Comprehensive Guide to Monitoring and Managing Blood Glucose Levels for Better Health
This comprehensive article explores the vital importance of blood glucose regulation for overall health. It covers how the body maintains stable blood sugar levels, the risks of abnormal readings such as hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia, and effective lifestyle strategies for managing blood sugar. The guide emphasizes early detection, symptoms, and treatment options for blood sugar-related conditions like diabetes, offering practical tips for everyday health. Maintaining optimal glucose levels is crucial to prevent serious complications, making awareness and proactive management essential for long-term wellness.

Comprehensive Guide to Monitoring and Managing Blood Glucose Levels for Better Health
Blood glucose, often referred to as blood sugar, is a critical indicator of metabolic health. It reflects the amount of glucose present in the bloodstream at any given time. Proper regulation of blood sugar is essential for overall well-being, as both high and low levels can have serious health implications. Understanding how blood glucose functions, what factors influence its fluctuations, and effective strategies to maintain optimal levels are vital for preventing chronic conditions like diabetes and other metabolic disorders. This comprehensive guide aims to provide detailed insights into blood glucose regulation, including how the body maintains stable levels, the significance of abnormal readings, and practical tips for managing blood sugar effectively.
Blood glucose levels serve as vital markers for metabolic health, providing insights into the body's energy management system. Critical for fueling cells and tissues, glucose must be maintained within specific ranges to ensure optimal organ function. When blood sugar is too high or too low, it not only signals underlying issues like diabetes but can also cause immediate health concerns. Continuous monitoring and understanding of blood glucose fluctuations enable individuals and healthcare providers to implement targeted interventions, promoting long-term health and preventing complications such as cardiovascular diseases, nerve damage, and hypoglycemic incidents.
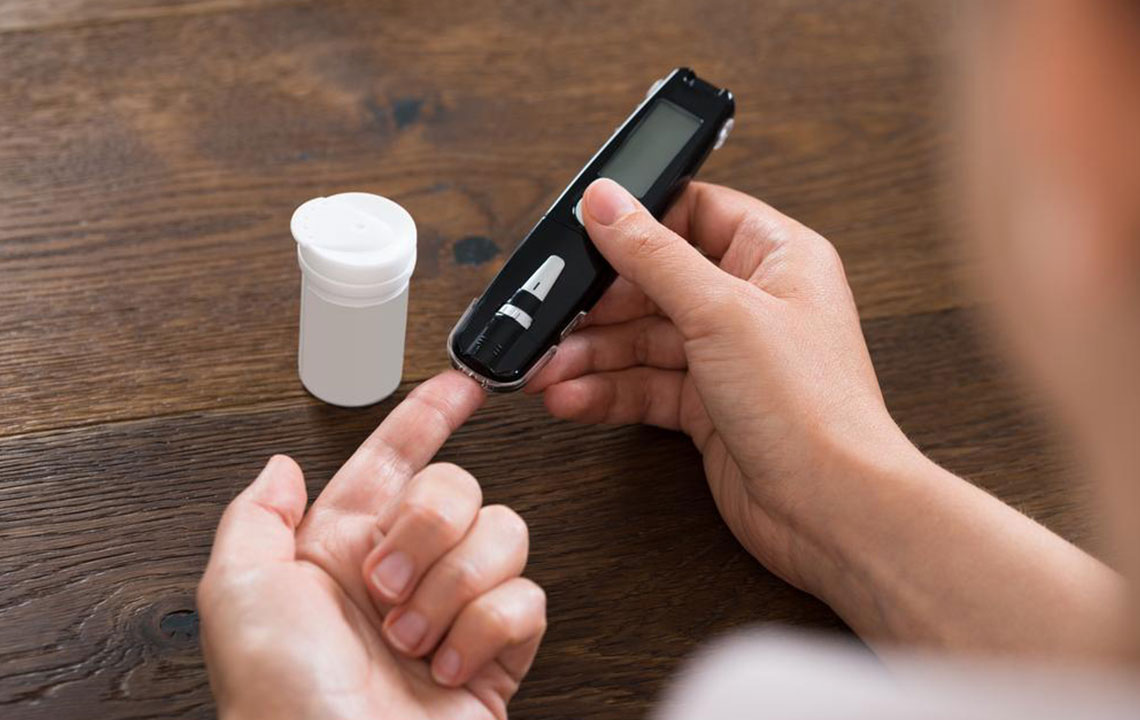
Normal blood glucose levels are crucial for maintaining overall health and are tightly regulated by various physiological mechanisms. The typical range for fasting blood glucose in healthy individuals is between 3.9 and 5.5 mmol/L (70 to 100 mg/dL). Post-meal, blood sugar may rise but should generally stay below 10 mmol/L (180 mg/dL). These fluctuations are controlled through insulin and other hormonal actions, which coordinate to ensure that energy supply meets demand without causing harmful spikes or drops. Understanding these dynamics helps individuals recognize early signs of imbalance and seek appropriate care.
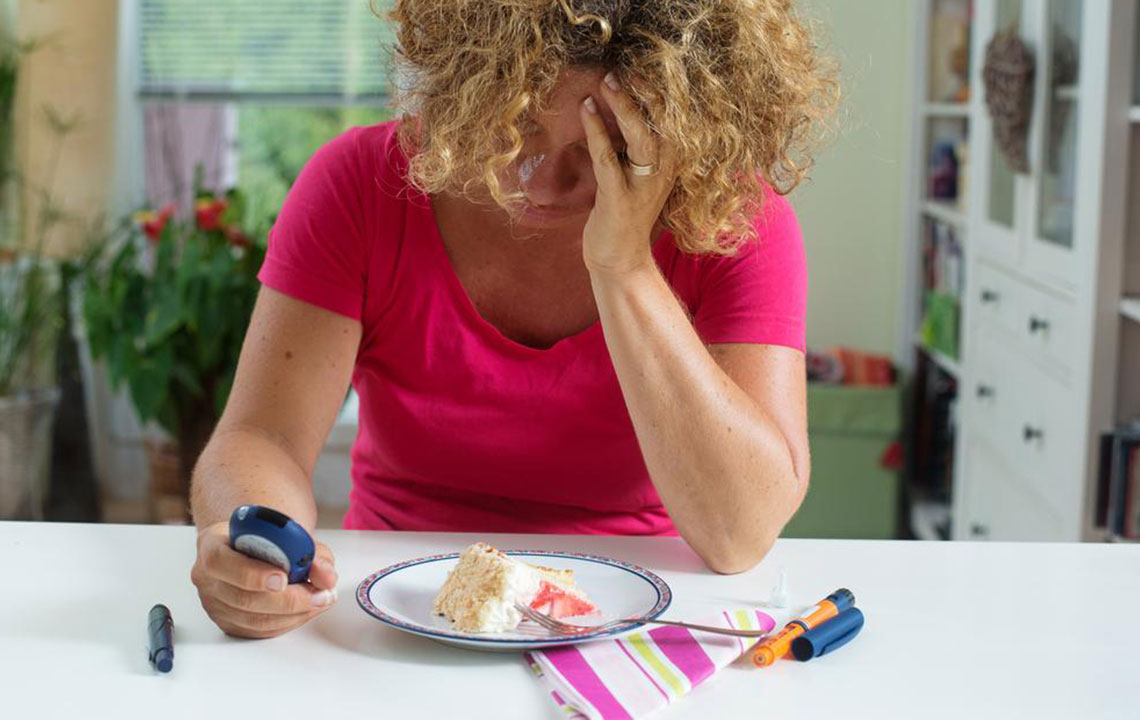
When blood glucose levels go beyond the normal range, it indicates issues that require attention. Hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar, is frequently associated with diabetes mellitus and can result from insufficient insulin production or the body's inability to use insulin effectively. Persistent elevated blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels, nerves, and organs, increasing the risk of heart disease, kidney failure, and visual impairment. Conversely, hypoglycemia, characterized by dangerously low blood sugar levels, causes symptoms such as dizziness, confusion, sweating, weakness, and in severe cases, loss of consciousness. Recognizing and managing these conditions is key to preventing acute and chronic health complications.
Maintaining blood glucose within healthy boundaries involves a combination of lifestyle choices, dietary habits, and medical management when necessary. Key strategies include regular physical activity, balanced nutrition, and monitoring blood sugar levels regularly. For individuals with diabetes or prediabetes, personalized treatment plans, including medication like Metformin or insulin therapy, are often required. Lifestyle factors such as stress management, adequate sleep, and avoiding excessive alcohol intake play significant roles in stabilizing blood sugar. Through these measures, people can reduce their risk of developing serious health conditions linked to abnormal glucose levels.
Understanding the symptoms and risks associated with abnormal blood sugar levels is essential for early detection and intervention. Chronic hyperglycemia can lead to cardiovascular complications, nerve damage (neuropathy), renal failure, and eye problems. On the other hand, hypoglycemia can cause life-threatening situations if not promptly treated, especially in individuals on insulin or other glucose-lowering medications. Regular screening, especially for those with risk factors such as obesity, family history, or sedentary lifestyles, helps catch abnormalities early and allows for timely management. Education about recognizing warning signs and responding appropriately is a vital aspect of maintaining metabolic health.
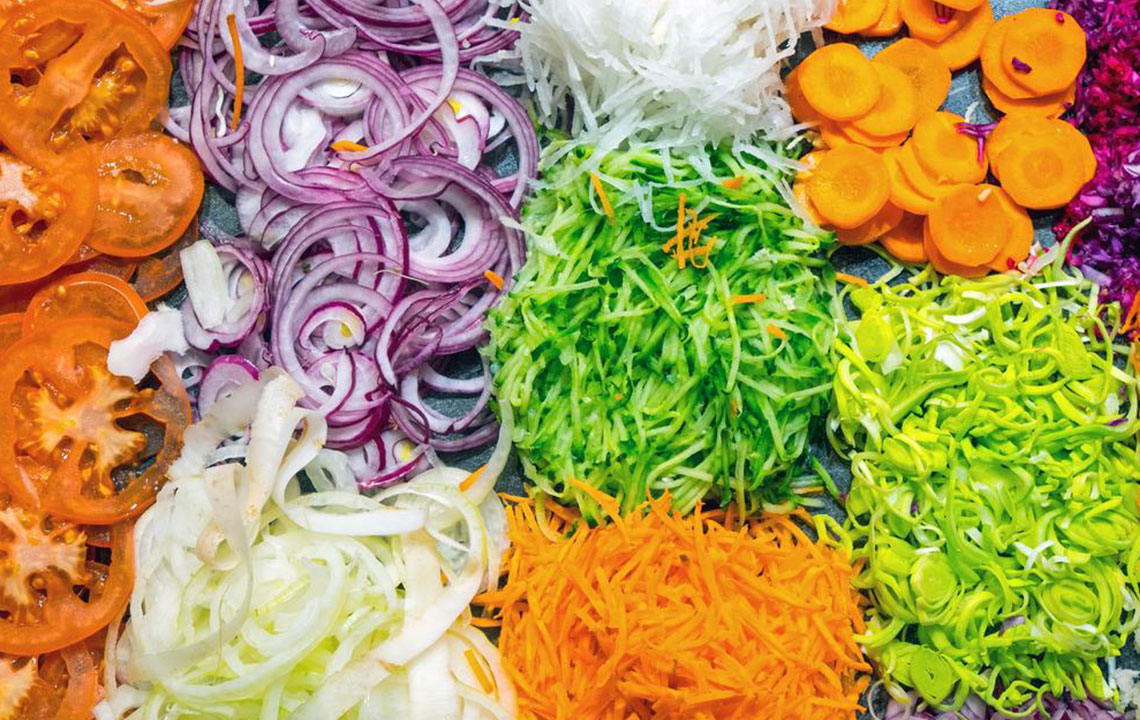
To effectively manage blood glucose levels, consider adopting the following lifestyle habits:
Incorporate healthy fats like nuts and seeds into your diet.
Opt for whole grains such as barley, oats, and brown rice instead of refined carbs.
Eat plenty of vegetables, especially non-starchy varieties like broccoli, spinach, and carrots.
Use spices like cinnamon, which may enhance insulin sensitivity and improve blood sugar control.
Consider adding natural vinegar, such as apple cider vinegar, with meals to help stabilize blood sugar spikes.
Avoid skipping meals to prevent sudden drops in blood sugar levels.
Limit alcohol consumption, particularly on an empty stomach, as it can disrupt glucose regulation.
Maintaining these habits consistently supports balanced blood glucose, reduces the risk of metabolic disorders, and promotes overall health. Given the increasing prevalence of lifestyle-related diseases globally, understanding and managing blood sugar is more important than ever for long-term wellness.