Essential Nutrients and Dietary Strategies for Maintaining Thyroid Health
Discover essential nutrients and dietary strategies to promote healthy thyroid function. This comprehensive guide covers key foods rich in iodine, selenium, magnesium, and probiotics, alongside practical tips for managing hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism through diet. Learn how to support your thyroid health naturally with foods like seafood, Brazil nuts, leafy greens, and fermented products, while understanding the importance of iodine and balanced nutrition. Ideal for those seeking to maintain hormonal balance and overall well-being through informed dietary choices.

Key Nutrients and Foods to Support a Healthy Thyroid Gland
The thyroid gland, a vital butterfly-shaped organ located in the neck, plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions through the production of hormones. These hormones, primarily thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), influence energy levels, body temperature, heart rate, and metabolic processes. Maintaining optimal thyroid health is essential for overall well-being, as both thyroid dysfunctions like hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can significantly impact quality of life. An important aspect of ensuring healthy thyroid function involves proper nutrition and dietary choices that provide the necessary nutrients for hormone synthesis and regulation.
Foods That Support and Enhance Thyroid Function
Many foods naturally contribute to thyroid health by supplying essential vitamins and minerals. Including these in your daily diet can help prevent deficiencies and support the gland's optimal functioning:
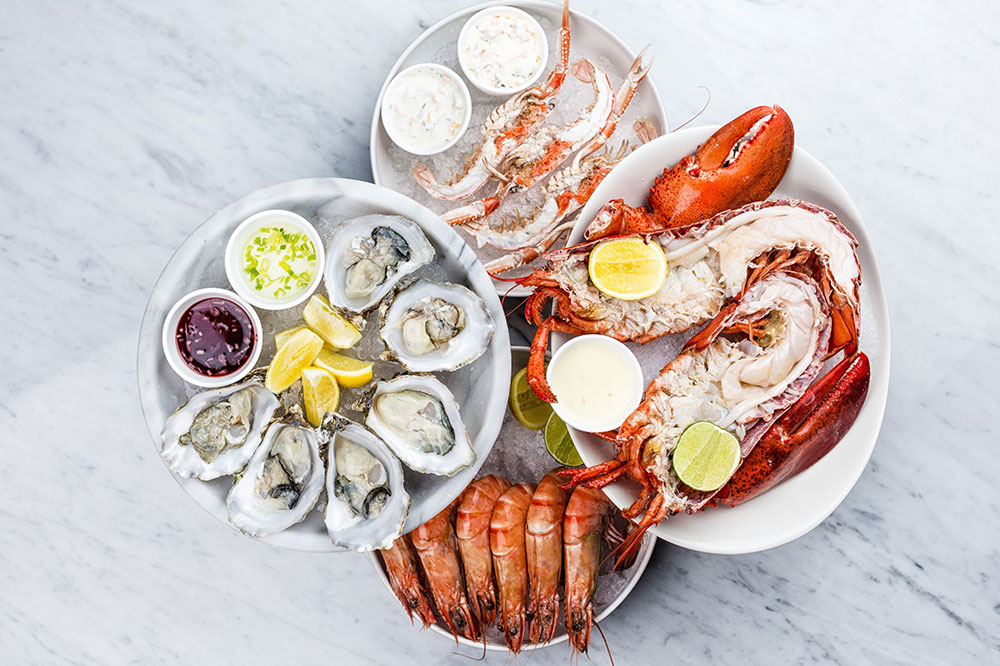
Seafood and Iodine-Rich Foods
Seafood such as salmon, sardines, and shrimp are some of the most potent sources of iodine, a mineral critically required for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. Iodine deficiency remains a widespread cause of hypothyroidism worldwide. Besides iodine, seafood supplies omega-3 fatty acids, which are known to reduce inflammation and promote healthy cellular function, including within the thyroid gland. Other iodine-rich sources include seaweed varieties like kelp and nori, which can be incorporated into meals in moderation. Remember, adequate iodine intake is essential, but excessive consumption can have adverse effects on thyroid health.
Brazil Nuts and Selenium
Brazil nuts are among the best dietary sources of selenium, a trace mineral with significant importance in thyroid health. Selenium is involved in converting the hormone thyroxine (T4) into its active form T3, which regulates metabolic rate. Deficiencies in selenium can impair thyroid function and contribute to autoimmune thyroid disorders such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Besides Brazil nuts, selenium can also be found in eggs, organ meats, and dairy products. Including these foods can support thyroid hormone production and immune function.
Dark Leafy Greens and Magnesium
Greens like spinach, kale, collard greens, and Swiss chard are rich in magnesium, which plays a supportive role in hormone production pathways. Magnesium helps convert T4 into T3, thus improving the efficiency of the thyroid gland. Incorporating these nutrient-dense greens into salads, smoothies, and cooked dishes can help maintain adequate magnesium levels necessary for optimal thyroid activity. Also, these vegetables provide antioxidants and fiber, contributing to overall health and metabolic regulation.
To further enhance thyroid health, including probiotics through fermented foods such as yogurt, kefir, tempeh, and kimchi can promote gut health, which is closely linked to hormonal balance. Consuming eggs provides high-quality proteins and vitamin D, both of which are essential for hormonal synthesis and immune regulation. Berries like blueberries, strawberries, or raspberries are high in antioxidants, protecting the thyroid against oxidative stress and cellular damage. Whole grains, such as brown rice, quinoa, and oats, help stabilize blood sugar levels, which is crucial for maintaining steady thyroid function. Consuming a balanced diet rich in iodine, selenium, magnesium, probiotics, antioxidants, proteins, and dietary fiber supports comprehensive thyroid health. It’s advisable to consult healthcare professionals or registered dietitians before making significant dietary changes, especially if you have existing thyroid conditions or are pregnant.
The Vital Importance of Iodine in Thyroid Health
Iodine is an essential element indispensable for the proper production of thyroid hormones. These hormones influence growth, development, metabolic rate, and overall physiological functions. A deficiency in iodine can lead to hypothyroidism, characterized by fatigue, weight gain, depression, and typical goiter formation. To prevent iodine deficiency, include iodine-rich foods like seafood, seaweed, dairy products, and iodized salt in your diet. However, moderation is key; excessive iodine intake can cause thyroid dysfunctions such as hyperthyroidism or autoimmune reactions. Seaweed, while beneficial, should be consumed in controlled amounts, as overconsumption can disrupt thyroid function. For individuals relying on iodized salt, using it judiciously ensures adequate iodine intake without risking excess. Pregnant women and those planning pregnancy should pay special attention to iodine intake, as it is critical for fetal brain development. Always consult healthcare providers regarding iodine supplementation, especially during pregnancy or if you have pre-existing thyroid issues.Strategies for Managing Thyroid Conditions through Nutritional Choices
Managing thyroid health effectively requires personalized dietary strategies that address specific conditions. For hypothyroidism, emphasizing nutrient-rich foods that support hormone production—such as foods high in iodine, selenium, and zinc—is vital. Additionally, managing stress through practices like meditation, yoga, or counseling can positively influence thyroid function, as stress hormones can interfere with hormonal balance. For hyperthyroidism, reducing intake of goitrogens (substances that can impair thyroid hormone synthesis) such as cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower) and soy products may be recommended, especially in raw forms. It is crucial to work closely with healthcare professionals to tailor a diet that complements medication and other treatments. Regular monitoring of thyroid function and adjusting dietary components accordingly can help maintain hormonal equilibrium and improve quality of life. In conclusion, a comprehensive approach combining balanced nutrition, stress management, and medical guidance can effectively support healthy thyroid function and prevent or manage thyroid-related disorders.