Comprehensive Guide to Shingles: Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and Effective Treatment Options
This comprehensive article explores shingles, including its causes, symptoms, risk factors, and various treatment strategies. It discusses how to identify shingles through visual symptoms, the role of the immune system, and how to manage outbreaks using home remedies and medical options. With a focus on prevention and early intervention, the guide aims to educate readers on preserving health and reducing complications related to shingles. It is particularly useful for older adults and immunocompromised individuals seeking detailed insights into this common condition.

Comprehensive Guide to Shingles: Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and Effective Treatment Options
Exploring the fundamental aspects of shingles, including its causes, symptoms, prevention strategies, and treatment options
Shingles, also known as herpes zoster, affects a significant portion of the population, with estimates suggesting that approximately one in three individuals will experience this painful condition at some stage in their lives. If not properly managed, shingles can lead to severe complications, including nerve damage and postherpetic neuralgia. Maintaining a strong immune system is essential in controlling and preventing the outbreak of shingles. This comprehensive guide delves into the origins of shingles, its early signs, how to identify it through visual symptoms, and the most effective treatment strategies available today.
Who is most vulnerable to developing shingles?
Individuals over the age of fifty are at increased risk, especially those who have previously contracted chickenpox.
People with compromised immune systems due to illnesses such as HIV/AIDS, cancer treatments, or autoimmune disorders are more susceptible.
Patients undergoing chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or long-term immunosuppressive medication use after organ transplants have a heightened risk.
What triggers shingles?
The primary cause of shingles is the varicella-zoster virus, the same virus responsible for chickenpox. After initial infection, this virus remains dormant in nerve tissues within the body.
Years or even decades later, the virus can reactivate due to weakened immunity, leading to shingles outbreaks.
Is shingles contagious?
Shingles itself is not contagious; however, the varicella-zoster virus can be transmitted from the shingles rash to individuals who have never had chickenpox or the chickenpox vaccine, resulting in chickenpox, not shingles.
To minimize the risk of spread, it is recommended to keep the rash covered, avoid contact with vulnerable populations, and practice good hygiene.
Can visual aids such as photos assist in identifying shingles symptoms?
Early signs often include flu-like symptoms such as fever, fatigue, and headache, which are common across many illnesses and may not be specific to shingles.
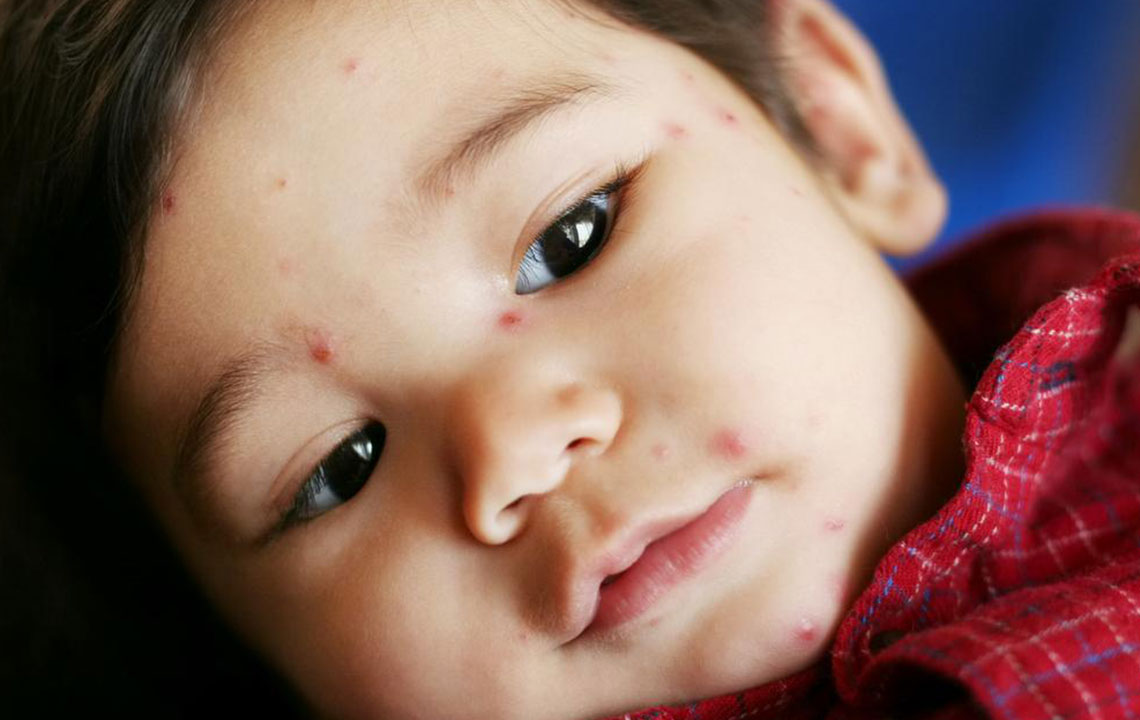
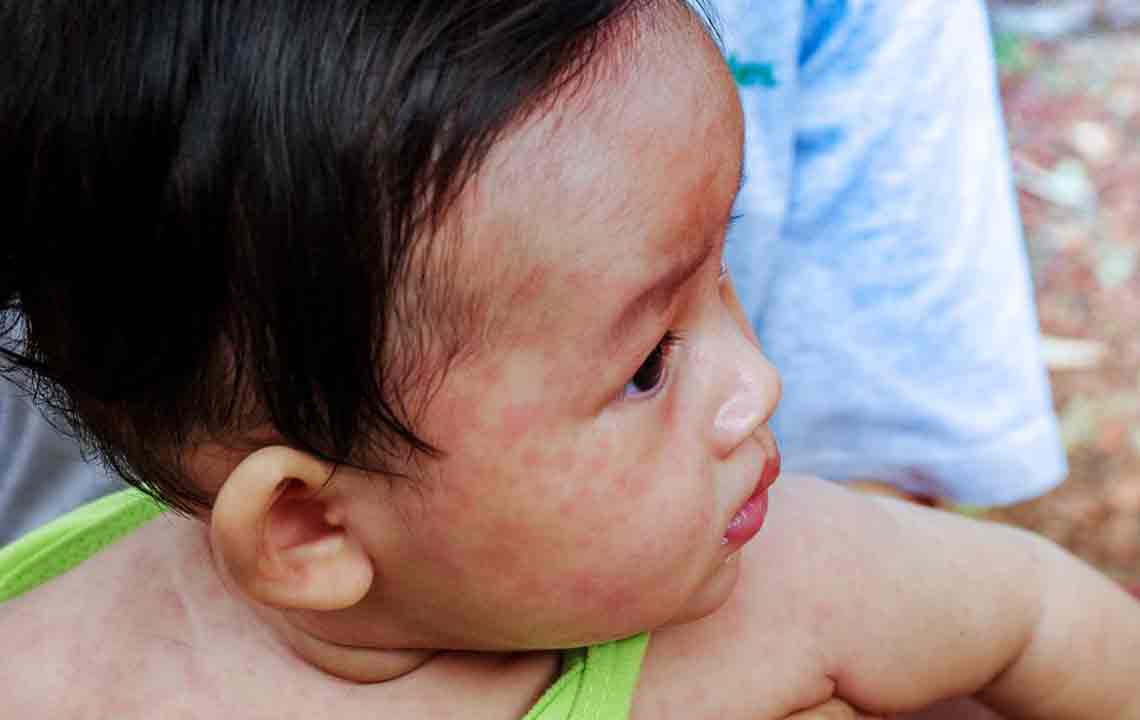
Characteristic visual symptoms like rashes, blisters, and skin eruptions are key indicators and can be confirmed through online images or photographs of shingles cases.
Examining rash images can help differentiate shingles from other skin conditions and determine severity and stage.
The appearance of pus-filled blisters localized on one side of the torso or face is a significant warning sign that requires prompt medical intervention.
Persistent pain, itching, and tingling sensation often accompany the rash, lasting even after the blisters heal.
Utilizing online resources and rash photos can be valuable for self-assessment and tracking the progression of the disease during home care.
Are there effective home remedies to manage shingles?
Gentle skin cleaning with lukewarm water and mild cleansers can reduce discomfort and prevent secondary infections.
Applying cold compresses or cool, damp cloths can soothe nerve pain and alleviate itching, ensuring ice contact is avoided to prevent skin damage.
Natural remedies—such as herbal supplements including melatonin, oregano oil, lemon balm, and antioxidant-rich green tea—may help in pain relief and immune support.
Maintaining a nutritious, balanced diet loaded with vitamins C and E, zinc, and other immune-supportive nutrients supports recovery and overall health.
Monitoring rash development and changes through online images and symptom checkers can assist in evaluating whether home treatment is sufficient or if medical attention is needed.
What are the current standard treatments for shingles?
Treatment options depend on the severity and stage of the shingles outbreak.
Early diagnosis and comparison with online images can guide effective therapeutic interventions.
Common medical treatments include antiviral medications such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir, which can shorten the duration and severity of symptoms if started promptly.
Supportive care with pain relievers—like analgesics, corticosteroids, or nerve stabilizers—helps manage discomfort and reduce nerve inflammation.
Vaccination, especially for adults aged 60 and above, offers significant protection against severe outbreaks and postherpetic neuralgia. Newer vaccines with longer-lasting immunity are under development and improving protection levels.
Researchers are continuously working on developing novel vaccines and treatments that can prevent reactivation and manage symptoms more effectively.
This detailed guide provides essential insights for understanding, preventing, and managing shingles, emphasizing the importance of early detection and medical intervention. Whether through home remedies or medical treatments, taking prompt action can significantly impact recovery and reduce complications associated with this condition.