Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing Early Symptoms of Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is a common and serious health risk for men, especially over 50. Recognizing early warning signs such as urinary problems, blood in urine or semen, bone pain, and erectile difficulties is crucial. This comprehensive guide covers risk factors, screening methods, and advanced symptoms to help men stay vigilant and seek timely medical care. Early detection through regular screenings can significantly improve treatment success rates, making awareness essential for men's health and well-being.
Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing Early Symptoms of Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is a prevalent and potentially life-threatening condition that develops within the prostate gland. As one of the most commonly diagnosed cancers among men in the United States, understanding its early warning signs is essential for timely diagnosis and effective treatment. This extensive guide aims to provide detailed insights into the warning signals, risk factors, and diagnosis options associated with prostate cancer to help men stay vigilant and proactive about their health.
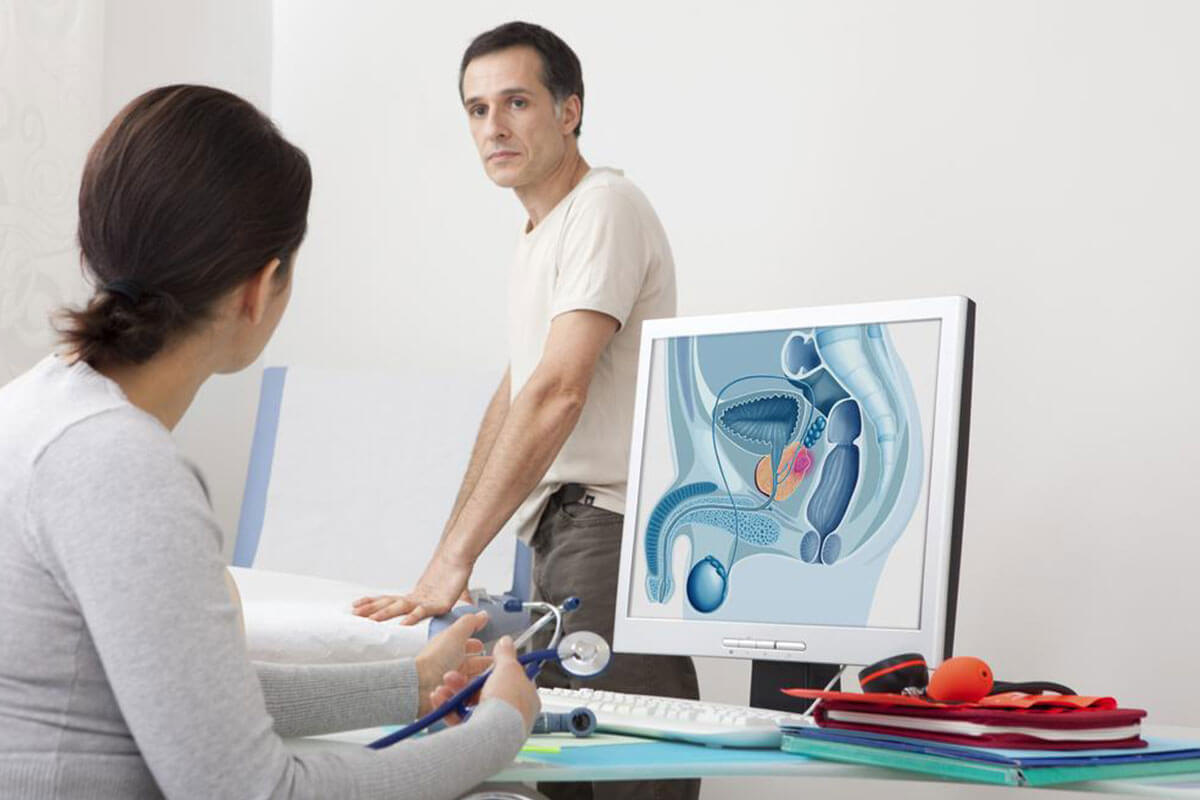
The prostate is a small, walnut-sized gland situated below the bladder and in front of the rectum. Its primary function is to produce seminal fluid that nourishes and transports sperm during ejaculation. When prostate cells grow uncontrollably, it results in prostate cancer, which may remain silent in early stages or manifest noticeable symptoms as it progresses.
Prostate cancer stands as the second leading cause of cancer-related death among men in the United States, highlighting its significant health impact. The American Cancer Society estimates that approximately 221,000 new cases are diagnosed annually, emphasizing the importance of awareness and early detection. The disease primarily affects men over 50 years of age, although it can occur earlier, especially in individuals with notable risk factors. These include a family history of prostate cancer, ethnicity (more common among African-American men), poor dietary habits, smoking, obesity, exposure to environmental toxins, vasectomy history, and sexually transmitted infections. While the exact cause of prostate cancer remains uncertain, research indicates that both genetic and environmental factors play roles in its development.
Reducing the risk of prostate cancer involves managing controllable factors such as maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, avoiding tobacco, and limiting exposure to harmful chemicals. Screening methods like the digital rectal exam (DRE) and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test are crucial for early detection. Confirmatory diagnosis often requires a biopsy to examine prostate tissue for cancer cells. Once diagnosed, treatment options are tailored based on factors like age, overall health, tumor stage, and aggressiveness. These treatments can include radiation therapy, surgical removal of the prostate (prostatectomy), chemotherapy, hormone therapy, or targeted biologic therapies, providing several avenues for managing the disease effectively.
Recognizing Early and Late Symptoms
In the initial stages, prostate cancer often does not produce noticeable symptoms because of its slow growth. However, as the disease advances, symptoms become more apparent and can significantly affect quality of life. Early warning signs to watch for include:
Urinary difficulties: Men may experience trouble starting urination, a weak or interrupted urine stream, increased frequency of urination (especially at night), urgency, blood in the urine (hematuria), pain or a burning sensation during urination, and a decreased force of urine flow. These signs are often mistaken for benign prostate conditions like benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), which underscores the importance of screening.
Other notable indicators: Symptoms such as pain during ejaculation, swelling or discomfort in the legs, blood in semen, persistent bone pain, numbness or weakness in the lower limbs, pelvic swelling, or erectile dysfunction may also occur. These signs often indicate that the cancer has spread beyond the prostate, requiring urgent medical attention.
In advanced stages, prostate cancer may metastasize to bones, lymph nodes, or other organs, leading to more severe symptoms like bone fractures, severe pain, or neurological deficits. Because these symptoms can resemble other health problems, routine screenings for men over 50 or those with identified risk factors are essential for early detection. Catching prostate cancer early dramatically improves treatment effectiveness and survival rates.
Awareness and regular health check-ups form the cornerstone of prevention and early intervention. Men are encouraged to discuss prostate health openly with their healthcare providers and undergo recommended screening tests regularly, especially if they fall into higher-risk categories. Timely diagnosis can lead to more effective treatment plans and better long-term outcomes, ultimately saving lives and improving quality of life.