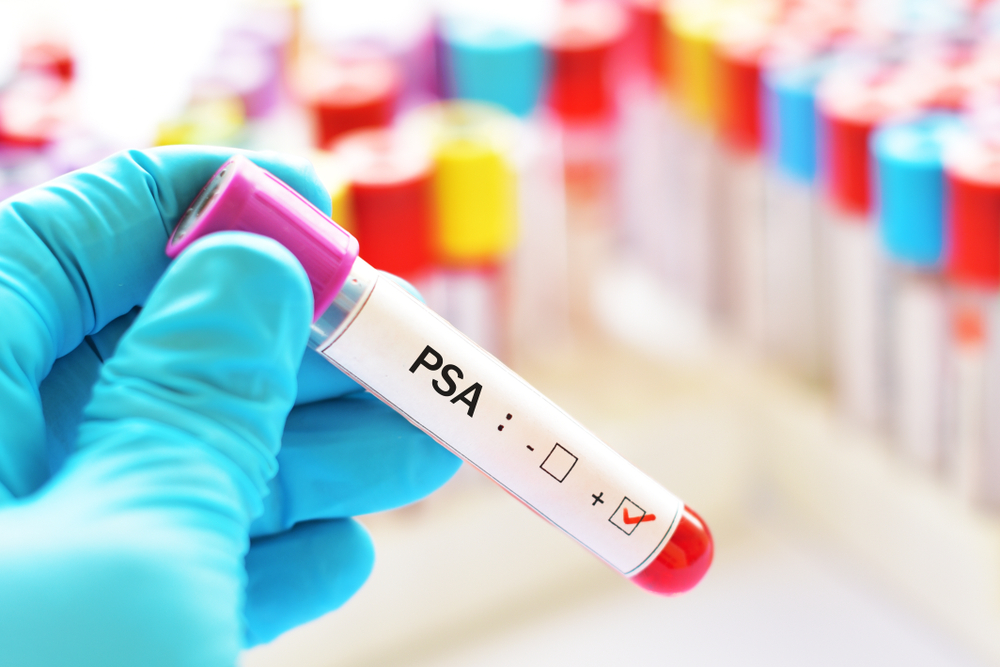
Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is a protein produced by prostate tissues, which normally enters semen and remains at low levels in the bloodstream. The PSA blood test measures the concentration of this antigen, providing valuable insights into prostate health. An elevated PSA level can indicate prostate inflammation, enlargement, or potential malignancy, but it does not confirm cancer on its own. Various factors, including age, family history, ethnicity, urinary infections, and recent activities like ejaculation or prostate exams, can influence PSA readings. Generally, PSA levels of 4.0 ng/ml or less are considered normal, although these thresholds may vary based on racial and age differences. Elevated PSA levels often prompt further diagnostic procedures such as biopsies, digital rectal exams (DRE), or imaging tests to determine the underlying cause.
It's important to understand that PSA levels tend to increase gradually with age. Thus, a higher PSA in older men may be normal; however, significant increases may warrant concern. Importantly, the PSA test alone cannot definitively diagnose prostate cancer, as some men with low PSA levels may still have cancer, and vice versa. Therefore, PSA screening should be complemented by other assessments and a thorough medical evaluation.
Beyond medical interventions, lifestyle and dietary modifications can play a crucial role in managing PSA levels naturally and supporting prostate health. Incorporating specific foods and avoiding harmful substances can influence PSA levels and overall prostate wellbeing.
Here are some proven dietary strategies to help lower PSA levels and promote prostate health:
Consume a diet rich in fruits and vegetables: Foods rich in lycopene, zinc, and L-lysine can help inhibit dihydrotestosterone (DHT) production, reduce inflammation, and support prostate tissue regeneration. Emphasize colorful fruits, leafy greens, and cruciferous vegetables.
Eat tomatoes and tomato-based products: Tomatoes are an exceptional source of lycopene, especially when cooked or processed, which enhances bioavailability. Regular consumption can help prevent prostate cancer progression.
Include pomegranates: Packed with antioxidants, pomegranates may slow tumor growth and reduce inflammation related to prostate issues.
Focus on cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, cabbage, and cauliflower: These contain sulfur compounds that can decrease PSA production and activate tumor suppressor genes, contributing to prostate detoxification.
Drink green tea: Known for its polyphenolic compounds, green tea can combat cancer cell proliferation and aid in lowering PSA levels over time.
Incorporate soy products: Soybeans and soy-derived foods are rich in protein and contain isoflavones that can decrease DHT levels, lowering the risk of prostate cancer development.
Conversely, it is advisable to limit or avoid foods and habits that may contribute to prostate health deterioration. These include excessive red meat consumption, high-fat dairy products, processed foods high in sugars and additives, and excessive alcohol intake.
By making informed dietary choices, maintaining an active lifestyle, and scheduling regular PSA screenings, men can significantly improve their chances of early detection and effective management of prostate health issues. Early intervention often yields better outcomes, reducing the risk of advanced prostate disease and improving overall quality of life.