Comprehensive Guide to Back Pain Relief: Symptoms, Causes, and Proven Home Strategies
This comprehensive article explores the causes, symptoms, and effective home remedies for back pain relief. It emphasizes the importance of understanding the root causes of discomfort, highlights practical strategies like cold/heat therapy, stretching, and maintaining an active lifestyle, and advises when to seek medical intervention. Ideal for those seeking safe, natural ways to manage minor back issues, the piece also outlines preventive measures to reduce future risks, making it a valuable resource for maintaining spinal health and overall well-being.

Comprehensive Guide to Back Pain Relief: Symptoms, Causes, and Proven Home Strategies
Back pain is one of the most prevalent health issues affecting millions globally and stands as a leading cause of disability worldwide. Almost everyone encounters some form of back discomfort at some point in their lives, whether due to minor strains or more serious underlying conditions. The good news is that many cases of mild back pain can be effectively managed at home with simple remedies and lifestyle adjustments. While severe or persistent back issues may necessitate medical intervention, a significant portion of back pain episodes resolve with conservative strategies. Surgery remains a last resort, reserved for cases involving significant structural damage or nerve impairment that do not respond to non-invasive treatments.
Common Causes of Back Pain
Understanding the root causes of back pain is essential for effective treatment. The primary causes include muscle strains, structural abnormalities within the spine, degenerative joint diseases like arthritis, and osteoporosis. Recognizing these causes can help you tailor your home management strategies and seek appropriate medical help when necessary.
Muscle Strain
Frequently, back pain results from overstretching or tearing of muscles due to improper lifting techniques, sudden movements, or overexertion during physical activities. Such strains cause soreness, stiffness, and limited mobility. Recognizing the signs early can help prevent further injury.
Structural Abnormalities
Damage or misalignments in the vertebrae, intervertebral disks, or supporting ligaments can lead to significant discomfort. Conditions like herniated, bulging, or ruptured disks put pressure on nearby nerves, leading to pain that radiates from the lower back down the legs—a condition known as sciatica. These issues often require medical assessment and targeted therapies.
Arthritis
Osteoarthritis affecting the spine involves cartilage wear and tear in the facet joints, causing narrowing of the spinal canal (spinal stenosis), pain, and reduced mobility. Patients may also experience stiffness and tenderness that impair daily activities.
Osteoporosis
As bones become fragile and thin, vertebral compression fractures can occur even after minor stresses. These fractures cause intense back pain and can severely impact posture and activity levels.
Besides these common causes, rarer conditions may include degenerative spondylolisthesis, cauda equina syndrome, spinal infections, tumors, and kidney-related issues. It is vital to consult a healthcare professional if back pain persists beyond a few days, worsens, or is accompanied by other symptoms like numbness, weakness, or loss of bladder control. Recognizing warning signs for urgent medical attention can prevent long-term complications.
Approaches to Managing Back Discomfort
Most mild back pains can be alleviated through over-the-counter medications such as NSAIDs—nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen or naproxen—that help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. For more severe or persistent issues, a doctor might prescribe stronger medications or recommend imaging diagnostics to identify structural problems. In certain cases, physical therapy, chiropractic adjustments, or minimally invasive procedures may be suggested. Alternative therapies like massage, relaxation techniques, and cognitive-behavioral therapy have also shown benefits, but it is important to seek medical advice before initiating such treatments.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Tips for Back Pain Relief
While severe back conditions require professional medical attention, many mild cases can be effectively managed with simple home strategies. These remedies aim to reduce inflammation, relax muscles, and promote recovery. Here are some evidence-based and practical approaches:
Cold and Heat Therapy
Use ice packs on acute injuries to diminish swelling and numb deep pain. Wrap a frozen gel pack in a cloth and apply for up to 20 minutes at a time, with intervals in between. For chronic muscle tension or stiffness, warm compresses or heating pads can enhance blood flow and relax tense muscles. Always follow safety guidelines to prevent burns or frostbite.
Endorphin Boosting Activities
Physical activities that stimulate endorphin release, such as massage, gentle yoga, meditation, or light aerobic exercise, can naturally reduce pain perception and emotional stress associated with back problems.
Stretching and Mobility Exercises
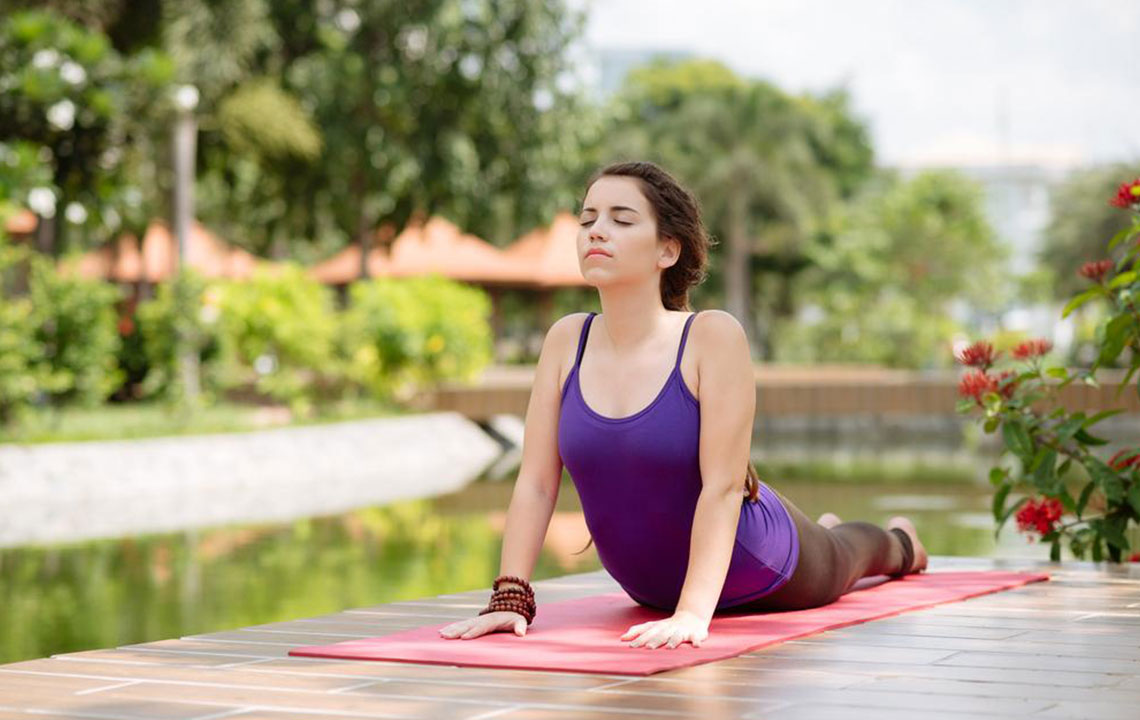
Gentle stretches facilitate flexibility and reduce stiffness. Exercises like toe touches, child's pose, cat-cow stretches, and cobra pose should be done slowly and comfortably, holding each stretch for around 30 seconds. Consistent stretching can prevent future episodes of back pain by maintaining muscle elasticity.
Improving Sleep Quality
Adequate restorative sleep supports tissue repair and overall recovery. Use supportive mattresses and pillows to maintain spinal alignment. Address sleep disturbances with routine adjustments, such as avoiding screens before bed, and consider medical advice if sleep issues persist, as poor sleep can aggravate back pain.
Maintaining Physical Activity
Keeping active helps prevent stiffness, improves circulation, and strengthens back-supporting muscles. Engage in daily movements like walking, swimming, or cycling, gradually increasing intensity as tolerated. Avoid high-impact or strenuous activities that worsen discomfort.
Core and Supporting Muscle Strengthening
Once pain subsides, focus on strengthening your core, glutes, hip, and pelvic muscles to better support your spine. Avoid strenuous abdominal exercises initially; consult a physical therapist for tailored exercises that promote stability without risking further injury.
Choosing Proper Footwear
Well-fitted, supportive shoes help maintain proper posture and reduce strain on the lower back. Avoid high heels and opt for cushioned, stability-enhanced footwear. If needed, consult a podiatrist about custom insoles or orthotics for optimal support.
In summary, mild back pain often responds well to conservative home remedies—cold/heat therapy, gentle stretching, staying active, and improving sleep hygiene. These strategies can effectively manage discomfort and prevent future episodes. However, persistent, worsening, or severe symptoms necessitate prompt medical evaluation to rule out underlying conditions. Proactive measures such as strengthening core muscles, wearing appropriate footwear, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk of recurrent back pain. Always seek professional medical advice for ongoing or intense pain to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.