Comprehensive Guide to Differentiating Bronchitis from Pneumonia
This comprehensive guide explains the key differences between bronchitis and pneumonia, two common lung illnesses. It covers causes, symptoms, severity, and treatment options, helping readers identify symptoms early and seek appropriate medical care promptly. Understanding these distinctions is vital for effective diagnosis and preventing serious complications, especially with pneumonia's rapid progression. Learn about prevention, diagnosis methods, and treatment strategies to protect your respiratory health effectively.

Comprehensive Guide to Differentiating Bronchitis from Pneumonia
Understanding respiratory illnesses can often be confusing, especially when symptoms overlap. Two common conditions affecting lung health are bronchitis and pneumonia. While they share similar symptoms such as coughing and chest discomfort, they are fundamentally different in their causes, severity, and treatment requirements. Properly distinguishing between these illnesses is crucial for timely and effective medical intervention, which can lead to better health outcomes and prevent complications. This detailed guide aims to clarify the differences, helping individuals recognize symptoms and understand when to seek medical attention.
What is Bronchitis?
Bronchitis primarily involves inflammation of the bronchi—the large air passages that carry air to the lungs. It's typically less severe than pneumonia and often resolves with minimal treatment, especially when it's acute. There are two main types: acute and chronic bronchitis. Acute bronchitis usually develops following a viral infection, such as the common cold or the flu, and lasts for a few weeks. Chronic bronchitis, on the other hand, is a long-term condition often associated with smoking or prolonged exposure to irritants, leading to ongoing inflammation and mucus production.
Common symptoms of bronchitis include persistent coughing, which may produce mucus of various colors—including yellow, green, or clear. Patients often experience a mild, lingering fever, along with wheezing and shortness of breath during coughing episodes. Fatigue is common, and many notice symptoms such as a runny or stuffy nose that may precede chest congestion. Additionally, chest discomfort resulting from vigorous coughing is typical. Because most bronchitis cases stem from viral infections, antibiotics are generally ineffective, and treatment focuses on symptom relief through hydration, cough suppressants, and humidified air.
Understanding Pneumonia
Pneumonia is a more severe respiratory illness characterized by the inflammation of lung tissue itself. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or, rarely, other microorganisms. This condition often progresses rapidly, making prompt diagnosis and treatment essential. Unlike bronchitis, pneumonia involves direct infection of the lungs, which can impair breathing and reduce oxygen exchange, leading to potentially serious health consequences if not treated swiftly.
The symptoms of pneumonia can be similar to bronchitis but are often more intense. Patients frequently experience difficulty breathing, sharp or stabbing chest pain that worsens with deep breaths or coughing, and persistent high fever. Confusion, especially among elderly patients, is a notable symptom indicating severe illness. The cough associated with pneumonia often produces thick, green, or yellow mucus, and chills accompanied by shaking are common. Because bacterial pneumonia is a primary cause, antibiotics are a standard treatment, but early detection is vital to prevent complications such as lung abscesses or sepsis.
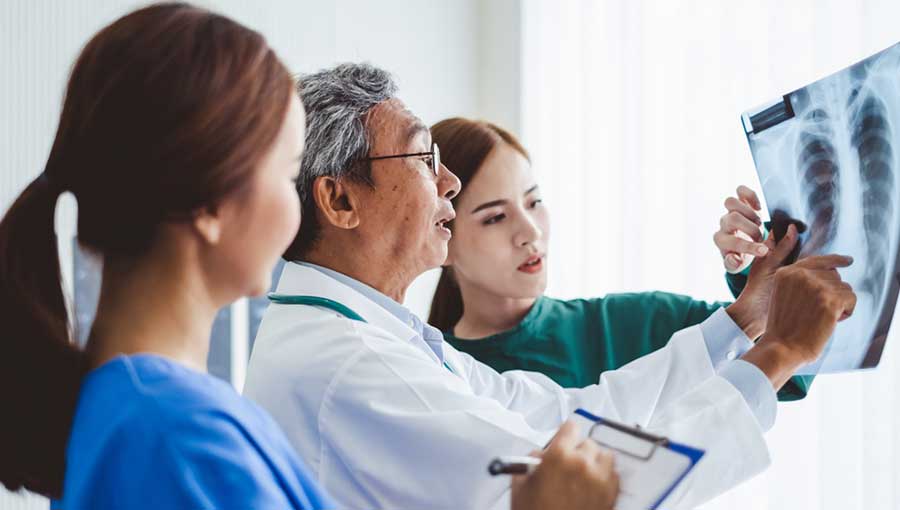
Diagnosing pneumonia usually involves a physical examination, chest X-rays, and sometimes blood tests or sputum analysis to identify the causative organism. Hospitalization may be required for severe cases, especially in vulnerable populations like children, the elderly, or those with compromised immune systems.
**Key Differences in Severity and Treatment**
While bronchitis is commonly self-limiting and less dangerous, pneumonia demands immediate medical intervention due to its potential to cause life-threatening complications. Recognizing symptoms early, differentiating between these two conditions, and understanding their respective treatments are essential steps toward effective disease management. Both illnesses can be prevented through vaccination—such as the influenza and pneumococcal vaccines—adopting good hygiene practices, and avoiding exposure to respiratory irritants.
In summary, knowing how to distinguish between bronchitis and pneumonia helps individuals seek appropriate medical care promptly, improving recovery chances and reducing the risk of severe health outcomes. If you're experiencing persistent symptoms like severe cough, chest pain, difficulty breathing, or high fever, consult a healthcare professional immediately for proper diagnosis and treatment.