Complete Guide to Glaucoma Eye Treatments: Options, Benefits, and How They Protect Your Vision
This comprehensive guide explores glaucoma eye treatments, focusing on the vital role of eye drops in managing intraocular pressure. It discusses various medication types, their benefits, importance of adherence, and how they help prevent vision loss. Emphasizing safety and convenience, this article provides essential insights for patients seeking effective glaucoma management. Regular monitoring and lifestyle adjustments further enhance treatment success, making eye drops a critical tool in protecting long-term eye health and vision preservation.
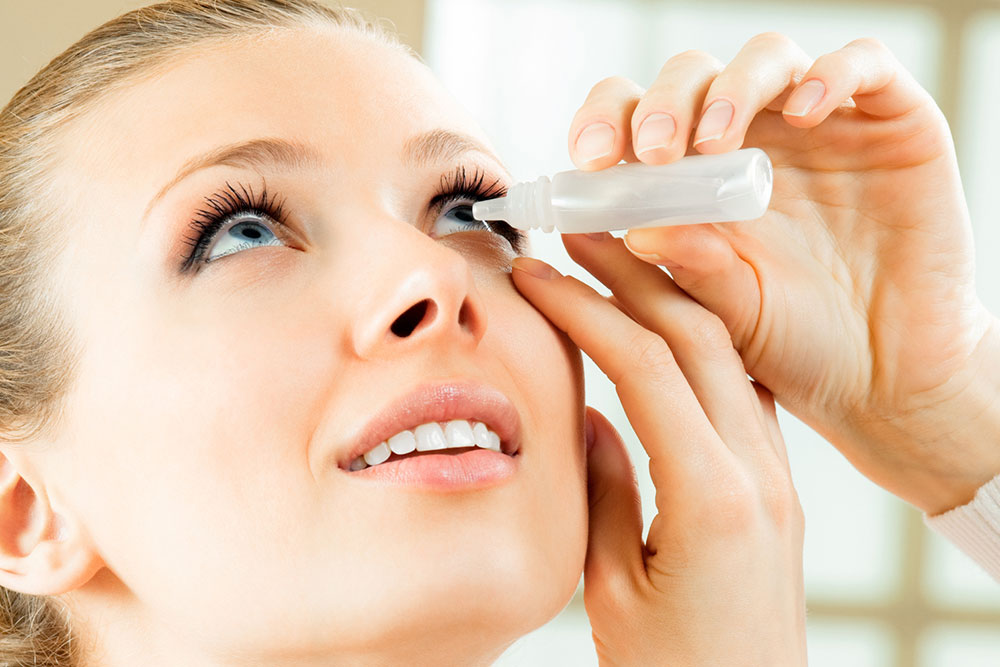

Understanding Glaucoma Treatments and Their Long-Term Benefits
Glaucoma is a complex eye condition that primarily involves damage to the optic nerve, which can lead to irreversible vision loss if not properly managed. This damage is often related to abnormal pressure inside the eye, known as intraocular pressure (IOP). Elevated IOP results from an imbalance in the production and drainage of aqueous humor, the fluid within the eye. The condition is more common among individuals over the age of 60, and those with underlying health concerns like diabetes are at higher risk. Although an outright cure for glaucoma has not yet been discovered, there are effective strategies to manage the disease, the most prominent being the use of topical eye medications — especially eye drops — aimed at controlling IOP and preserving vision over time.
In this comprehensive guide, we explore the various types of glaucoma treatments available, their mechanisms, and the benefits they offer. We will also discuss how these medications work to slow disease progression, their advantages over invasive procedures, and how adherence to treatment regimens plays a critical role in effectiveness.
How Glaucoma Eye Drops Help Protect Vision
The use of eye drops in glaucoma treatment is grounded in their ability to modulate the flow of fluid within the eye, thus reducing intraocular pressure — a major factor in the progression of the disease. These medications work by either decreasing aqueous humor production or increasing its drainage, depending on the specific drug type. The primary goal is to keep IOP within a range that minimizes damage to the optic nerve, thereby reducing the risk of worsening vision loss.
By controlling pressure levels, eye drops prevent further nerve damage, thereby preserving the remaining sight for the patient. Regular use of these medications forms the cornerstone of non-invasive glaucoma management and can be highly effective when combined with routine eye examinations and lifestyle modifications.
Advantages of Using Glaucoma Eye Drops
Lowering intraocular pressure (IOP) to prevent optic nerve damage: Eye drops are designed to normalize fluid dynamics inside the eye, effectively reducing elevated pressure caused by overproduction or poor drainage of aqueous humor. This is especially crucial because sustained high IOP is a primary risk factor for glaucoma-related vision loss.
Preventing progression of vision deterioration: Consistent application of eye drops significantly diminishes the likelihood of the disease advancing to more severe stages, thus providing a shield against potential blindness.
Non-invasive, safe, and patient-friendly management: Unlike surgical options, medicated eye drops are minimally invasive, carry fewer risks, and can be used safely at home. This ease of use encourages patient adherence and reduces the need for hospital visits or surgical interventions.
Ease of administration and quick results: Applying eye drops is a straightforward process, typically requiring just a few seconds. Many patients notice immediate benefits, including reduction in discomfort or dryness, along with prompt IOP lowering effects.
Slowing disease progression: Even though glaucoma damage cannot be reversed, ongoing use of these medications helps delay or prevent further nerve deterioration, extending the window of functional vision.
Other Benefits of Glaucoma Medications
Besides pressure reduction and disease management, glaucoma medications contribute to overall ocular health. They are often part of a holistic approach that includes lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining balanced blood sugar levels, engaging in regular exercise, ensuring proper nutrition, and scheduling periodic eye exams. Such measures not only support medication efficacy but also promote overall eye wellness.
Types of Glaucoma Eye Medications
Patients may be prescribed a variety of topical medications, each working via different mechanisms. The choice depends on disease severity, individual tolerance, and specific health considerations. Here’s an overview of common drug classes:
Prostaglandin Analogs: These increase outflow of aqueous humor through the uveoscleral pathway, effectively lowering IOP. Common examples include latanoprost, bimatoprost, and travoprost. Side effects may include increased eyelash growth, eye redness, and light sensitivity, but their efficacy in pressure reduction is well-established.
Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors (CAIs): Available as both eye drops and oral medications, CAIs reduce the production of aqueous humor. They are useful for quick pressure reduction and can be combined with other treatments for enhanced effect. Side effects might include a metallic taste and rare allergic reactions.
Beta-Blockers: These compounds inhibit beta receptors in the eye, decreasing aqueous humor secretion. Examples include timolol and betaxolol. Patients with respiratory issues or cardiovascular disease should consult their doctors before use due to potential side effects like bronchospasm.
Alpha Agonists: Medications such as brimonidine promote both a decrease in fluid production and an increase in outflow, providing a dual action. They are often prescribed multiple times daily, with potential side effects including dry mouth and fatigue.
Rho Kinase Inhibitors: A newer class of drugs, these enhance the natural drainage pathways of aqueous humor, providing additional IOP-lowering options. They’re especially effective in patients who are resistant to other medications and are under active clinical evaluation.
Ensuring Effective Glaucoma Management
Achieving optimal results with glaucoma eye drops depends heavily on proper usage and regular monitoring. Patients should adhere strictly to prescribed schedules, avoid discontinuing medication without consulting their healthcare professional, and report any side effects promptly. Routine ophthalmologic assessments are essential for tracking disease progression and adjusting treatment plans as necessary.
In addition, lifestyle factors such as staying physically active, maintaining a healthy diet rich in vitamins A, C, and E, and protecting eyes from excessive exposure to sunlight can support overall eye health. Educating oneself about glaucoma, its risks, and treatment options empowers patients to participate actively in their care, leading to better outcomes and preserved vision.
In conclusion, medical management with eye drops remains the frontline defense against glaucoma progression. While no cure exists yet, these medications offer a safe, effective, and manageable way to safeguard eyesight, especially when combined with routine checkups and lifestyle modifications. With ongoing advancements in pharmacology and treatment strategies, patients have increasingly effective options to control IOP and extend the quality of life.