Comprehensive Approaches to Managing and Overcoming Persistent Pain
This comprehensive article explores effective strategies for managing and overcoming persistent pain. It covers pain classification, diagnosis, personalized treatment options, lifestyle changes, and prevention tips. With insights into physical, psychological, and alternative therapies, it aims to help individuals improve quality of life through tailored pain management plans. Understanding the complex nature of chronic pain is essential for effective treatment and long-term relief, making this guide a valuable resource for patients and healthcare providers alike.

Comprehensive Approaches to Managing and Overcoming Persistent Pain
Pain management is a critical yet often underappreciated aspect of healthcare, as many overlook the diverse nature of pain and its impact on daily life. While most people focus on the intensity of pain, understanding its different types, causes, and treatment options is essential for effective management. Pain can manifest in various forms and durations, necessitating tailored strategies for each individual. This extensive guide explores the complexities of pain, distinguishes between acute and chronic pain, and provides practical approaches for overcoming persistent discomfort.
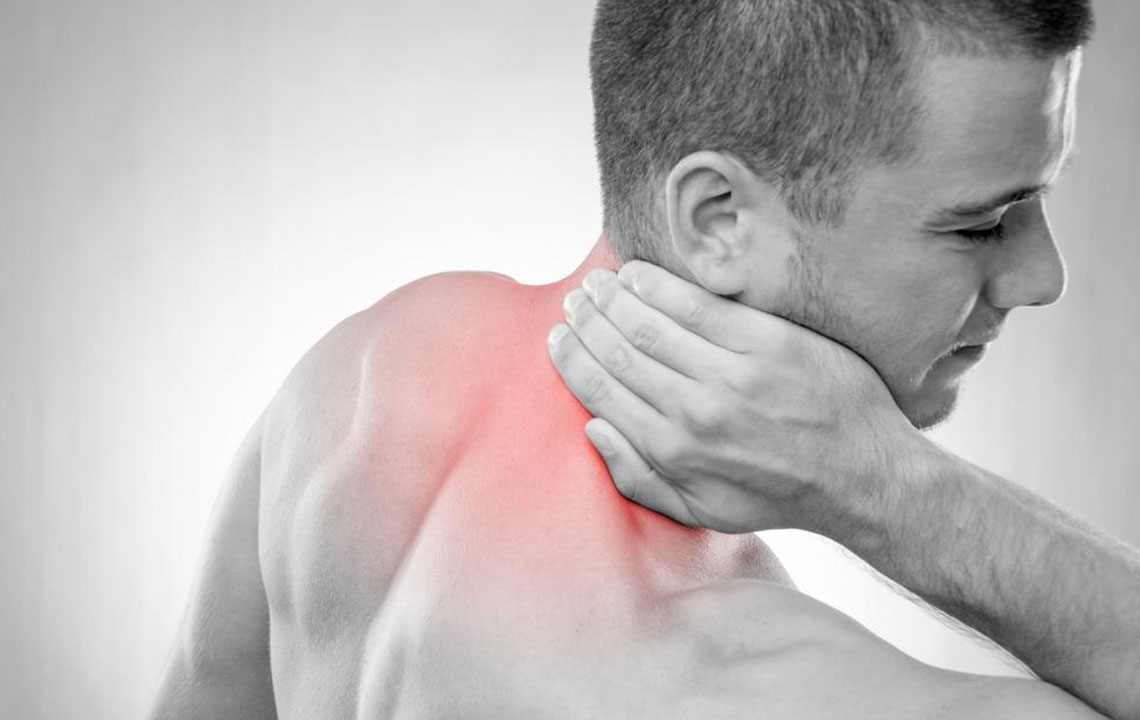
Understanding the fundamentals of pain classification is crucial. Typically, pain is categorized into two major types: acute and chronic. Acute pain serves as the body's immediate response to injury or harm, acting as a warning signal that prompts protective behavior. This form of pain tends to be temporary, lasting only until the underlying injury heals. Conversely, chronic pain persists beyond the normal healing process, often extending for months or even lifelong, significantly impacting an individual’s physical and emotional well-being.
Definitions and Duration of Pain Types:
Acute pain: Generally lasts less than 6 weeks and is directly related to tissue damage or injury, such as cuts, burns, or fractures. It often resolves with proper treatment or healing.
Chronic pain: Defined as pain that persists for longer than 12 weeks, regardless of whether an injury is still present. Sometimes, it offers no clear cause and can become a disease itself, affecting all aspects of life.
Chronic pain, by its nature, can be particularly challenging to treat. It may stem from internal injuries, repetitive movements, nerve damage, or conditions like arthritis, fibromyalgia, or nerve entrapment. Over time, it can reduce flexibility, weaken muscles, and decrease stamina. Moreover, persistent pain often leads to psychological effects such as helplessness, anxiety, and depression, which can further complicate treatment outcomes.
Living with chronic pain might seem overwhelming, but there are effective strategies that individuals and healthcare providers can implement to manage and even overcome it. Recognizing that chronic pain is not just a symptom but a complex condition requiring ongoing care is fundamental for improving quality of life.
Diagnosing Pain: The Role of Medical Evaluation
Healthcare providers rely heavily on detailed patient reports to identify and evaluate pain. Since pain is subjective, objective testing is often complemented by patient history, physical examinations, and diagnostic imaging to locate the source accurately. Tests may include MRI, X-rays, nerve conduction studies, or blood tests to rule out underlying conditions.
Customized Treatment Plans: Restoring Function and Comfort
The primary goal of treating chronic pain is to reduce discomfort and restore the ability to perform daily activities. Treatment approaches are highly individualized, depending on the pain's severity, location, and underlying causes. Combining medication with various therapies helps achieve better results. This holistic approach may include:
Medications: Over-the-counter analgesics, muscle relaxants, or nerve pain medications are common options.
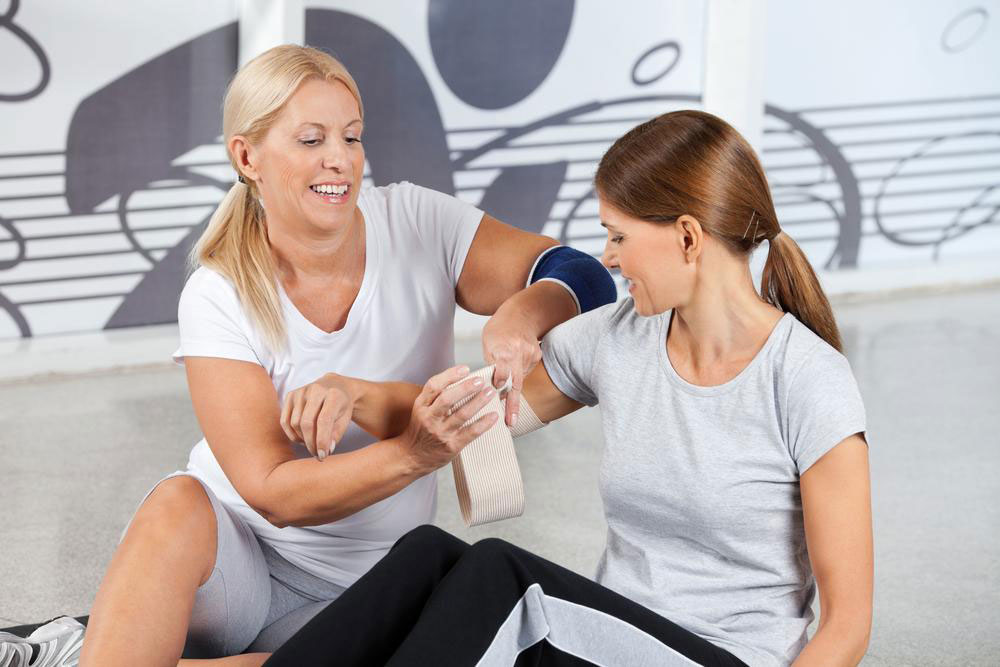
Physical Therapy: Enhances flexibility, strength, and movement, often tailored to the patient's specific needs.
Psychotherapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can help manage emotional responses and reduce suffering.
Complementary Therapies: Techniques such as acupuncture, massage, meditation, and relaxation exercises have shown promising results.
Surgical Interventions: Considered a last resort when conservative methods fail to provide relief, and only after thorough evaluation.
Importance of Lifestyle Adjustments and Medical Guidance
Adopting an active lifestyle and seeking professional medical advice are essential components of managing chronic pain effectively. Maintaining movement within pain limits helps prevent muscle atrophy and stiffness, contributing to better overall function. Additionally, selecting the right healthcare providers and treatment options significantly impacts outcomes. Education about pain management strategies empowers patients and encourages adherence to prescribed therapies.
Preventing Chronic Pain and Enhancing Well-being
Prevention is generally preferable to treatment. Investing in regular exercise, ergonomic practices, stress reduction, and early intervention at the first signs of pain can prevent some persistent conditions from worsening. Recognizing the importance of mental health support and social engagement also plays a vital role in overcoming the emotional burden associated with chronic pain.
In conclusion, managing persistent pain requires a comprehensive, multi-faceted approach. By understanding the distinctions between acute and chronic pain, utilizing accurate diagnostic tools, and combining various treatment modalities, individuals can regain control over their lives. Active participation in treatment plans, lifestyle adjustments, and ongoing medical support are key to overcoming pain and enhancing overall well-being.