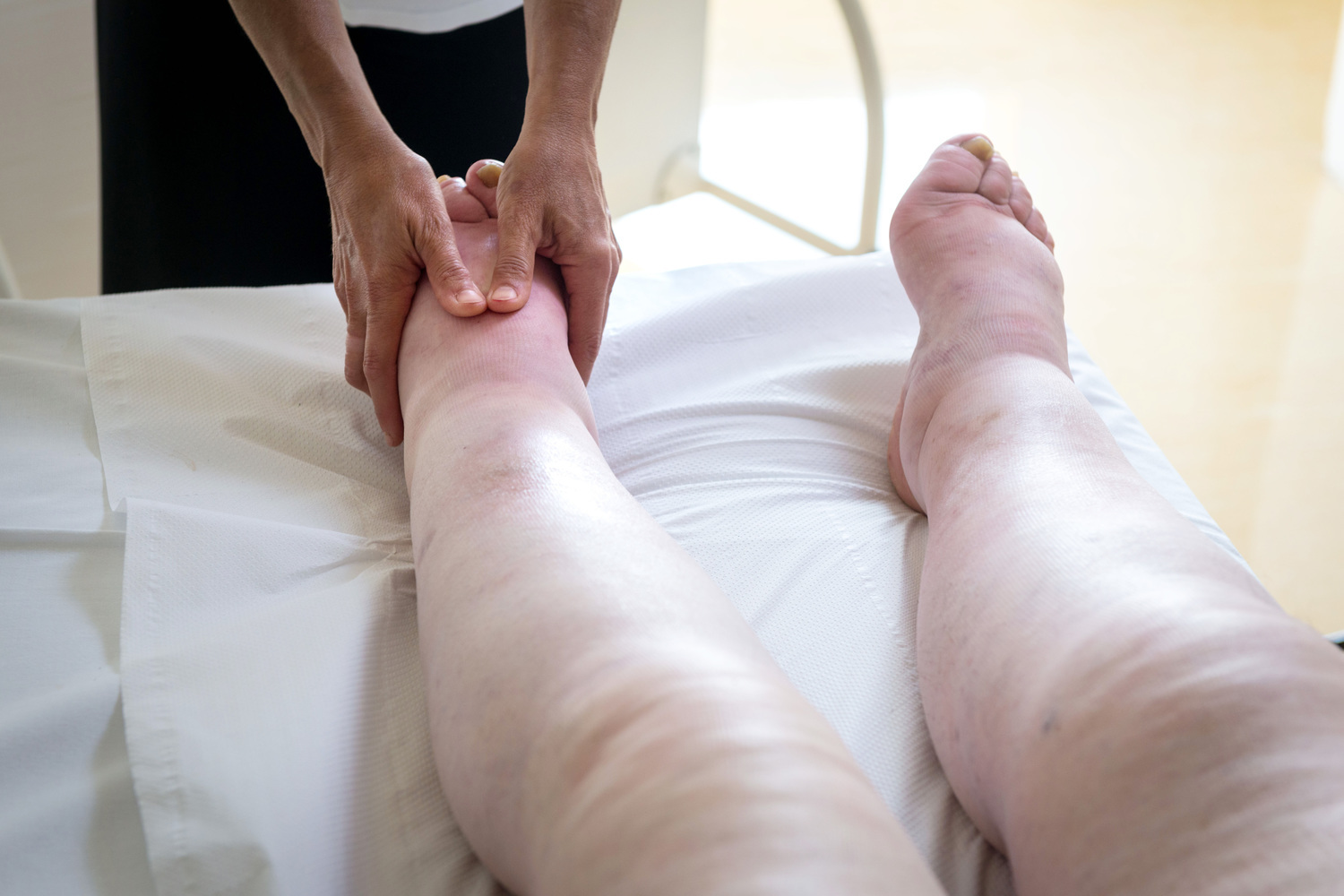
Comprehensive Guide to Swollen Feet and Ankles: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Remedies
Swollen feet and ankles are common but can indicate underlying health issues such as pregnancy, infections, cardiovascular problems, or injuries. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and effective remedies is essential for proper management. This comprehensive guide explores various causes, preventive tips, and treatment options to help you address swelling effectively and improve your overall well-being.
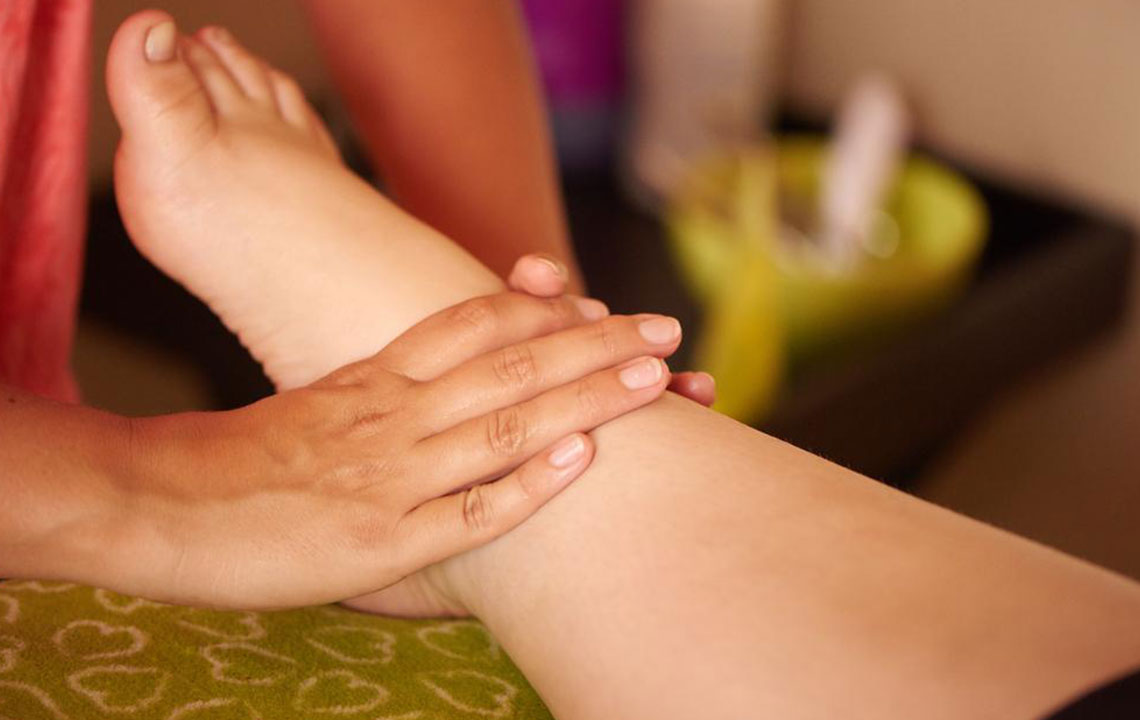

Understanding the Common Causes Behind Swelling in Feet and Ankles
Foot and ankle swelling is a frequent concern that can significantly impact daily life, causing discomfort, pain, and limited mobility. Since these regions bear much of the body's weight and are vital for movement and stability, any inflammation or swelling warrants careful attention. Recognizing the underlying causes of swollen feet and ankles is crucial for effective treatment and relief. If you experience persistent or severe swelling, consulting a healthcare professional is recommended to determine the appropriate course of action.
What Causes Feet and Ankle Swelling?
Swelling in the feet and ankles can result from a wide range of health conditions, injuries, or lifestyle factors. Understanding these causes can help in managing symptoms effectively. Below are some of the most common reasons why your feet and ankles might swell:
Pregnancy and Fluid Retention
During pregnancy, especially in the later stages, hormonal changes and increased blood volume can lead to fluid retention in the lower limbs. The growing uterus adds pressure on the pelvic veins, which impedes normal blood flow from the legs back to the heart. As a result, fluid accumulates in the feet and ankles, causing swelling, a condition known as edema. While mild swelling is typical, excessive or painful swelling should be evaluated by a healthcare provider. Additionally, if swelling is accompanied by symptoms like headaches, visual disturbances, or abdominal pain, it may suggest preeclampsia, a serious pregnancy complication requiring immediate medical attention.
Infections and Injuries
Infection is another common cause of swelling, particularly following foot injuries or wounds. People with chronic illnesses such as diabetes are at higher risk because impaired healing and circulation can exacerbate swelling. Damaged skin, blisters, or cuts may become infected, resulting in inflammation, redness, tenderness, and swelling. Regular foot inspections are vital for early detection and treatment of infections, especially for individuals with decreased sensation or neuropathy.
Cardiovascular, Kidney, and Liver Conditions
The proper regulation of body fluids heavily depends on the health of vital organs such as the heart, kidneys, and liver. When these organs are compromised, fluid balance becomes disrupted, leading to swelling, particularly in the lower extremities. Conditions like congestive heart failure cause the heart to pump inadequately, causing blood to pool and fluid to leak into surrounding tissues. Kidney failure impairs waste elimination and fluid excretion, resulting in edema. Liver diseases, such as cirrhosis, reduce the production of plasma proteins like albumin, which help maintain fluid balance, leading to fluid leakage and swelling.
Lymphedema and Venous Insufficiency
Lymphedema is a condition resulting from the disruption or blockage of the lymphatic system, leading to fluid buildup and persistent swelling. Often caused by lymph node removal during cancer treatments or infections, lymphedema requires careful management.
Venous insufficiency occurs when damaged, weakened, or blocked veins in the legs impair the normal return of blood to the heart. This leads to pooling of blood and fluids in the lower limbs, causing swelling, heaviness, and sometimes skin changes. Both conditions necessitate medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Injuries and Medication Side Effects
Traumatic injuries such as sprains, strains, fractures, or ligament tears can cause localized swelling due to inflammation, bleeding, or tissue damage. Rest, elevation, ice application, and compression are initial treatments to reduce swelling.
Some medications are known to cause fluid retention as side effects. Common culprits include hormone therapies, calcium channel blockers used for hypertension, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and certain diabetic medications. Additionally, conditions like arthritis, obesity, hypothyroidism, varicose veins, insect bites, or allergic reactions to clothing or substances can contribute to swelling.
Natural and Medical Remedies for Swelling
Managing swollen feet and ankles involves both lifestyle modifications and medical interventions. Simple at-home remedies include soaking your feet in Epsom salt baths, which can help reduce inflammation and soothe sore tissues. Elevating your legs while resting encourages proper fluid drainage back towards the upper body, alleviating swelling. Wearing compression stockings can also help promote healthy circulation.
However, persistent or worsening swelling should never be ignored. Consulting a healthcare professional is essential to diagnose underlying causes accurately and develop a personalized treatment plan. Treatments may include medication adjustments, physiotherapy, compression therapy, or addressing specific health issues such as heart, kidney, or liver problems.
In summary, swelling in the feet and ankles can stem from numerous causes, ranging from benign to serious health conditions. Recognizing the signs and seeking appropriate medical evaluation is vital for effective management and relief. Taking proactive measures, combining lifestyle changes with medical treatment, can significantly improve your quality of life and prevent potential complications.